|
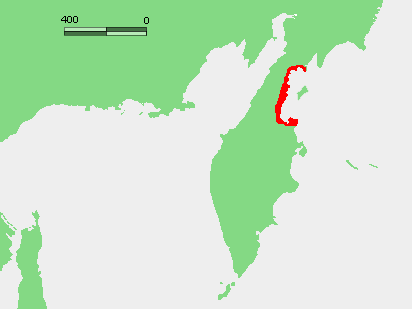
Korfa Bay
Korf Bay (russian: залив Корфа) is a bay on the Kamchatka Peninsula coast of the Bering Sea in Russia. Geography It is approximately triangular being about wide at the mouth and extending inland about . On the west side, the Ilpinsky Peninsula separates it from Anapka Bay which forms the north end of Karaginsky Gulf. On the east, the Govena Peninsula (Cape Govensky) separates it from the Olyutor Gulf. The northern coast contains the Skrytaya Harbor, which is a major salmon fishing ground. The largest settlements on the gulf are Tilichiki and Olyutorovka. History The bay is named after Baron Andrey Korf, the first Governor General of Priamurye. This is the Baron Koff or Barankoff Bay mentioned by the American travelers Washington Vanderlip and Olaf Swenson. The 2006 Kamchatka earthquakes The 2006 Kamchatka earthquake occurred on . This shock had a moment magnitude of 7.6 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of X (''Extreme''). The hypocenter was located near t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrey Korf
Baron Andrey Nikolayevich Korf or Korff (russian: Андрей Николаевич Корф; 1831–1893) was the first Viceroy (Governor General) of the Russian Far East (1884–93). The names of the village of Korf and the Korfa Bay commemorate him. He came from the Korff noble family. He was an Imperial Russian baron of Baltic German descent and an infantry general of the Imperial Russian Army. Andrey Korff took part in the Caucasian War and led an attack on Veden in 1859. He initiated the establishment of the Officers Infantry School. In 1884, Korf was put in charge of the newly established Maritime Governorate-General, which included the Russian Far East from the island of Sakhalin in the east to Lake Baikal in the west. Korff undertook some measures that facilitated further development of the region. He worked to improve education, to encourage colonization of the Ussuri River basin, to protect the sealskin trade, to create commercial relations with Japan and China, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bays Of Kamchatka Krai
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a narrow entrance. A fjord is an elongated bay formed by glacial action. A bay can be the estuary of a river, such as the Chesapeake Bay, an estuary of the Susquehanna River. Bays may also be nested within each other; for example, James Bay is an arm of Hudson Bay in northeastern Canada. Some large bays, such as the Bay of Bengal and Hudson Bay, have varied marine geology. The land surrounding a bay often reduces the strength of winds and blocks waves. Bays may have as wide a variety of shoreline characteristics as other shorelines. In some cases, bays have beaches, which "are usually characterized by a steep upper foreshore with a broad, flat fronting terrace".Maurice Schwartz, ''Encyclopedia of Coastal Science'' (2006), p. 129. Bays were sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bays Of Russia
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a narrow entrance. A fjord is an elongated bay formed by glacial action. A bay can be the estuary of a river, such as the Chesapeake Bay, an estuary of the Susquehanna River. Bays may also be nested within each other; for example, James Bay is an arm of Hudson Bay in northeastern Canada. Some large bays, such as the Bay of Bengal and Hudson Bay, have varied marine geology. The land surrounding a bay often reduces the strength of winds and blocks waves. Bays may have as wide a variety of shoreline characteristics as other shorelines. In some cases, bays have beaches, which "are usually characterized by a steep upper foreshore with a broad, flat fronting terrace".Maurice Schwartz, ''Encyclopedia of Coastal Science'' (2006), p. 129. Bays were si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bays Of The Bering Sea
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a narrow entrance. A fjord is an elongated bay formed by glacial action. A bay can be the estuary of a river, such as the Chesapeake Bay, an estuary of the Susquehanna River. Bays may also be nested within each other; for example, James Bay is an arm of Hudson Bay in northeastern Canada. Some large bays, such as the Bay of Bengal and Hudson Bay, have varied marine geology. The land surrounding a bay often reduces the strength of winds and blocks waves. Bays may have as wide a variety of shoreline characteristics as other shorelines. In some cases, bays have beaches, which "are usually characterized by a steep upper foreshore with a broad, flat fronting terrace".Maurice Schwartz, ''Encyclopedia of Coastal Science'' (2006), p. 129. Bays were s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korf, Russia
Korf (russian: Корф) is a rural locality (a '' selo'') and a port in Olyutorsky District of Koryak Okrug in Kamchatka Krai, Russia, located on a narrow sand spit opposite Tilichiki. Population: 18 (2012 est.);Аргументы и Факты. КамчаткаМуниципальное образование «Село Корф» будет упразднено History It was established in 1925 on the coast of the Skrytaya Harbor of the Korfa Bay as a settlement of salmon fishers. In 1994, it was demoted in status from that of an urban-type settlement to rural locality. On April 21, 2006, Korf was destroyed by the 2006 Kamchatka earthquakes. Over eight hundred families were evacuated and the ''selo'' was slated to be abandoned. As of 2013, however, Korf has not been officially abolished.Law #46 The names of the village and the Korfa Bay commemorate the Russian German Andrey Korf (1831–1893), the first Viceroy (Governor General) of the Russian Far East (1884–93). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2006 Kamchatka Earthquakes
The 2006 Kamchatka earthquake occurred on . This shock had a moment magnitude of 7.6 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of X (''Extreme''). The hypocenter was located near the coast of Koryak Autonomous Okrug at an estimated depth of 22 km, as reported by the International Seismological Centre. This event caused damage in three villages and was followed by a number of large aftershocks. Two M6.6 earthquakes struck on April 29 at 16:58 UTC and again on May 22 at 11:12 UTC. These earthquakes caused no deaths; however, 40 people were reported injured. Tectonic setting The northern part of the Kamchatka Peninsula lies away from the convergent boundaries of the Kuril–Kamchatka Trench and the Aleutian Trench but across the boundary between two blocks within the North American Plate, the Kolyma-Chukotka and Bering Sea microplates. This boundary accommodates both active shortening and right lateral strike-slip across a series of large SW–NE trending faults. Earthquake The focal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olaf Swenson
Olaf Swenson ( December 16, 1883 – August 23, 1938) was a Seattle-based fur trader and adventurer active in Siberia and Alaska in the first third of the 20th century. His career intersected with activities of notable explorers of the period, and with the Russian Civil War. He is credited with leading the rescue of the ''Karluk'' survivors from Wrangel Island in 1914. According to historian Thomas C. Owen, Swenson's "practicality and zest for adventure made him an ideal entrepreneur on the arctic frontier..."Owen Born and raised in Michigan, Swenson first reached the far north as a Nome prospector in 1901. The next year he signed on for a prospecting venture in Siberia, spending two summers and one winter on the Chukchi Peninsula. He returned to Siberia in 1905, this time with his wife and their infant son. His introduction to trading came when their ship was wrecked and he contracted to salvage cargo on a share basis. He continued to trade at Anadyr until 1911. In 1913, Swenson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington Vanderlip
Washington commonly refers to: * Washington (state), United States * Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States ** A metonym for the federal government of the United States ** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered on Washington, D.C. * George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States Washington may also refer to: Places England * Washington, Tyne and Wear, a town in the City of Sunderland metropolitan borough ** Washington Old Hall, ancestral home of the family of George Washington * Washington, West Sussex, a village and civil parish Greenland * Cape Washington, Greenland * Washington Land Philippines *New Washington, Aklan, a municipality *Washington, a barangay in Catarman, Northern Samar *Washington, a barangay in Escalante, Negros Occidental *Washington, a barangay in San Jacinto, Masbate *Washington, a barangay in Surigao City United States * Washington, Wisconsin (other) * Fort Washington (disambiguati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priamurye
Amur Oblast ( rus, Аму́рская о́бласть, r=Amurskaya oblast, p=ɐˈmurskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast), located on the banks of the Amur and Zeya Rivers in the Russian Far East. The administrative center of the oblast, the city of Blagoveshchensk, is one of the oldest settlements in the Russian Far East, founded in 1856. It is a traditional center of trade and gold mining. The territory is accessed by two railways: the Trans-Siberian Railway and the Baikal–Amur Mainline. As of the 2010 Census, the oblast's population was 830,103. Amur Krai () or Priamurye () were unofficial names for the Russian territories by the Amur River used in the late Russian Empire that approximately correspond to modern Amur Oblast. Geography Amur Oblast is located in the southeast of Russia, between Stanovoy Range in the north and the Amur River in the south, and borders with the Sakha Republic in the north, Khabarovsk Krai and the Jewish Autonomo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamchatka Peninsula
The Kamchatka Peninsula (russian: полуостров Камчатка, Poluostrov Kamchatka, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and western coastlines, respectively. Immediately offshore along the Pacific coast of the peninsula runs the Kuril–Kamchatka Trench. The Kamchatka Peninsula, the Commander Islands, and the Karaginsky Island, constitute the Kamchatka Krai of the Russia, Russian Federation. The vast majority of the 322,079 inhabitants are ethnic Russians, although about 13,000 are Koryaks (2014). More than half of the population lives in Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky (179,526 in 2010) and nearby Yelizovo (38,980). The Kamchatka peninsula contains the volcanoes of Kamchatka, a World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage Site. Geography Politically, the peninsula forms part of Kamchatka Krai. The southern tip is called Cape Lopatka. (Lopatka is Russian for s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |