|
KolibriOS Desktop, Summer 2024
KolibriOS is an open-source operating system for x86 computers, written completely in FASM assembly language. It has been developed since 2004, forked from MenuetOS, and supports i586 CPUs or newer. KolibriOS is small sized and fits on a single 3.5" floppy disk; despite this, it features a full graphical user interface, preemptive multitasking, networking capabilities, and many pieces of bundled software. The name "Kolibri" is the Slavic word for hummingbird and symbolizes the operating system's tiny size and fast speed. Development KolibriOS was forked from MenuetOS, a similar operating system that was built in 32-bit and 64-bit editions. It attracted much popularity in Russia and a number of other countries in the region, leading to a community contributing to the project. The first version of KolibriOS, meant to be a driver fix for the Russian-language distribution, was released by Marat Zakiyanov "mario79" in 2004. Shortly after the start of the KolibriOS project, Menu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical User Interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such as secondary notation. In many applications, GUIs are used instead of text-based user interface, text-based UIs, which are based on typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of command-line interfaces (CLIs), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard. The actions in a GUI are usually performed through direct manipulation interface, direct manipulation of the graphical elements. Beyond computers, GUIs are used in many handheld mobile devices such as MP3 players, portable media players, gaming devices, smartphones and smaller household, office and Distributed control system, industrial controls. The term ''GUI'' tends not to be applied to other lower-displa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ext2
ext2, or second extended file system, is a file system for the Linux kernel (operating system), kernel. It was initially designed by French software developer Rémy Card as a replacement for the extended file system (ext). Having been designed according to the same principles as the Berkeley Fast File System from Berkeley Software Distribution, BSD, it was the first commercial-grade filesystem for Linux. The canonical implementation of ext2 is the "ext2fs" filesystem driver in the Linux kernel. Other implementations (of varying quality and completeness) exist in GNU Hurd, MINIX 3, some BSD kernels, in MiNT, Haiku (operating system), Haiku and as third-party Microsoft Windows and macOS (via Filesystem_in_Userspace, FUSE) drivers. This driver was deprecated in Linux version 6.9 in favor of the ext4 driver, as the ext4 driver works with ext2 filesystems. ext2 was the default filesystem in several Linux distributions, including Debian and Red Hat Linux, until supplanted by ext3, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NTFS
NT File System (NTFS) (commonly called ''New Technology File System'') is a proprietary journaling file system developed by Microsoft in the 1990s. It was developed to overcome scalability, security and other limitations with File Allocation Table, FAT. NTFS adds several features that File Allocation Table, FAT and HPFS (file system), HPFS lack, including: access control lists (ACLs); filesystem encryption; transparent compression; sparse files; Journaling file system, file system journaling and shadow copy, volume shadow copy, a feature that allows backups of a system while in use. Starting with Windows NT 3.1, it is the default file system of the Windows NT family superseding the File Allocation Table (FAT) file system. NTFS read/write support is available on Linux and Berkeley Software Distribution, BSD using NTFS3 in Linux kernel, Linux and NTFS-3G in BSD. NTFS uses several files hidden from the user to store metadata about other files stored on the drive which can help impr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
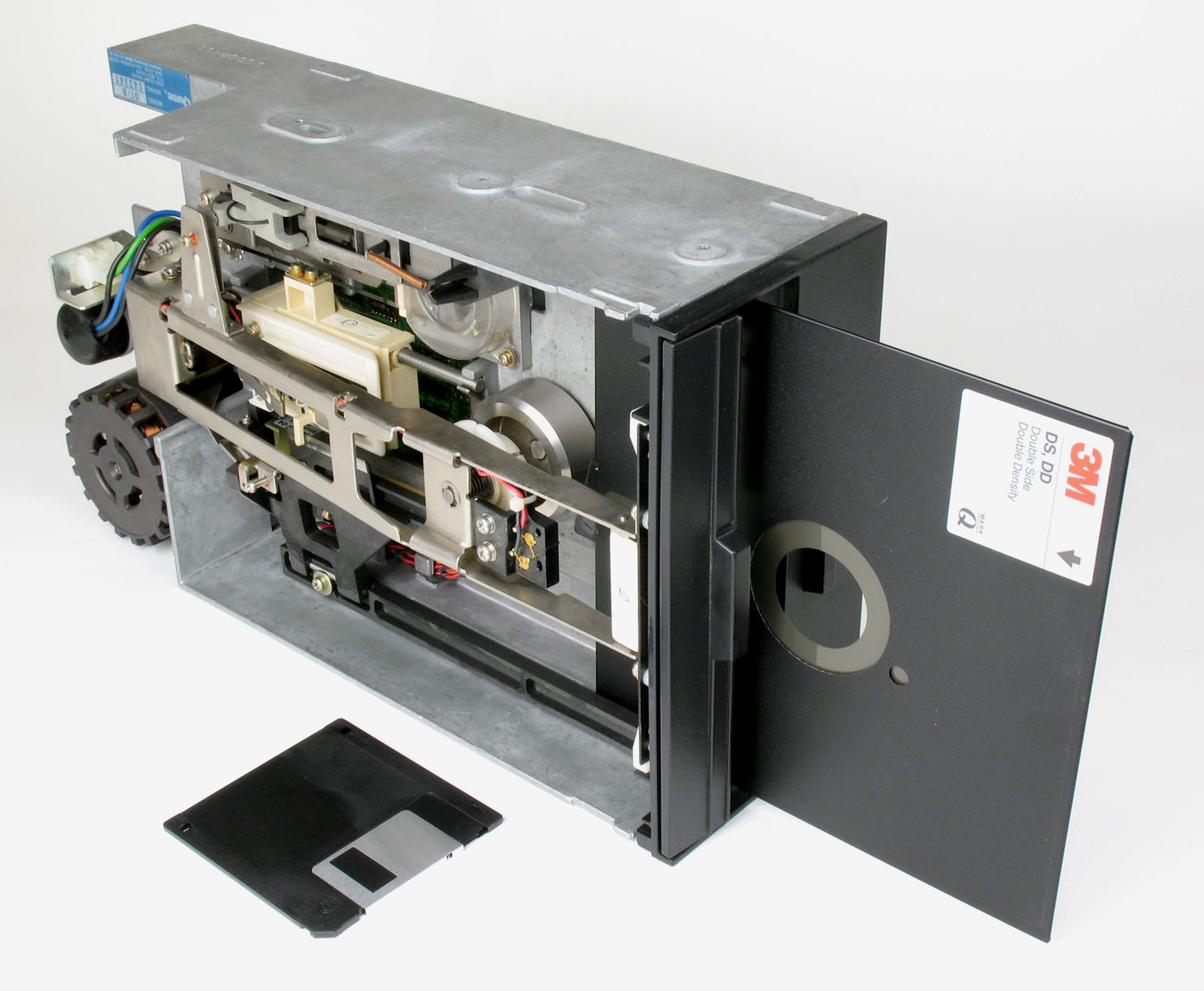
Floppy Disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, a diskette, or a disk) is a type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a fabric that removes dust particles from the spinning disk. The three most popular (and commercially available) floppy disks are the 8-inch, 5¼-inch, and 3½-inch floppy disks. Floppy disks store digital data which can be read and written when the disk is inserted into a floppy disk drive (FDD) connected to or inside a computer or other device. The first floppy disks, invented and made by IBM in 1971, had a disk diameter of . Subsequently, the 5¼-inch (133.35 mm) and then the 3½-inch (88.9 mm) became a ubiquitous form of data storage and transfer into the first years of the 21st century. 3½-inch floppy disks can still be used with an external USB floppy disk drive. USB drives for 5¼-inch, 8-inch, and other-size floppy disks are rare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMD APU
AMD Accelerated Processing Unit (APU), formerly known as Fusion, is a series of 64-bit microprocessors from Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), combining a general-purpose AMD64 central processing unit ( CPU) and 3D integrated graphics processing unit (IGPU) on a single die. AMD announced the first generation APUs, ''Llano'' for high-performance and ''Brazos'' for low-power devices, in January 2011 and launched the first units on June 14. The second generation ''Trinity'' for high-performance and ''Brazos-2'' for low-power devices were announced in June 2012. The third generation ''Kaveri'' for high performance devices were launched in January 2014, while ''Kabini'' and ''Temash'' for low-power devices were announced in the summer of 2013. Since the launch of the Zen microarchitecture, Ryzen and Athlon APUs have released to the global market as Raven Ridge on the DDR4 platform, after Bristol Ridge a year prior. AMD has also supplied semi-custom APUs for consoles starting with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Hardware
Computer hardware includes the physical parts of a computer, such as the central processing unit (CPU), random-access memory (RAM), motherboard, computer data storage, graphics card, sound card, and computer case. It includes external devices such as a Computer monitor, monitor, Computer mouse, mouse, Computer keyboard, keyboard, and Computer speakers, speakers. By contrast, software is a set of written instructions that can be stored and run by hardware. Hardware derived its name from the fact it is ''Hardness, hard'' or rigid with respect to changes, whereas software is ''soft'' because it is easy to change. Hardware is typically directed by the software to execute any command or Instruction (computing), instruction. A combination of hardware and software forms a usable computing system, although Digital electronics, other systems exist with only hardware. History Early computing devices were more complicated than the ancient abacus date to the seventeenth century. French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embedded System
An embedded system is a specialized computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including electrical or electronic hardware and mechanical parts. Because an embedded system typically controls physical operations of the machine that it is embedded within, it often has real-time computing constraints. Embedded systems control many devices in common use. , it was estimated that ninety-eight percent of all microprocessors manufactured were used in embedded systems. Modern embedded systems are often based on microcontrollers (i.e. microprocessors with integrated memory and peripheral interfaces), but ordinary microprocessors (using external chips for memory and peripheral interface circuits) are also common, especially in more complex systems. In either case, the processor(s) us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exokernel
Exokernel is an operating system kernel developed by the MIT Parallel and Distributed Operating Systems group, and also a class of similar operating systems. Operating systems generally present hardware resources to applications through high-level abstractions such as (virtual) file systems. The idea behind exokernels is to force as few abstractions as possible on application developers, enabling them to make as many decisions as possible about hardware abstractions. Exokernels are tiny, since functionality is limited to ensuring protection and multiplexing In telecommunications and computer networking, multiplexing (sometimes contracted to muxing) is a method by which multiple analog or digital signals are combined into one signal over a shared medium. The aim is to share a scarce resource� ... of resources, which is considerably simpler than conventional microkernels' implementation of message passing and monolithic kernels' implementation of high-level abstractions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ACPI
Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) is an open standard that operating systems can use to discover and configure computer hardware components, to perform power management (e.g. putting unused hardware components to sleep), auto configuration (e.g. Plug and Play and hot swapping), and status monitoring. It was first released in December 1996. ACPI aims to replace Advanced Power Management (APM), the MultiProcessor Specification, and the Plug and Play BIOS (PnP) Specification. ACPI brings power management under the control of the operating system, as opposed to the previous BIOS-centric system that relied on platform-specific firmware to determine power management and configuration policies. The specification is central to the Operating System-directed configuration and Power Management (OSPM) system. ACPI defines hardware abstraction interfaces between the device's firmware (e.g. BIOS, UEFI), the computer hardware components, and the operating systems. Internally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closed Source
Proprietary software is software that grants its creator, publisher, or other rightsholder or rightsholder partner a legal monopoly by modern copyright and intellectual property law to exclude the recipient from freely sharing the software or modifying it, and—in some cases, as is the case with some patent-encumbered and EULA-bound software—from making use of the software on their own, thereby restricting their freedoms. Proprietary software is a subset of non-free software, a term defined in contrast to free and open-source software; non-commercial licenses such as CC BY-NC are not deemed proprietary, but are non-free. Proprietary software may either be closed-source software or source-available software. Types Origin Until the late 1960s, computers—especially large and expensive mainframe computers, machines in specially air-conditioned computer rooms—were usually leased to customers rather than sold. Service and all software available were usually supplie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hummingbird
Hummingbirds are birds native to the Americas and comprise the Family (biology), biological family Trochilidae. With approximately 366 species and 113 genus, genera, they occur from Alaska to Tierra del Fuego, but most species are found in Central America, Central and South America. As of 2024, 21 hummingbird species are listed as Endangered species, endangered or critically endangered, with numerous species declining in population. Hummingbirds have varied specialized characteristics to enable rapid, maneuverable flight: exceptional metabolism, metabolic capacity, adaptations to high altitude, sensitive visual and communication abilities, and long-distance migration in some species. Among all birds, male hummingbirds have the widest diversity of plumage color, particularly in blues, greens, and purples. Hummingbirds are the smallest mature birds, measuring in length. The smallest is the bee hummingbird, which weighs less than , and the largest is the giant hummingbird, weig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |