|
Kocurypelta
''Kocurypelta'' is an extinct genus of paratypothoracin aetosaur from the Late Triassic (Norian)-aged Lissauer Breccia of southern Poland. Only the type species is known, which is ''K. silvestris'', described by Czepiński ''et al.'' in 2021. Discovery and naming The holotype (ZPAL V.66/4), which consists of part of the maxilla, and referred material (three dorsal paramedial plates and a ventral plate fragment), was found in a layer of the Lissauer Breccia, of which the location was believed to have been lost after the formation was studied by Friedrich von Huene while describing ''Velocipes'' in 1932,Huene, F. von. (1932). ''Die fossile Reptil-Ordnung Saurischia, ihre Entwicklung und Geschichte''. ''Monogr. Geol. Pal''. 4 (1) pts. 1 and 2, viii + 361 pp. near Kocury, during excavations that began in 2012, that re-discovered and re-explored the formation. The remains were described as the new species ''Kocurypelta silvestris'' in 2021. Description According to Czepiński ''et a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lissauer Breccia
The Lissauer Breccia, sometimes referred to as the Kocury Locality, is a Norian geologic formation that is part of the larger Keuper limestone, which dominates across most of west and central Europe. Dinosaur remains diagnostic to the genus level are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.Weishampel, et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution." Pp. 517-607. The site was studied in 1932 and was later forgotten and not explored until excavations began in 2012, and the Lissauer Breccia was re-described in 2021. Fossil content * '' Kocurypelta silvestris'' * cf. ''Metaceratodus'' sp. * ''Proterochersis'' cf. ''porebensis'' * '' Velocipes guerichi'' See also * List of dinosaur-bearing rock formations ** List of stratigraphic units with few dinosaur genera This list of stratigraphic units with few non-avian dinosaur genera includes Mesozoic stratigraphic units of formation rank or higher that have produced dinosaur body fossils which have been referred to at m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
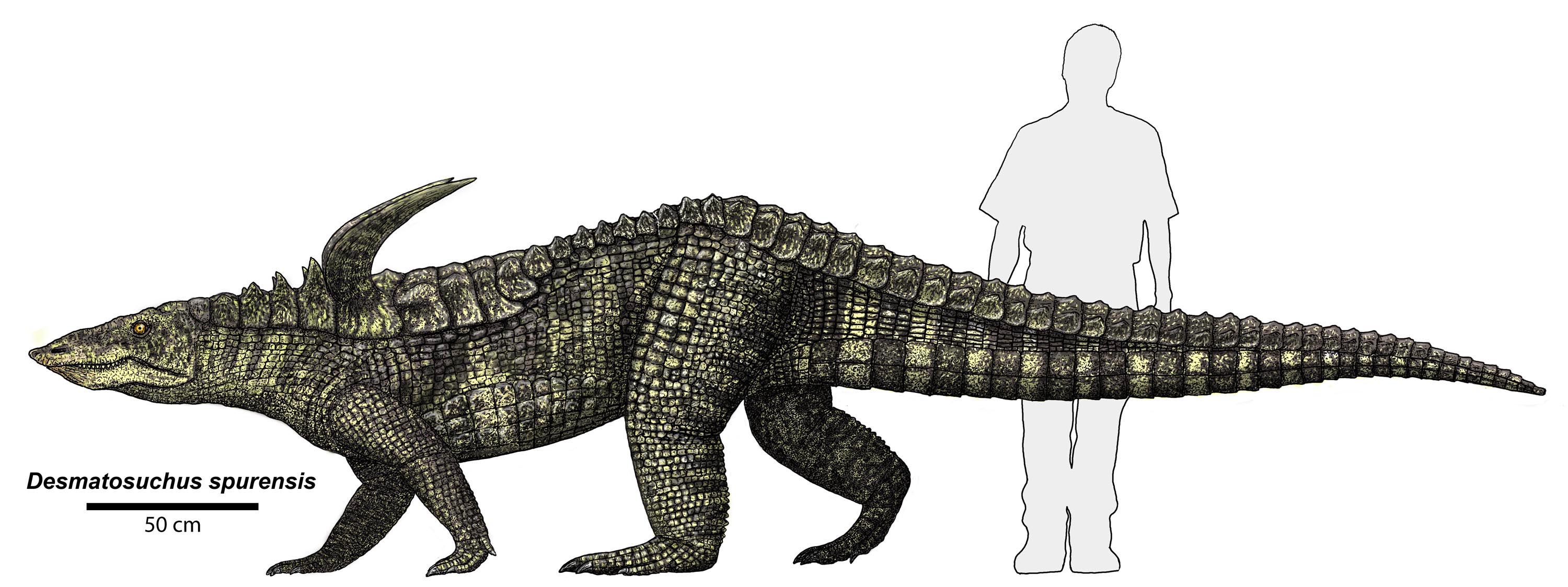
Aetosaurs
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order Aetosauria (; from Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized omnivorous or herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stratigraphic ranges were relatively short. Therefore, the presence of particular aetosaurs can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2021 In Archosaur Paleontology
This article records new taxa of fossil archosaurs of every kind that are scheduled binomial nomenclature, described during the year 2021, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleontology of archosaurs that are scheduled to occur in the year 2021. General research * A study on the relationship between full potential joint mobility and the poses used during locomotion in extant American alligator and helmeted guineafowl, evaluating its implications for reconstructions of locomotion of extinct archosaurs, is published by Manafzadeh, Kambic & Gatesy (2021). * A study on the Femur, femoral shape variation and on the relationship between femoral morphology and locomotor habits in early archosaurs and non-archosaur Archosauriformes, archosauriforms is published by Pintore ''et al.'' (2021). * A study estimating moment arms for major Pelvis, pelvic limb muscles in extant and fossil archosaurs, aiming to investigate the idea that bird-line archosaurs switched fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velocipes
''Velocipes'' (meaning "quick foot") is a saurischian dinosaur genus from the Late Triassic that may have been a theropod; its fossils were found in the Norian-age Lissauer Breccia of southern Poland.''Velocipes'' on the Dinosaur Mailing List Upon discovery, ''Velocipes'' was thought to have been a , but more recent studies have shown that ''Velocipes'' was probably a basal theropod or . History and taxonomy The |
Aetosaur
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order Aetosauria (; from Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized omnivorous or herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stratigraphic ranges were relatively short. Therefore, the presence of particular aetosaurs can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paratypothoracini
Paratypothoracini is a clade of aetosaurs within the group Typothoracinae. It is a node-based taxon that includes ''Rioarribasuchus'' (=''Heliocanthus''), ''Paratypothorax'', ''Tecovasuchus'', and all descendants of their most recent common ancestor. The clade was first named in 2007 under the spelling Paraypothoracisini, after its namesake ''Paratypothorax''. However, this spelling was based on incorrect taxonomic nomenclature, and the clade's name was corrected to Paratypothoracinae in 2016. All synapomorphies that diagnose Paratypothoracini can be found in their osteoderm Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, temnospondyls (extinct amp ...s. The paramedian osteoderms are wide and lie flat, without any apparent flexure (a trait convergent with some desmatosuchin aetosaurs) The paramedians possess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norian
The Norian is a division of the Triassic Period. It has the rank of an age (geochronology) or stage (chronostratigraphy). It lasted from ~227 to million years ago. It was preceded by the Carnian and succeeded by the Rhaetian. Stratigraphic definitions The Norian was named after the Noric Alps in Austria. The stage was introduced into scientific literature by Austrian geologist Edmund Mojsisovics von Mojsvar in 1869. The Norian Stage begins at the base of the ammonite biozones of '' Klamathites macrolobatus'' and '' Stikinoceras kerri'', and at the base of the conodont biozones of '' Metapolygnathus communisti'' and '' Metapolygnathus primitius''. A global reference profile for the base (a GSSP) had in 2009 not yet been appointed. The top of the Norian (the base of the Rhaetian) is at the first appearance of ammonite species '' Cochloceras amoenum''. The base of the Rheatian is also close to the first appearance of conodont species '' Misikella spp.'' and '' Epigondolella mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 2021
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proterochersis
''Proterochersis'' is an extinct genus of turtle from the Late Triassic period ( Norian stage) of Europe. It is known from a large number of fossils uncovered in Germany and Poland.Fraas E (1913)"''Proterochersis'', eine pleurodire Schildkröte aus dem Keuper" ''Jahreshefte des Vereins für Vaterländische Naturkunde in Württemberg'' 69: p. 13–30Szczygielski T & Sulej T (2016). "Revision of the Triassic European turtles ''Proterochersis'' and ''Murrhardtia'' (Reptilia, Testudinata, Proterochersidae), with the description of new taxa from Poland and Germany". ''Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society'' 177(2): pp. 395–427. Szczygielski1 T, Słowiak J & Dróżdż1 D (2018). "Shell variability in the stem turtles ''Proterochersis'' spp". ''PeerJ'' 6: The genus was named from fossil remains from Germany in 1913 by Fraas, who recognized two species: ''P. robusta'' (type species) and ''P. intermedia''. Since then, Szczygielski and Sulej have found that the differences described by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proterochersidae
Proterochersidae is an extinct family of stem-turtles belonging to Testudinata. List of genera There are two genera: * '' Keuperotesta'' Szczygielski & Sulej, 2016 (junior synonym of ''Proterochersis''?) ** '' Keuperotesta limendorsa'' Szczygielski & Sulej, 2016 * ''Proterochersis ''Proterochersis'' is an extinct genus of turtle from the Late Triassic period ( Norian stage) of Europe. It is known from a large number of fossils uncovered in Germany and Poland.Fraas E (1913)"''Proterochersis'', eine pleurodire Schildkröte aus ...'' Fraas, 1913 ** ''Proterochersis intermedia'' Fraas, 1913 (synonym of ''P. robusta''?) ** '' Proterochersis porebensis'' Szczygielski & Sulej, 2016 ** '' Proterochersis robusta'' Fraas, 1913 References Testudinata Triassic reptiles of Europe Taxa named by Franz Nopcsa von Felső-Szilvás Fossil taxa described in 1928 {{paleo-turtle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked turtles), which differ in the way the head retracts. There are 360 living and recently extinct species of turtles, including land-dwelling tortoises and freshwater terrapins. They are found on most continents, some islands and, in the case of sea turtles, much of the ocean. Like other amniotes (reptiles, birds, and mammals) they breathe air and do not lay eggs underwater, although many species live in or around water. Turtle shells are made mostly of bone; the upper part is the domed carapace, while the underside is the flatter plastron or belly-plate. Its outer surface is covered in scales made of keratin, the material of hair, horns, and claws. The carapace bones develop from ribs that grow sideways and develop into broad flat plates th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaceratodus
''Metaceratodus'' is an extinct genus of prehistoric lungfish in the family Ceratodontidae, with an indeterminate specimen known from the Late Triassic (Norian)-aged Lissauer Breccia of Poland and more complete specimens known from the Late Cretaceous of Queensland, Australia and Argentina ( Malargue Group). The genus was named and described by Frederick Chapman in 1914. Species The seven identified species of ''Metaceratodus'' are listed below, while an eighth unnamed species is known from Poland: * cf. ''Metaceratodus'' sp. * ''Metaceratodus baibianorum'' * ''Metaceratodus bonei'' * ''Metaceratodus ellioti'' * ''Metaceratodus kaopen'' (=''Ptychoceratodus kaopen'', ''P. cionei'') * ''Metaceratodus palmeri'' * ''Metaceratodus wichmanni'' (=''Ceratodus wichmanni'') * ''Metaceratodus wollastoni'' See also * Sarcopterygii * List of sarcopterygians * List of prehistoric bony fish A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |