|
Knapsack Problem
The knapsack problem is the following problem in combinatorial optimization: :''Given a set of items, each with a weight and a value, determine which items to include in the collection so that the total weight is less than or equal to a given limit and the total value is as large as possible.'' It derives its name from the problem faced by someone who is constrained by a fixed-size knapsack and must fill it with the most valuable items. The problem often arises in resource allocation where the decision-makers have to choose from a set of non-divisible projects or tasks under a fixed budget or time constraint, respectively. The knapsack problem has been studied for more than a century, with early works dating as far back as 1897. The subset sum problem is a special case of the decision and 0-1 problems where each kind of item, the weight equals the value: w_i=v_i. In the field of cryptography, the term ''knapsack problem'' is often used to refer specifically to the subset sum pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knapsack Problem Illustration
A backpack, also called knapsack, schoolbag, rucksack, pack, booksack, bookbag, haversack, packsack, or backsack, is in its simplest frameless form, a fabric sack carried on one's back and secured with two straps that go over the shoulders; but it can have an external or internal frame, and there are bodypacks. Backpacks are commonly used by hiking, hikers and students, and are often preferred to handbags for carrying heavy loads or carrying any sort of equipment, because of the limited capacity to carry heavy weights for long periods of time with hands. Large backpacks, used to carry loads over , as well as smaller sports backpacks (e.g. running, cycling, hiking, and hydration), usually offload the largest part (up to about 90%) of their weight onto padded hip belts, leaving the shoulder straps mainly for stabilizing the load. This improves the potential to carry heavy loads, as the hips are stronger than the shoulders, and also increases agility and balance, since the load ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-polynomial Time
In computational complexity theory, a numeric algorithm runs in pseudo-polynomial time if its running time is a polynomial in the ''numeric value'' of the input (the largest integer present in the input)—but not necessarily in the ''length'' of the input (the number of bits required to represent it), which is the case for polynomial time algorithms.Michael R. Garey and David S. Johnson. Computers and Intractability: A Guide to the Theory of NP-Completeness. W.H. Freeman and Company, 1979. In general, the numeric value of the input is exponential in the input length, which is why a pseudo-polynomial time algorithm does not necessarily run in polynomial time with respect to the input length. An NP-complete problem with known pseudo-polynomial time algorithms is called weakly NP-complete. An NP-complete problem is called strongly NP-complete if it is proven that it cannot be solved by a pseudo-polynomial time algorithm unless . The strong/weak kinds of NP-hardness are defined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branch And Bound
Branch and bound (BB, B&B, or BnB) is a method for solving optimization problems by breaking them down into smaller sub-problems and using a bounding function to eliminate sub-problems that cannot contain the optimal solution. It is an algorithm design paradigm for discrete and combinatorial optimization problems, as well as mathematical optimization. A branch-and-bound algorithm consists of a systematic enumeration of candidate solutions by means of state space search: the set of candidate solutions is thought of as forming a rooted tree with the full set at the root. The algorithm explores ''branches'' of this tree, which represent subsets of the solution set. Before enumerating the candidate solutions of a branch, the branch is checked against upper and lower estimated ''bounds'' on the optimal solution, and is discarded if it cannot produce a better solution than the best one found so far by the algorithm. The algorithm depends on efficient estimation of the lower and u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subset-sum Problem
The subset sum problem (SSP) is a decision problem in computer science. In its most general formulation, there is a multiset S of integers and a target-sum T, and the question is to decide whether any subset of the integers sum to precisely T''.'' The problem is known to be NP-complete. Moreover, some restricted variants of it are NP-complete too, for example: * The variant in which all inputs are positive. * The variant in which inputs may be positive or negative, and T=0. For example, given the set \, the answer is ''yes'' because the subset \ sums to zero. * The variant in which all inputs are positive, and the target sum is exactly half the sum of all inputs, i.e., T = \frac(a_1+\dots+a_n) . This special case of SSP is known as the partition problem. SSP can also be regarded as an optimization problem: find a subset whose sum is at most ''T'', and subject to that, as close as possible to ''T''. It is NP-hard, but there are several algorithms that can solve it reasonably quic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real RAM
In computing, especially computational geometry, a real RAM (random-access machine) is a mathematical model of a computer that can compute with exact real numbers instead of the binary fixed-point or floating-point numbers used by most actual computers. The real RAM was formulated by Michael Ian Shamos in his 1978 Ph.D. dissertation. Model The "RAM" part of the real RAM model name stands for "random-access machine". This is a model of computing that resembles a simplified version of a standard computer architecture. It consists of a stored program, a computer memory unit consisting of an array of cells, and a central processing unit with a bounded number of registers. Each memory cell or register can store a real number. Under the control of the program, the real RAM can transfer real numbers between memory and registers, and perform arithmetic operations on the values stored in the registers. The allowed operations typically include addition, subtraction, multiplication, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rationals
In mathematics, a rational number is a number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction of two integers, a numerator and a non-zero denominator . For example, is a rational number, as is every integer (for example, The set of all rational numbers is often referred to as "the rationals", and is closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division by a nonzero rational number. It is a field under these operations and therefore also called the field of rationals or the field of rational numbers. It is usually denoted by boldface , or blackboard bold A rational number is a real number. The real numbers that are rational are those whose decimal expansion either terminates after a finite number of digits (example: ), or eventually begins to repeat the same finite sequence of digits over and over (example: ). This statement is true not only in base 10, but also in every other integer base, such as the binary and hexadecimal ones (see ). A real number t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Number
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a continuous one- dimensional quantity such as a duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that pairs of values can have arbitrarily small differences. Every real number can be almost uniquely represented by an infinite decimal expansion. The real numbers are fundamental in calculus (and in many other branches of mathematics), in particular by their role in the classical definitions of limits, continuity and derivatives. The set of real numbers, sometimes called "the reals", is traditionally denoted by a bold , often using blackboard bold, . The adjective ''real'', used in the 17th century by René Descartes, distinguishes real numbers from imaginary numbers such as the square roots of . The real numbers include the rational numbers, such as the integer and the fraction . The rest of the real numbers are called irrational numbers. Some irrational numbers (as well as all the rationals) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affine Function
In Euclidean geometry, an affine transformation or affinity (from the Latin, ''wikt:affine, affinis'', "connected with") is a geometric transformation that preserves line (geometry), lines and parallel (geometry), parallelism, but not necessarily Euclidean distances and angles. More generally, an affine transformation is an automorphism of an affine space (Euclidean spaces are specific affine spaces), that is, a Function (mathematics), function which Map (mathematics), maps an affine space onto itself while preserving both the dimension of any affine subspaces (meaning that it sends points to points, lines to lines, planes to planes, and so on) and the ratios of the lengths of Parallel (geometry), parallel line segments. Consequently, sets of parallel affine subspaces remain parallel after an affine transformation. An affine transformation does not necessarily preserve angles between lines or distances between points, though it does preserve ratios of distances between points lyin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
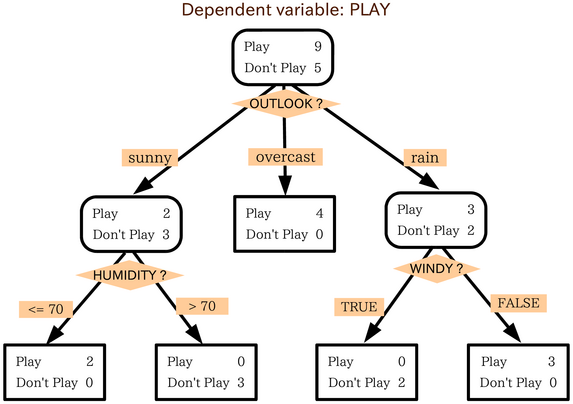
Decision Tree Model
In computational complexity theory, the decision tree model is the model of computation in which an algorithm can be considered to be a decision tree, i.e. a sequence of ''queries'' or ''tests'' that are done adaptively, so the outcome of previous tests can influence the tests performed next. Typically, these tests have a small number of outcomes (such as a yes–no question) and can be performed quickly (say, with unit computational cost), so the worst-case time complexity of an algorithm in the decision tree model corresponds to the depth of the corresponding tree. This notion of computational complexity of a problem or an algorithm in the decision tree model is called its decision tree complexity or query complexity. Decision tree models are instrumental in establishing lower bounds for the complexity of certain classes of computational problems and algorithms. Several variants of decision tree models have been introduced, depending on the computational model and type of quer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turing Machine
A Turing machine is a mathematical model of computation describing an abstract machine that manipulates symbols on a strip of tape according to a table of rules. Despite the model's simplicity, it is capable of implementing any computer algorithm. The machine operates on an infinite memory tape divided into discrete mathematics, discrete cells, each of which can hold a single symbol drawn from a finite set of symbols called the Alphabet (formal languages), alphabet of the machine. It has a "head" that, at any point in the machine's operation, is positioned over one of these cells, and a "state" selected from a finite set of states. At each step of its operation, the head reads the symbol in its cell. Then, based on the symbol and the machine's own present state, the machine writes a symbol into the same cell, and moves the head one step to the left or the right, or halts the computation. The choice of which replacement symbol to write, which direction to move the head, and whet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strongly NP-complete
In computational complexity, strong NP-completeness is a property of computational problems that is a special case of NP-completeness. A general computational problem may have numerical parameters. For example, the input to the bin packing problem is a list of objects of specific sizes and a size for the bins that must contain the objects—these object sizes and bin size are numerical parameters. A problem is said to be strongly NP-complete (NP-complete in the strong sense), if it remains NP-complete even when all of its numerical parameters are bounded by a polynomial in the length of the input. A problem is said to be strongly NP-hard if a strongly NP-complete problem has a pseudo-polynomial reduction to it. This pseudo-polynomial reduction is more restrictive than the usual poly-time reduction used for NP-hardness proofs. In special, the pseudo-polynomial reduction cannot output a numerical parameter that is not polinomially bounded by the size and value of numbers in the inp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weakly NP-complete
In computational complexity, an NP-complete (or NP-hard) problem is weakly NP-complete (or weakly NP-hard) if there is an algorithm for the problem whose running time is polynomial in the dimension of the problem and the magnitudes of the data involved (provided these are given as integers), rather than the base-two logarithms of their magnitudes. Such algorithms are technically exponential functions of their input size and are therefore not considered polynomial. For example, the NP-hard knapsack problem can be solved by a dynamic programming algorithm requiring a number of steps polynomial in the size of the knapsack and the number of items (assuming that all data are scaled to be integers); however, the runtime of this algorithm is exponential time since the input sizes of the objects and knapsack are logarithmic in their magnitudes. However, as Garey and Johnson (1979) observed, “A pseudo-polynomial-time algorithm … will display 'exponential behavior' only when confronted w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |