|
Koenigs–Knorr Reaction
The Koenigs–Knorr reaction in organic chemistry is the substitution reaction of a glycosyl halide with an alcohol to give a glycoside. It is one of the oldest glycosylation reactions. It is named after Wilhelm Koenigs (1851–1906), a student of von Baeyer and fellow student with Hermann Emil Fischer, and Edward Knorr, a student of Koenigs. In its original form, Koenigs and Knorr treated ''acetobromoglucose'' with alcohols in the presence of silver carbonate. Shortly afterwards Fischer and Armstrong reported very similar findings. In the above example, the stereochemical outcome is determined by the presence of the neighboring group at C2 that lends anchimeric assistance, resulting in the formation of a 1,2-trans stereochemical arrangement. Esters (e.g. acetyl, benzoyl, pivalyl) generally provide good anchimeric assistance, whereas ethers (e.g. benzyl, methyl etc.) do not, leading to mixtures of stereoisomers. Mechanism In the first step of the mechanism, the glycosyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical ( in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but also containing other elements, especially oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus (included in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl or aryl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin. Structure and bonding Ethers feature bent C–O–C linkages. In dimethyl ether, the bond angle is 111° and C–O distances are 141 pm. The barrier to rotation about the C–O bonds is low. The bonding of oxygen in ethers, alcohols, and water is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helferich Method
The Helferich method may refer to: #Glycosylation of an alcohol using a glycosyl acetate as glycosyl donor and a Lewis acid (e.g. a metal halide) as promoter #Glycosylation of an alcohol using a glycosyl halide as a glycosyl donor and a mercury Mercury commonly refers to: * Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun * Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg * Mercury (mythology), a Roman god Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to: Companies * Merc ... salt as promoter (cf the Koenigs-Knorr reaction, which uses silver salts as promoters).B. Helferich, J. Zirner, Chem. Ber. 95, 2604 (1962) References {{reflist Organic reactions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemische Berichte
''Chemische Berichte'' (usually abbreviated as ''Ber.'' or ''Chem. Ber.'') was a German-language scientific journal of all disciplines of chemistry founded in 1868. It was one of the oldest scientific journals in chemistry, until it merged with ''Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas'' to form ''Chemische Berichte/Recueil'' in 1997. ''Chemische Berichte/Recueil'' was then merged with other European journals in 1998 to form ''European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry''. History Founded in 1868 as ''Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft'' (, CODEN BDCGAS), it operated under this title until 1928 (Vol. 61). The journal was then split into: * ''Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft, A: Vereins-Nachrichten'' (, CODEN BDCAAS), and * ''Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft, B: Abhandlungen'' (, CODEN BDCBAD). Vol. 78 and 79 (1945–1946) were omitted and not published due to World War II. The journal was renamed ''Chemische Berichte'' (, CODEN CHBEAM) in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Triflate
Silver trifluoromethanesulfonate, or silver triflate is the triflate (CF3SO3−) salt of Ag+. It is a white or colorless solid that is soluble in water and some organic solvents including, benzene. It is a reagent used in the synthesis of organic and inorganic triflates. Synthesis An early preparation method starts from the barium salt of trifluoromethanesulfonic acid (TfOH), from which the free TfOH is formed with dilute sulfuric acid, which is then neutralized with silver carbonate (Ag2CO3). :Ba^2+ SO2CF3 -> ce-\ce] CF3SO2OH -> ceCF3SO2O^- Ag+ The silver triflate is thereby obtained in a yield of 95% and can be recrystallized from benzene/tetrachloromethane or ether/tetrachloromethane Carbon tetrachloride, also known by many other names (such as tetrachloromethane, also recognised by the IUPAC, carbon tet in the cleaning industry, Halon-104 in firefighting, and Refrigerant-10 in HVACR) is an organic compound with the chemica ... for purification. In an improved vers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercuric Cyanide
Mercury(II) cyanide, also known as mercuric cyanide, is a compound of mercury. It is an odorless, toxic white powder. It is highly soluble in polar solvents such as water, alcohol, and ammonia; slightly soluble in ether; and insoluble in benzene and other hydrophobic solvents.Kocovsky, P., G. Wang, and V. Sharma. "Mercury(II) Cyanide." ''e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis.'' Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., 2001. http://www.mrw.interscience.wiley.com/eros/articles/rm034/sect0-fs.html Molecular and crystal structure At ambient temperature and ambient pressure, Hg(CN)2 takes the form of tetragonal crystals. These crystals are composed of nearly linear Hg(CN)2 molecules with a C-Hg-C bond angle of 175.0° and an Hg-C-N bond angle of 177.0° (AylettAylett, B.J. "Mercury (II) Pseudohalides: Cyanide, Thiocyanate, Selenocyanate, Azide, Fulminate." ''Comprehensive Inorganic Chemistry'' 3:304-306. J.C. Bailar, Harry Julius Emeléus, Sir Ronald Nyholm, and A.F. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercuric Oxide
Mercury(II) oxide, also called mercuric oxide or simply mercury oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula Mercury (element), Hgoxygen, O. It has a red or orange color. Mercury(II) oxide is a solid at room temperature and pressure. The mineral form montroydite is very rarely found. History An experiment for the preparation of mercuric oxide was first described by 11th century Arab-Spanish alchemist, Maslama al-Majriti, in ''Rutbat al-hakim.'' In 1774, Joseph Priestley discovered that oxygen was released by heating mercuric oxide, although he did not identify the gas as oxygen (rather, Priestley called it "Phlogiston, dephlogisticated air," as that was the paradigm that he was working under at the time). Synthesis The red form of HgO can be made by heating Hg in oxygen at roughly 350 °C, or by pyrolysis of mercury(II) nitrate, Hg(NO3)2. The yellow form can be obtained by precipitation of aqueous Hg2+ with alkali. The difference in color is due to particle size; b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercuric Bromide
Mercury(II) bromide or mercuric bromide is an inorganic compound with the formula HgBr2. This white solid is a laboratory reagent. Like all mercury salts, it is highly toxic. Preparation Mercury(II) bromide can be produced by reaction of metallic mercury with bromine. Reactions Mercury(II) bromide is used as a reagent in the Koenigs–Knorr reaction, which forms glycoside linkages on carbohydrates. It is also used to test for the presence of arsenic, as recommended by the Pharmacopoeia. The arsenic in the sample is first converted to arsine gas by treatment with hydrogen. Arsine reacts with mercury(II) bromide: : AsH3 + 3HgBr2 → As(HgBr)3 + 3 HBr The white mercury(II) bromide will turn yellow, brown, or black if arsenic is present in the sample. Mercury(II) bromide reacts violently with elemental indium at high temperatures and, when exposed to potassium Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleophilic Substitution
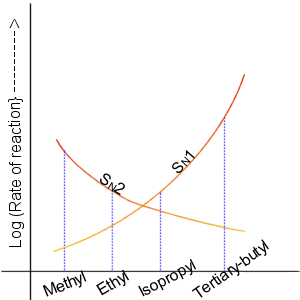
In chemistry, a nucleophilic substitution is a class of chemical reactions in which an electron-rich chemical species (known as a nucleophile) replaces a functional group within another electron-deficient molecule (known as the electrophile). The molecule that contains the electrophile and the leaving functional group is called the substrate. The most general form of the reaction may be given as the following: :\text\mathbf + \ce + \text\mathbf The electron pair (:) from the nucleophile (Nuc) attacks the substrate () and bonds with it. Simultaneously, the leaving group (LG) departs with an electron pair. The principal product in this case is . The nucleophile may be electrically neutral or negatively charged, whereas the substrate is typically neutral or positively charged. An example of nucleophilic substitution is the hydrolysis of an alkyl bromide, R-Br under basic conditions, where the attacking nucleophile is hydroxyl () and the leaving group is bromide (). :R-Br + OH- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Bromide
Silver bromide (AgBr) is a soft, pale-yellow, water-insoluble salt well known (along with other silver halides) for its unusual sensitivity to light. This property has allowed silver halides to become the basis of modern photographic materials. AgBr is widely used in photographic films and is believed by some to have been used for making the Shroud of Turin. The salt can be found naturally as the mineral bromargyrite. Preparation Although the compound can be found in mineral form, AgBr is typically prepared by the reaction of silver nitrate with an alkali bromide, typically potassium bromide: :AgNO3(aq) + KBr(aq) → AgBr(s)+ KNO3(aq) Although less convenient, the compound can also be prepared directly from its elements. Modern preparation of a simple, light-sensitive surface involves forming an emulsion of silver halide crystals in a gelatine, which is then coated onto a film or other support. The crystals are formed by precipitation in a controlled environment to produce smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs. A chemical mechanism is a theoretical conjecture that tries to describe in detail what takes place at each stage of an overall chemical reaction. The detailed steps of a reaction are not observable in most cases. The conjectured mechanism is chosen because it is thermodynamically feasible, and has experimental support in isolated intermediates (see next section) or other quantitative and qualitative characteristics of the reaction. It also describes each reactive intermediate, activated complex, and transition state, and which bonds are broken (and in what order), and which bonds are formed (and in what order). A complete mechanism must also explain the reason for the reactants and catalyst used, the stereochemistry observed in reactants and products, all products formed and the amount of each. The electron or arrow pushing method is often used in i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |