|
Klonimir Strojimirović
Klonimir ( gr, Κλονίμηρος, sr-cyr, Клонимир; fl. 896) was a Serbian prince of the Vlastimirović dynasty, and pretender to the throne of the Serbian Principality. His father and uncle, co-princes Strojimir and Gojnik, had been exiled to Bulgaria with their families after their eldest brother Mutimir had ousted them and taken the Serbian throne. Klonimir married a Bulgarian noblewoman chosen by Khan Boris I himself. She later gave birth to a son named Časlav. The descendants of the three Vlastimirović branches continued the feud over the Serbian throne which spanned over the century, and Klonimir returned to Serbia in ca. 896 and attempted to take the country from his cousin Petar, who had ruled since 891. He managed to take over the Serbian city of Destinikon, but the much more powerful Petar defeated him, and it is presumed that Klonimir died in battle. His son Časlav later became the most powerful of the Vlastimirović dynasty, as Prince of Serbia from 92 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petar Of Serbia
Petar Gojniković or Peter of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Петар Гојниковић, gr, Πέτρος; ca. 870 – 917) was Prince of the Serbs from 892 to 917. He ruled and expanded the First Serbian Principality and won several wars against other family members that sought the crown. He was the first Serbian monarch with a Christian (non-Slavic) name. Petar was the son of Gojnik, the youngest son of Vlastimir (r. 831–851) of the first Serbian dynasty (ruling since the early 7th century). Early life Petar was born between 870 and 874, as the son of the Prince Gojnik, the youngest son of dynastic founding father Vlastimir. His Byzantine Christian name, in relation to the previous generation of pagan names, shows the spread of Christianization among the Serbs.''The entry of the Slavs into Christendom''p. 209/ref> At the time of his birth, Serbia was ruled as an oligarchy consisting of the three brothers Mutimir, Gojnik and Strojimir, although Mutimir, the oldest, had sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Of Bulgaria
Vladimir-Rasate (, ) was the ruler of the First Bulgarian Empire from 889 to 893. Biography In 853 or 854, the Bulgar Army led by Vladimir, the son of Boris I of Bulgaria, invaded Serbia in an attempt to exact vengeance for the previous defeat of Presian in 839-842 against Vlastimir. The Serbian Army, led by Mutimir and his brothers, defeated the Bulgars, capturing Vladimir and 12 boyars.''The early medieval Balkans''p. 141/ref> Boris I and Mutimir agreed on peace (and perhaps an alliance), and Mutimir sent his sons Pribislav and Stefan to the border to escort the prisoners, where they exchanged items as a sign of peace. Boris gave them "rich gifts", while he was given "two slaves, two falcons, two dogs, and 80 furs". Vladimir became ruler (Knyaz) of Bulgaria when his father Boris-Mihail I (Boris adopted the name Mihail - Michael - after his baptism) decided to retire to a monastery after a reign of 36 years. Preserved seals with the inscription "Michael the Monk, who is archo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
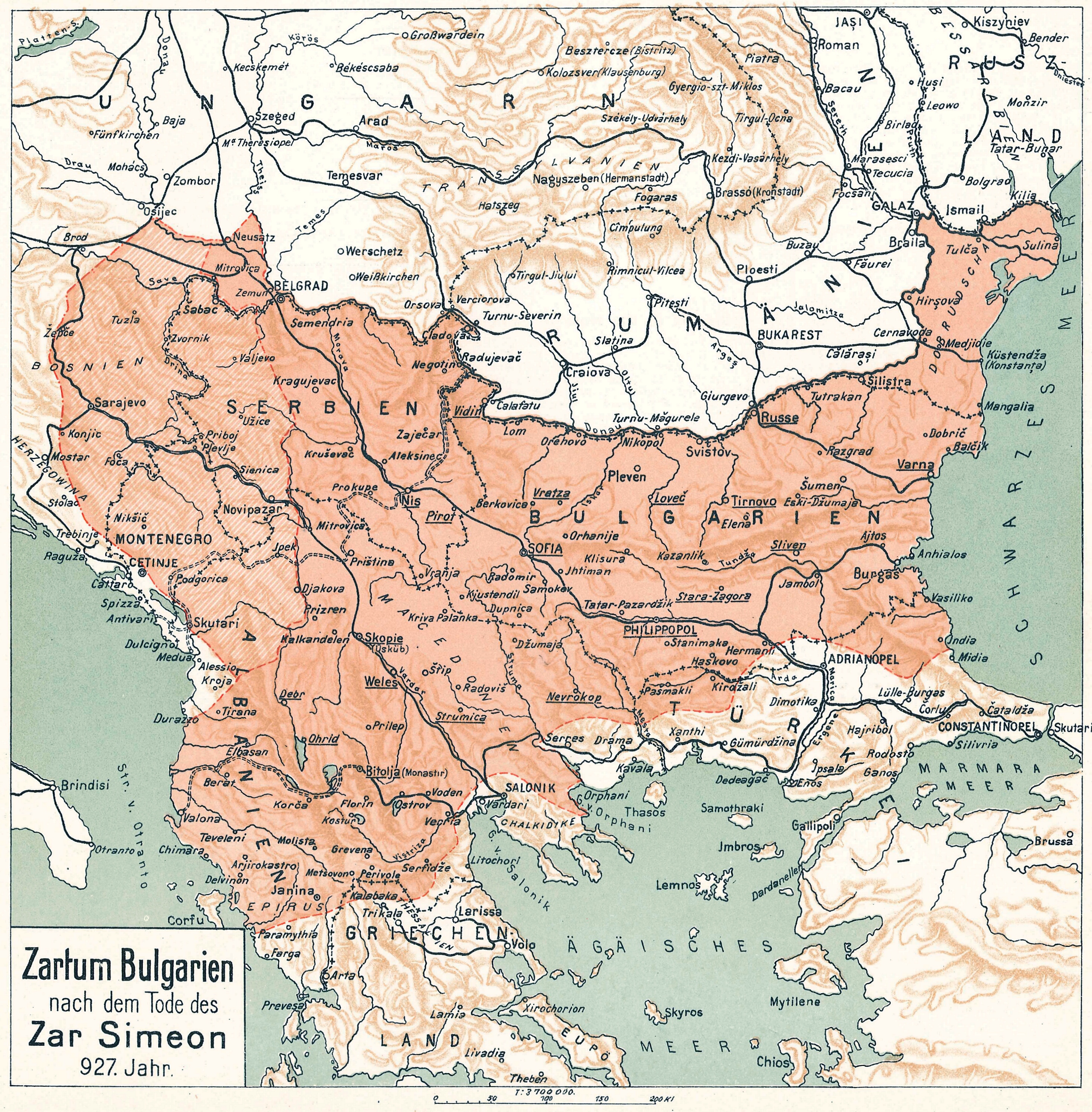
Byzantine–Bulgarian Wars
The Byzantine–Bulgarian wars were a series of conflicts fought between the Byzantines and Bulgarians which began when the Bulgars first settled in the Balkan peninsula in the 5th century, and intensified with the expansion of the Bulgarian Empire to the southwest after 680 AD. The Byzantines and Bulgarians continued to clash over the next century with variable success, until the Bulgarians, led by Krum, inflicted a series of crushing defeats on the Byzantines. After Krum died in 814, his son Omurtag negotiated a thirty-year peace treaty. Simeon I had multiple successful campaigns against the Byzantines during his rule from 893 to 927. His son Peter I negotiated another long-lasting peace treaty. His rule was followed by a period of decline of the Bulgarian state. In 971 John I Tzimiskes, the Byzantine emperor, subjugated much of the weakening Bulgarian Empire by defeating Boris II and capturing Preslav, the Bulgarian capital. Samuel managed to stabilize the Bulgarian state w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seal Of Strojimir
Seal may refer to any of the following: Common uses * Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly: ** Earless seal, or "true seal" ** Fur seal * Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of authentication, on paper, wax, clay or another medium (the impression is also called a seal) * Seal (mechanical), a device which helps prevent leakage, contain pressure, or exclude contamination where two systems join Arts, entertainment and media * ''Seal'' (1991 album), by Seal * ''Seal'' (1994 album), sometimes referred to as ''Seal II'', by Seal * '' Seal IV'', a 2003 album by Seal * '' Seal Online'', a 2003 massively multiplayer online role-playing game Law * Seal (contract law), a legal formality for contracts and other instruments * Seal (East Asia), a stamp used in East Asia as a form of a signature * Record sealing Military * ''Fairey Seal'', a 1930s British carrier-borne torpedo bomber airc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symeon I Of Bulgaria
Tsar Simeon (also Symeon) I the Great ( cu, цѣсар҄ь Сѷмеѡ́нъ А҃ Вели́къ, cěsarĭ Sỳmeonŭ prĭvŭ Velikŭ bg, цар Симеон I Велики, Simeon I Veliki el, Συμεών Αʹ ὁ Μέγας, Sumeṓn prôtos ho Mégas) ruled over Bulgaria from 893 to 927,Lalkov, ''Rulers of Bulgaria'', pp. 23–25. during the First Bulgarian Empire. Simeon's successful campaigns against the Byzantines, Magyars and Serbs led Bulgaria to its greatest territorial expansion ever, making it the most powerful state in contemporary Eastern and Southeast Europe. His reign was also a period of unmatched cultural prosperity and enlightenment later deemed the Golden Age of Bulgarian culture. During Simeon's rule, Bulgaria spread over a territory between the Aegean, the Adriatic and the Black Sea.Bakalov, ''Istorija na Bǎlgarija'', "Simeon I Veliki". The newly independent Bulgarian Orthodox Church became the first new patriarchate besides the Pentarchy, and Bulgarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomorje
Pomorje ( sr-Cyrl, Поморје), also known (in plural) as the Lands of Pomorje ( sr, / ), is a medieval term, used to designate several maritime regions of Upper Dalmatia and its hinterland, that at the end of the 12th century, during the reign of Stefan Nemanja (1166–1196), became part of the Grand Principality of Serbia, and remained part of the medieval Kingdom of Serbia, whose rulers were styled with the title: "''crowned king and autocrat of all Serbian and coastal lands''". The term ''Pomorje'' (or ''Primorje'') literally means: coastland (coastal, littoral). Today, regions of medieval Pomorje belong to modern Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia. History Pomorje included most of the coastal regions of modern-day Montenegro, southern halves of Dalmatia and Herzegovina region.Nevill Forbes, ''The Balkans: A History of Bulgaria, Serbia, Greece, Rumania, Turkey''p. 59 Digital Antiquaria, 2004, , Medieval Pomorje included most of the coastal regions of mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Mutilation In Byzantine Culture
Mutilation was a common method of punishment for criminals in the Byzantine Empire, but it also had a role in the empire's political life. By blinding a rival, one would not only restrict his mobility but also make it almost impossible for him to lead an army into battle, then an important part of taking control of the empire. Castration was also used to eliminate potential opponents. In the Byzantine Empire, for a man to be castrated meant that he was no longer a man—half-dead, "life that was half death". Castration also eliminated any chance of heirs being born to threaten either the emperor’s or the emperor's children's place at the throne. Other mutilations were the severing of the nose (rhinotomy), or the amputating of limbs. Rationale The mutilation of political rivals by the emperor was deemed an effective way of side-lining from the line of succession a person who was seen as a threat. Castrated men were not seen as a threat, as no matter how much power they gained t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stefan Mutimirović
Stefan Mutimirović ( sr, Стефан Мутимировић, gr, Στέφανος) was a 9th-century Serbian royal member of the ruling dynasty, the Vlastimirović. He was the younger son of Mutimir of the ruling Serbian dynasty, the Vlastimirovići. His father had with his brothers Strojimir and Gojnik, defeated the Bulgar Army sent by Tsar Boris, led by his son Vladimir. They were captured with 12 boyar A boyar or bolyar was a member of the highest rank of the Feudalism, feudal nobility in many Eastern European states, including Kievan Rus', Bulgarian Empire, Bulgaria, Russian nobility, Russia, Boyars of Moldavia and Wallachia, Wallachia and ...s, but were soon freed in exchange for good relations between the peoples. Peace was agreed upon and Stefan and his older brother, Pribislav, escorted the prisoners towards the border beyond Rascia. There, Boris gave them rich gifts and received 2 slaves, 2 falcons, two dogs, and 80 furs from Mutimir. References Sources ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bran Mutimirović
Bran Mutimirović ( la, Branus) was a Serbian prince, son of Serbian ruler Mutimir. He and Stefan escorted Khan Boris I of Bulgaria to the Rascian-Bulgar border after the Serbs successfully fought off the Khan's army in an attempted revenge to the defeat of Presian years earlier by their grandfather Vlastimir. Bran and Stefan were given presents for the escort, and in turn gifted 2 slaves, 2 falcons, 2 dogs, and 80 furs as a symbol of friendship, the Bulgars were pleased with the tribute. After the death of his father Mutimir, his elder brother Pribislav took the Serbian crown, but was deposed after a year by their cousin Petar Gojniković and fled with Bran and Stefan to Croatia. Three years after the accession of Petar, Bran rebelled against him but was captured and blinded. He was married and had a son, Pavle Branović.''The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest''. John Van Antwerp Fine John V. A. Fine Jr. (born 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pribislav Of Serbia
Pribislav ( sr, Прибислав, gr, Πριβέσθλαβος) was Prince of the Serbs for a year, in 891–892, before being deposed by his cousin Petar. He was the eldest son of Mutimir (r. 851–891) of the Vlastimirović dynasty, who ruled during the expanding and Christianization of Serbia. Life His father had with his brothers Strojimir and Gojnik, defeated the Bulgar Army sent by ''Tsar'' Boris I of Bulgaria and led by his son Vladimir.''The early medieval Balkans''p. 141/ref> Vladimir was captured together with 12 boyars. Boris I and Mutimir agreed on peace (and perhaps an alliance), and Mutimir sent his sons Bran and Stefan beyond the border to escort the prisoners, where they exchanged items as a sign of peace: Boris himself gave them "rich gifts", while he was given "two slaves, two falcons, two dogs, and eighty furs". In the 880s, Mutimir seized the throne, exiling his younger brothers and Klonimir, Strojimir's son, to the court of Boris I in the Bulgar Kha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petar Gojniković
Petar Gojniković or Peter of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Петар Гојниковић, gr, Πέτρος; ca. 870 – 917) was List of Serbian monarchs, Prince of the Serbs from 892 to 917. He ruled and expanded the Principality of Serbia (early medieval), First Serbian Principality and won several wars against other family members that sought the crown. He was the first Serbian monarch with a Christian (non-Slavic) name. Petar was the son of Gojnik, the youngest son of Vlastimir (r. 831–851) of House of Vlastimirović, the first Serbian dynasty (ruling since the early 7th century). Early life Petar was born between 870 and 874, as the son of the Prince Gojnik, the youngest son of dynastic founding father Vlastimir of Serbia, Vlastimir. His Byzantine Christian name, in relation to the previous generation of pagan names, shows the spread of Christianization among the Serbs.''The entry of the Slavs into Christendom''p. 209/ref> At the time of his birth, Serbia was ruled as an o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliska
Pliska ( , cu, Пльсковъ, translit=Plĭskovŭ) was the first capital of the First Bulgarian Empire during the Middle Ages and is now a small town in Shumen Province, on the Ludogorie plateau of the Danubian Plain, 20 km northeast of the provincial capital, Shumen. Pliska was the first capital of Bulgaria, and according to legend founded by Asparuh of Bulgaria in the late 7th century; this legend is archaeologically unsubstantiated. The site was originally an encampment, with the first tent-shaped buildings at Pliska of uncertain date. No evidence exists of a settlement before the 9th century, and claims that the site dates from Late Antiquity have been contested. By the early 9th century, Pliska was surrounded by a defensive wall and of land was further enclosed by an outer earthwork with stone revetment long. After the Byzantine army sacked and burned Pliska in 811, led by the emperor Nikephoros I (), Pliska was rebuilt by Omurtag (), who used ''spolia'' from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)