|
Klein's Inequality
In mathematics, there are many kinds of inequality (mathematics), inequalities involving matrix (mathematics), matrices and linear operators on Hilbert spaces. This article covers some important operator inequalities connected with Trace (linear algebra), traces of matrices.E. Carlen, Trace Inequalities and Quantum Entropy: An Introductory Course, Contemp. Math. 529 (2010) 73–140 B. Simon, Trace Ideals and their Applications, Cambridge Univ. Press, (1979); Second edition. Amer. Math. Soc., Providence, RI, (2005). Basic definitions Let H''n'' denote the space of Hermitian matrix, Hermitian × matrices, H''n''+ denote the set consisting of Positive-definite matrix#Negative-definite, semidefinite and indefinite matrices, positive semi-definite × Hermitian matrices and H''n''++ denote the set of Positive-definite matrix#Negative-definite, semidefinite and indefinite matrices, positive definite Hermitian matrices. For operators on an infinite dimensional Hilbert space we require that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
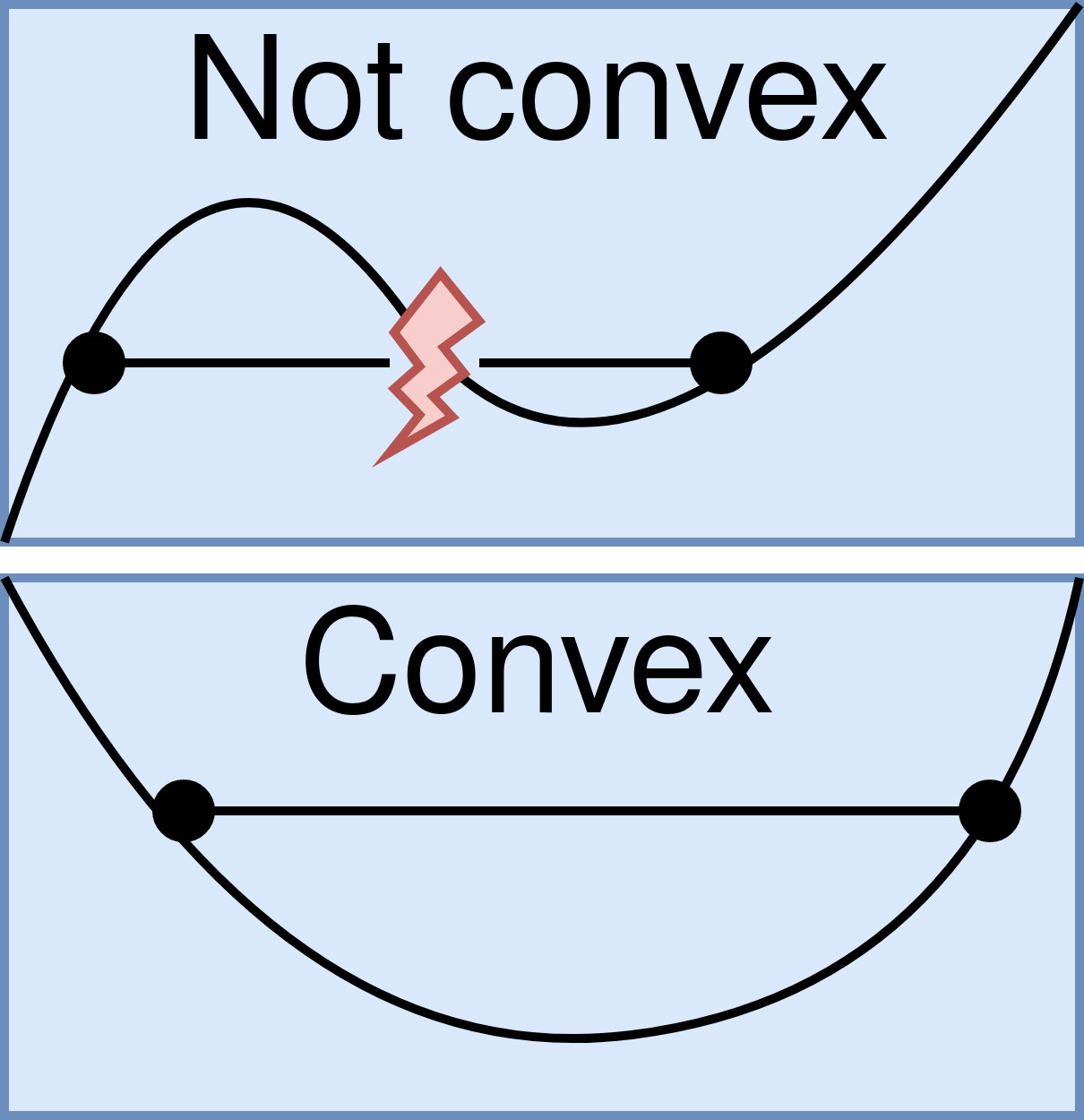
Convex Function
In mathematics, a real-valued function is called convex if the line segment between any two points on the graph of a function, graph of the function lies above the graph between the two points. Equivalently, a function is convex if its epigraph (mathematics), epigraph (the set of points on or above the graph of the function) is a convex set. A twice-differentiable function of a single variable is convex if and only if its second derivative is nonnegative on its entire domain. Well-known examples of convex functions of a single variable include the quadratic function x^2 and the exponential function e^x. In simple terms, a convex function refers to a function whose graph is shaped like a cup \cup, while a concave function's graph is shaped like a cap \cap. Convex functions play an important role in many areas of mathematics. They are especially important in the study of optimization problems where they are distinguished by a number of convenient properties. For instance, a st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eigenvalue
In linear algebra, an eigenvector () or characteristic vector of a linear transformation is a nonzero vector that changes at most by a scalar factor when that linear transformation is applied to it. The corresponding eigenvalue, often denoted by \lambda, is the factor by which the eigenvector is scaled. Geometrically, an eigenvector, corresponding to a real nonzero eigenvalue, points in a direction in which it is stretched by the transformation and the eigenvalue is the factor by which it is stretched. If the eigenvalue is negative, the direction is reversed. Loosely speaking, in a multidimensional vector space, the eigenvector is not rotated. Formal definition If is a linear transformation from a vector space over a field into itself and is a nonzero vector in , then is an eigenvector of if is a scalar multiple of . This can be written as T(\mathbf) = \lambda \mathbf, where is a scalar in , known as the eigenvalue, characteristic value, or characteristic root ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singular Value
In mathematics, in particular functional analysis, the singular values, or ''s''-numbers of a compact operator T: X \rightarrow Y acting between Hilbert spaces X and Y, are the square roots of the (necessarily non-negative) eigenvalues of the self-adjoint operator T^*T (where T^* denotes the adjoint of T). The singular values are non-negative real numbers, usually listed in decreasing order (''σ''1(''T''), ''σ''2(''T''), …). The largest singular value ''σ''1(''T'') is equal to the operator norm of ''T'' (see Min-max theorem). If ''T'' acts on Euclidean space \Reals ^n, there is a simple geometric interpretation for the singular values: Consider the image by T of the unit sphere; this is an ellipsoid, and the lengths of its semi-axes are the singular values of T (the figure provides an example in \Reals^2). The singular values are the absolute values of the eigenvalues of a normal matrix ''A'', because the spectral theorem can be applied to obtain unitary diagonalization of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Von Neumann
John von Neumann (; hu, Neumann János Lajos, ; December 28, 1903 – February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian-American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist, engineer and polymath. He was regarded as having perhaps the widest coverage of any mathematician of his time and was said to have been "the last representative of the great mathematicians who were equally at home in both pure and applied mathematics". He integrated pure and applied sciences. Von Neumann made major contributions to many fields, including mathematics (foundations of mathematics, measure theory, functional analysis, ergodic theory, group theory, lattice theory, representation theory, operator algebras, matrix theory, geometry, and numerical analysis), physics (quantum mechanics, hydrodynamics, ballistics, nuclear physics and quantum statistical mechanics), economics ( game theory and general equilibrium theory), computing ( Von Neumann architecture, linear programming, numerical meteo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrum (functional Analysis)
In mathematics, particularly in functional analysis, the spectrum of a bounded linear operator (or, more generally, an unbounded linear operator) is a generalisation of the set of eigenvalues of a matrix. Specifically, a complex number \lambda is said to be in the spectrum of a bounded linear operator T if T-\lambda I is not invertible, where I is the identity operator. The study of spectra and related properties is known as spectral theory, which has numerous applications, most notably the mathematical formulation of quantum mechanics. The spectrum of an operator on a finite-dimensional vector space is precisely the set of eigenvalues. However an operator on an infinite-dimensional space may have additional elements in its spectrum, and may have no eigenvalues. For example, consider the right shift operator ''R'' on the Hilbert space ℓ2, :(x_1, x_2, \dots) \mapsto (0, x_1, x_2, \dots). This has no eigenvalues, since if ''Rx''=''λx'' then by expanding this expression we see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jensen's Inequality
In mathematics, Jensen's inequality, named after the Danish mathematician Johan Jensen, relates the value of a convex function of an integral to the integral of the convex function. It was proved by Jensen in 1906, building on an earlier proof of the same inequality for doubly-differentiable functions by Otto Hölder in 1889. Given its generality, the inequality appears in many forms depending on the context, some of which are presented below. In its simplest form the inequality states that the convex transformation of a mean is less than or equal to the mean applied after convex transformation; it is a simple corollary that the opposite is true of concave transformations. Jensen's inequality generalizes the statement that the secant line of a convex function lies ''above'' the graph of the function, which is Jensen's inequality for two points: the secant line consists of weighted means of the convex function (for ''t'' ∈ ,1, :t f(x_1) + (1-t) f(x_2), while t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Relative Entropy
In quantum information theory, quantum relative entropy is a measure of distinguishability between two density matrix, quantum states. It is the quantum mechanical analog of relative entropy. Motivation For simplicity, it will be assumed that all objects in the article are finite-dimensional. We first discuss the classical case. Suppose the probabilities of a finite sequence of events is given by the probability distribution ''P'' = , but somehow we mistakenly assumed it to be ''Q'' = . For instance, we can mistake an unfair coin for a fair one. According to this erroneous assumption, our uncertainty about the ''j''-th event, or equivalently, the amount of information provided after observing the ''j''-th event, is :\; - \log q_j. The (assumed) average uncertainty of all possible events is then :\; - \sum_j p_j \log q_j. On the other hand, the Shannon entropy of the probability distribution ''p'', defined by :\; - \sum_j p_j \log p_j, is the real amount of uncertainty befor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density Matrix
In quantum mechanics, a density matrix (or density operator) is a matrix that describes the quantum state of a physical system. It allows for the calculation of the probabilities of the outcomes of any measurement performed upon this system, using the Born rule. It is a generalization of the more usual state vectors or wavefunctions: while those can only represent pure states, density matrices can also represent ''mixed states''. Mixed states arise in quantum mechanics in two different situations: first when the preparation of the system is not fully known, and thus one must deal with a statistical ensemble of possible preparations, and second when one wants to describe a physical system which is entangled with another, without describing their combined state. Density matrices are thus crucial tools in areas of quantum mechanics that deal with mixed states, such as quantum statistical mechanics, open quantum systems, quantum decoherence, and quantum information. Definition and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieb's Concavity Theorem
In mathematics, there are many kinds of inequalities involving matrices and linear operators on Hilbert spaces. This article covers some important operator inequalities connected with traces of matrices.E. Carlen, Trace Inequalities and Quantum Entropy: An Introductory Course, Contemp. Math. 529 (2010) 73–140 B. Simon, Trace Ideals and their Applications, Cambridge Univ. Press, (1979); Second edition. Amer. Math. Soc., Providence, RI, (2005). Basic definitions Let H''n'' denote the space of Hermitian × matrices, H''n''+ denote the set consisting of positive semi-definite × Hermitian matrices and H''n''++ denote the set of positive definite Hermitian matrices. For operators on an infinite dimensional Hilbert space we require that they be trace class and self-adjoint, in which case similar definitions apply, but we discuss only matrices, for simplicity. For any real-valued function on an interval ⊂ ℝ, one may define a matrix function for any operator with eigenvalue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermitian Adjoint
In mathematics, specifically in operator theory, each linear operator A on a Euclidean vector space defines a Hermitian adjoint (or adjoint) operator A^* on that space according to the rule :\langle Ax,y \rangle = \langle x,A^*y \rangle, where \langle \cdot,\cdot \rangle is the inner product on the vector space. The adjoint may also be called the Hermitian conjugate or simply the Hermitian after Charles Hermite. It is often denoted by in fields like physics, especially when used in conjunction with bra–ket notation in quantum mechanics. In finite dimensions where operators are represented by matrices, the Hermitian adjoint is given by the conjugate transpose (also known as the Hermitian transpose). The above definition of an adjoint operator extends verbatim to bounded linear operators on Hilbert spaces H. The definition has been further extended to include unbounded '' densely defined'' operators whose domain is topologically dense in—but not necessarily equal to— ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliott Lieb
Elliott Hershel Lieb (born July 31, 1932) is an American mathematical physicist and professor of mathematics and physics at Princeton University who specializes in statistical mechanics, condensed matter theory, and functional analysis. Lieb is a prolific author, with over 400 publications both in physics and mathematics. In particular, his scientific works pertain to quantum and classical many-body problem, atomic structure, the stability of matter, functional inequalities, the theory of magnetism, and the Hubbard model. Biography He received his B.S. in physics from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1953 and his PhD in mathematical physics from the University of Birmingham in England in 1956. Lieb was a Fulbright Fellow at Kyoto University, Japan (1956–1957), and worked as the Staff Theoretical Physicist for IBM from 1960 to 1963. In 1961–1962, Lieb was on leave as professor of applied mathematics at Fourah Bay College, the University of Sierra Leone. He has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |