|
Kitai-gorod Wall
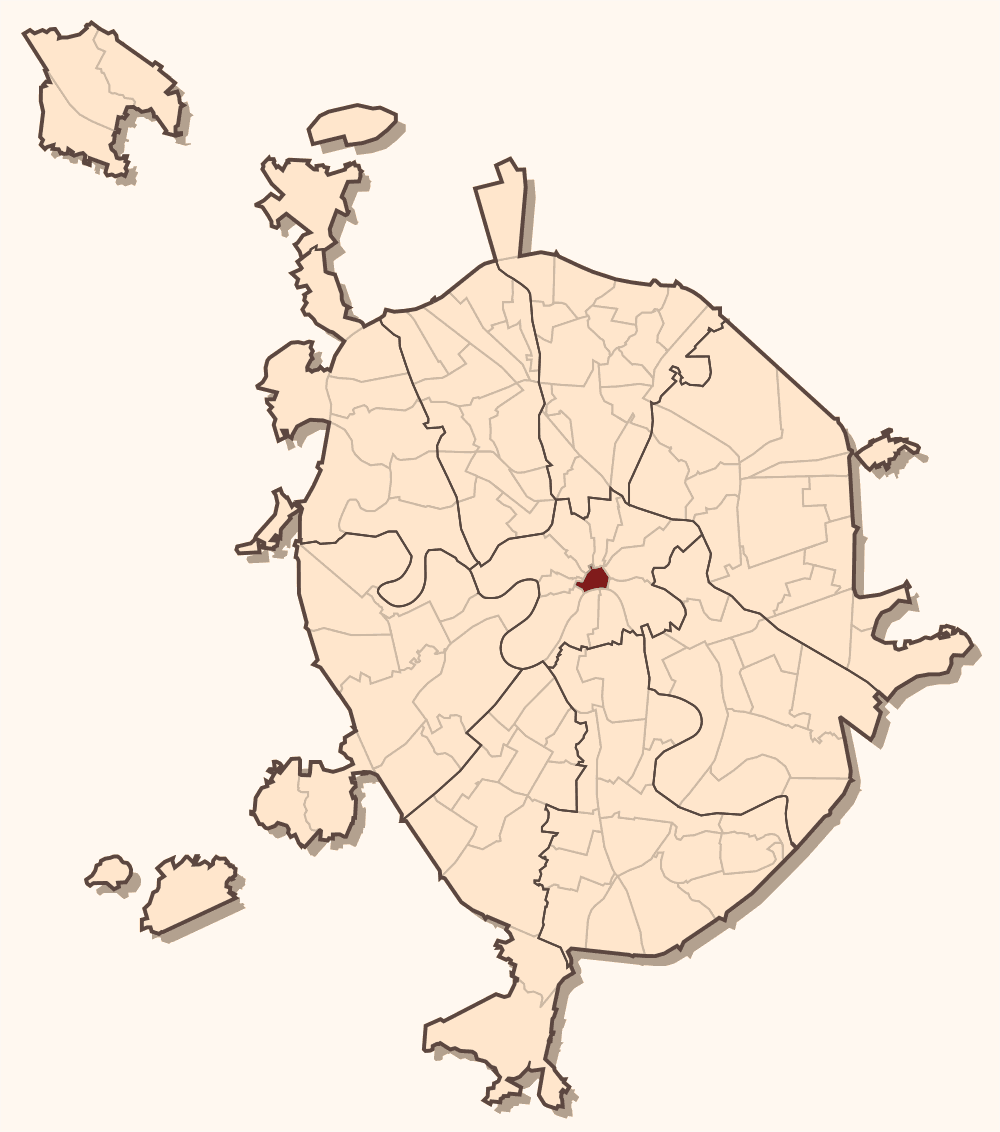
Kitay-gorod ( rus, Китай-город, p=kʲɪˈtaj ˈɡorət), also referred to as the Great Possad () in the 16th and 17th centuries, is a cultural and historical area within the central part of Moscow in Russia, defined by the remnants of now almost entirely razed fortifications, narrow streets and very densely built cityscape. It is separated from the Kremlin by Red Square. Kitay-gorod does not constitute a district (''raion''), as there are no resident voters, thus, municipal elections are not possible. Rather, the territory has been part of Tverskoy District, and the Central Administrative Okrug authorities have managed the area directly since 2003. Etymology Beside Kitay-gorod in Moscovia in ancient Russia, Kitay was also a name for a sea. A sea called Kitay exists in Odessa in Ukraine. Older sources said that people with darker skin than other ethnic groups of Russia sold goods and traded with other peoples in the area of the Kitay sea. ''Kita'' (pl. ''kity'') i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathay
Cathay (; ) is a historical name for China that was used in Europe. During the early modern period, the term ''Cathay'' initially evolved as a term referring to what is now Northern China, completely separate and distinct from China, which was a reference to southern China. As knowledge of East Asia increased, Cathay came to be seen as the same polity as China as a whole. The term ''Cathay'' became a poetic name for China. The name ''Cathay'' originates from the word '' Khitan'', a name of a para-Mongolic nomadic people who ruled the Liao dynasty in northern China from 916 to 1125, and who later migrated west after they were overthrown by the Jin dynasty to form the Qara Khitai (Western Liao dynasty) for another century thereafter. Originally, this name was the name applied by Central and Western Asians and Europeans to northern China; the name was also used in Marco Polo's book on his travels in Yuan dynasty China (he referred to southern China as '' Mangi''). Od ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilyinka Street
Ilyinka (russian: Ильинка) is the name of several inhabited localities in Russia. Modern localities Altai Krai As of 2012, two rural localities in Altai Krai bear this name: *Ilyinka, Shelabolikhinsky District, Altai Krai, a '' selo'' in Ilyinsky Selsoviet of Shelabolikhinsky District; *Ilyinka, Shipunovsky District, Altai Krai, a ''selo'' in Ilyinsky Selsoviet of Shipunovsky District; Altai Republic As of 2012, one rural locality in the Altai Republic bears this name: *Ilyinka, Altai Republic, a '' selo'' in Ilyinskoye Rural Settlement of Shebalinsky District; Astrakhan Oblast As of 2012, two inhabited localities in Astrakhan Oblast bear this name: ;Urban localities *Ilyinka, Ikryaninsky District, Astrakhan Oblast, a work settlement in Ikryaninsky District; ;Rural localities *Ilyinka, Volodarsky District, Astrakhan Oblast, a '' selo'' in Bolshemogoysky Selsoviet of Volodarsky District; Republic of Bashkortostan As of 2012, two rural localities in the Republic o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavyanskaya Square
Slavyanskaya Square () is a square in central Moscow, also known in 1924-1991 as northern side of Nogina Square (Площадь Ногина); the southern side of former Nogina Square is now called Varvarka Gates Square (Площадь Варварских Ворот). These two square separates central Kitai-gorod from eastward Tagansky District. They connect to Varvarka Street (west), Solyanka Street (east), Kitaigorodsky Lane (south), Staraya Square and Lubyansky Lane (north), completing the half-circle of Central Squares of Moscow around Moscow Kremlin and Kitai-gorod. Disambiguation Slavyanskaya Square and southbound Varvarka Gates Square form a contiguous city square, but are officially different locations, a fact that may confuse even Muscovites. To add to this confusion, Staraya Square is not a square per se but a city street (closed to regular traffic) that discharges into Varvarka Gates Square. In the past, Staraya (Old) and Novaya (New) Squares frequently inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubyanka (KGB)
The Lubyanka ( rus, Лубянка, p=lʊˈbʲankə) is the popular name for the building which contains the headquarters of the FSB, and its affiliated prison, on Lubyanka Square in the Meshchansky District of Moscow, Russia. It is a large Neo-Baroque building with a facade of yellow brick designed by Alexander V. Ivanov in 1897 and augmented by Aleksey Shchusev from 1940 to 1947. It was previously the national headquarters of the KGB. Soviet hammer and sickles can be seen on the building's facade. Description The Lubyanka building is home to the Lubyanka prison, the headquarters of the Border Guard Service, a KGB museum, and a subsection of the FSB. Part of the prison was turned into a prison museum, but a special authorization is required for visits. The lower floors are made of granite with emblazoned Soviet crests. History Origins The Lubyanka was originally built in 1898 as the headquarters of the All-Russia Insurance Company (''Rossiya Insurance Company'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubyanka Square
Lubyanskaya Square (, Lubyanskaya ploshchad'), or simply Lubyanka in Moscow lies about north-east of Red Square. History first records its name in 1480, when Grand Prince Ivan III of Moscow, who had conquered Novgorod in 1471, settled many Novgorodians in the area. They built the church of St Sophia, modelled after St Sophia Cathedral in Novgorod, and called the area ''Lubyanka'' after the Lubyanitsa street of their native city. Name The square was renamed Dzerzhinsky Square for many years (1926–1990) in honor of the founder of the Soviet security service Felix Dzerzhinsky. Square center A fountain used to stand in front of the building, at the center of the Lubyanka Square. In 1958, the fountain at the center of the Lubyanka Square was replaced by an 11-ton statue of Felix Dzerzhinsky ("Iron Felix"), founder of the Cheka, made by Yevgeny Vuchetich. On October 30, 1990, the Memorial organization erected the Solovetsky Stone, a monument to the victims of the Gulag, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
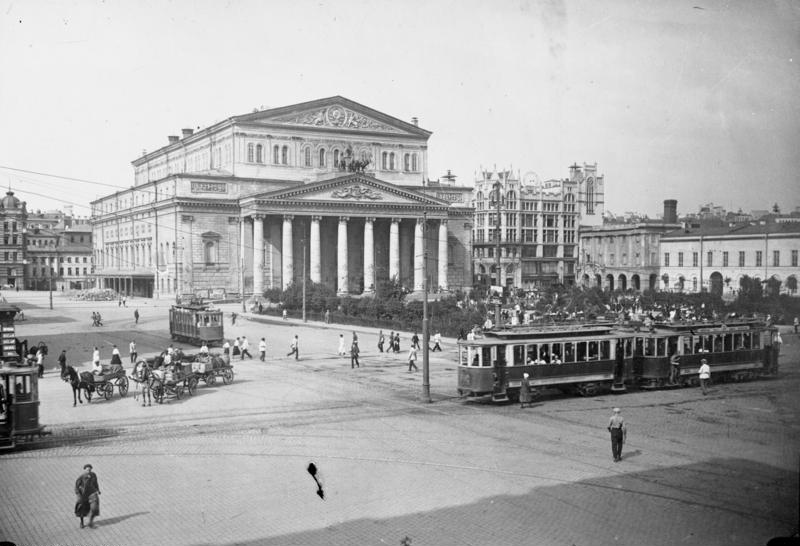
Bolshoi Theatre
The Bolshoi Theatre ( rus, Большо́й теа́тр, r=Bol'shoy teatr, literally "Big Theater", p=bɐlʲˈʂoj tʲɪˈatər) is a historic theatre in Moscow, Russia, originally designed by architect Joseph Bové, which holds ballet and opera performances. Before the October Revolution it was a part of the Imperial Theatres of the Russian Empire along with Maly Theatre (''Small Theatre'') in Moscow and a few theatres in Saint Petersburg ( Hermitage Theatre, Bolshoi (Kamenny) Theatre, later Mariinsky Theatre and others). The Bolshoi Ballet and Bolshoi Opera are among the oldest and best known ballet and opera companies in the world. It is by far the world's biggest ballet company, with more than 200 dancers. The theatre is the parent company of The Bolshoi Ballet Academy, a leading school of ballet. It has a branch at the Bolshoi Theater School in Joinville, Brazil. The main building of the theatre, rebuilt and renovated several times during its history, is a landmark o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theatre Square (Moscow)
Theatre Square or Teatralnaya Square (russian: Театральная площадь, ''Teatralnaya ploshchad''), known as Sverdlov Square between 1919 and 1991, is a city square in the Tverskoy District of central Moscow, Russia. It is at the junction of Kuznetsky Bridge Street, Petrovka Street, and Theatre Drive (north-west of the latter; the square south-east of Theatre Drive is the separate Revolution Square). The square is named after the three theatres located on it: the Bolshoi Theatre, Maly Theatre, and Russian Academic Youth Theatre. The square is served by the Moscow metro at the Teatralnaya station on the Zamoskvoretskaya Line; Okhotny Ryad station on the Sokolnicheskaya Line; and Ploshchad Revolyutsii station on the Arbatsko-Pokrovskaya Line. History The square emerged after the 1812 Fire of Moscow and conversion of the Neglinnaya River into an underground channel. The river still flows diagonally under the square's park. It was designed in a symmetric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Squares Of Moscow
The Central Squares of Moscow consists of a chain of squares around the historical Moscow Kremlin and Kitai-gorod areas of central Moscow, Russia, following the historical and now mostly razed down Kitai-gorod wall. These squares and avenues connecting them form the innermost ring road in Moscow open to regular traffic. The names of central squares changed frequently for political reasons and as a result of urban redevelopment; some of these squares are actually city streets (Staraya Square, Novaya Square); other locations are shaped like squares, but have no names of their own. List This is a list of the Central Squares and their connecting avenues, clockwise from Bolshoy Kamenny Bridge: * Borovitskaya Square ** Manege Street (inner ring, closed to traffic) and Mokhovaya Street (outer ring) * Manezhnaya Square, Moscow ** Okhotny Ryad Street * Revolution Square, Moscow (inner ring) and Theatre Square (outer ring) ** Teatralny Lane * Lubyanka Square ** Novaya Square (inner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hotel Metropol (Moscow)
The Hotel Metropol Moscow (russian: Метропо́ль, ) is a historic hotel in the center of Moscow, Russia, built in 1899–1905 in Art Nouveau style. It is notable as the largest extant Moscow hotel built before the Russian Revolution of 1917, and for the unique collaboration of architects ( William Walcot, Lev Kekushev, Vladimir Shukhov) and artists (Mikhail Vrubel, Alexander Golovin, Nikolai Andreev). Since 2012, the hotel has been owned by Alexander Klyachin, who also is proprietor of the Moscow-based Azimut Hotels chain. History In 1898, Savva Mamontov and Petersburg Insurance consolidated a large lot of land around the former Chelyshev Hotel. Mamontov, manager and sponsor of Private Opera, intended to redevelop the area into a large cultural center built around an opera hall. Mamontov eventually hired Kekushev as a construction manager. Soon, Savva Mamontov was jailed for fraud and the project was taken over by Petersburg Insurance, omitting the opera hall tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow Metro
The Moscow Metro) is a metro system serving the Russian capital of Moscow as well as the neighbouring cities of Krasnogorsk, Reutov, Lyubertsy and Kotelniki in Moscow Oblast. Opened in 1935 with one line and 13 stations, it was the first underground railway system in the Soviet Union. , the Moscow Metro, excluding the Moscow Central Circle, the Moscow Central Diameters and the Moscow Monorail, has 250 stations (287 with Moscow Central Circle) and its route length is , making it the fifth-longest in the world and the longest outside China. The system is mostly underground, with the deepest section underground at the Park Pobedy station, one of the world's deepest underground stations. It is the busiest metro system in Europe, and is considered a tourist attraction in itself. Operations The Moscow Metro, a state-owned enterprise, is long and consists of 15 lines and 250 stations organized in a spoke-hub distribution paradigm, with the majority of rail lines running rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okhotny Ryad (Moscow Metro)
Okhotny Ryad (russian: Охотный ряд) is a station on the Sokolnicheskaya Line of the Moscow Metro. It is situated in the very centre of Moscow in the Tverskoy District, near the Kremlin, Manezhnaya Square and State Duma. It is named after a nearby street, whose name literally means "hunters' row". History Okhotny Ryad station is located under what was originally the swamplands of the upper Neglinnaya River. Later two ancient churches stood on the site, and their graveyards were excavated during the construction of the station. The station opened as part of the original Metro line on 15 May 1935. Okhotny Ryad has been renamed more times than any other Metro station. Planned to be called Okhotnoryadskaya, it was opened as Okhotny Ryad instead. The station was renamed Imeni Kaganovicha in honour of Lazar Kaganovich during the brief period between 25 November 1955 and 1957, when its original name was restored. The station's name was changed once more on 30 November 1961, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)