|
Kirklington Hall Research Station
Kirklington Hall Research Station was a geophysical research institute of BP in Kirklington, Nottinghamshire. During the 1950s it was the main research site of BP. History As part of the East Midlands Oil Province, oil was found in eastern Nottinghamshire. It was also known as the BP Research Centre or the Geophysical Centre, part of BP's Exploration Division. The research centre was established in 1950. Its first employee was Jack Birks, later Managing Director of BP. From 1950 it was the main research site of BP, until BP sold the site in 1957 for £12,000. Research moved to Sunbury-on-Thames, in Surrey, in 1957. Sunbury had been built around the same time as the Kirklington site, in the early 1950s. Kirklington Hall today is a private school. Structure The former site is situated north of the A617. Function It conducted geophysical research for exploration for BP. This part of BP is now known as BP Exploration. Work would be conducted on core samples and with seismi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirklington Oil Well - Geograph
Kirklington may refer to: *Kirklington, North Yorkshire, England *Kirklington, Nottinghamshire, England See also *Kirklinton Kirklinton is a village in the Carlisle district, in the English county of Cumbria. The population of the civil parish of Kirklinton Middle, taken at the 2011 census was 384. It is a few miles away from the large village of Longtown. It has ..., Cumbria, England * Kirtlington, Oxfordshire, England {{Geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Institutes In England
Research is " creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion on past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, discovery, interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific, humanities, artistic, econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Institutes Established In 1950
Research is " creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion on past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, discovery, interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific, humanities, artistic, ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petroleum Organizations
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude oil and petroleum products that consist of refined crude oil. A fossil fuel, petroleum is formed when large quantities of dead organisms, mostly zooplankton and algae, are buried underneath sedimentary rock and subjected to both prolonged heat and pressure. Petroleum is primarily recovered by oil drilling. Drilling is carried out after studies of structural geology, sedimentary basin analysis, and reservoir characterisation. Recent developments in technologies have also led to exploitation of other unconventional reserves such as oil sands and oil shale. Once extracted, oil is refined and separated, most easily by distillation, into innumerable products for direct use or use in manufacturing. Products include fuels such as gasoline (pet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
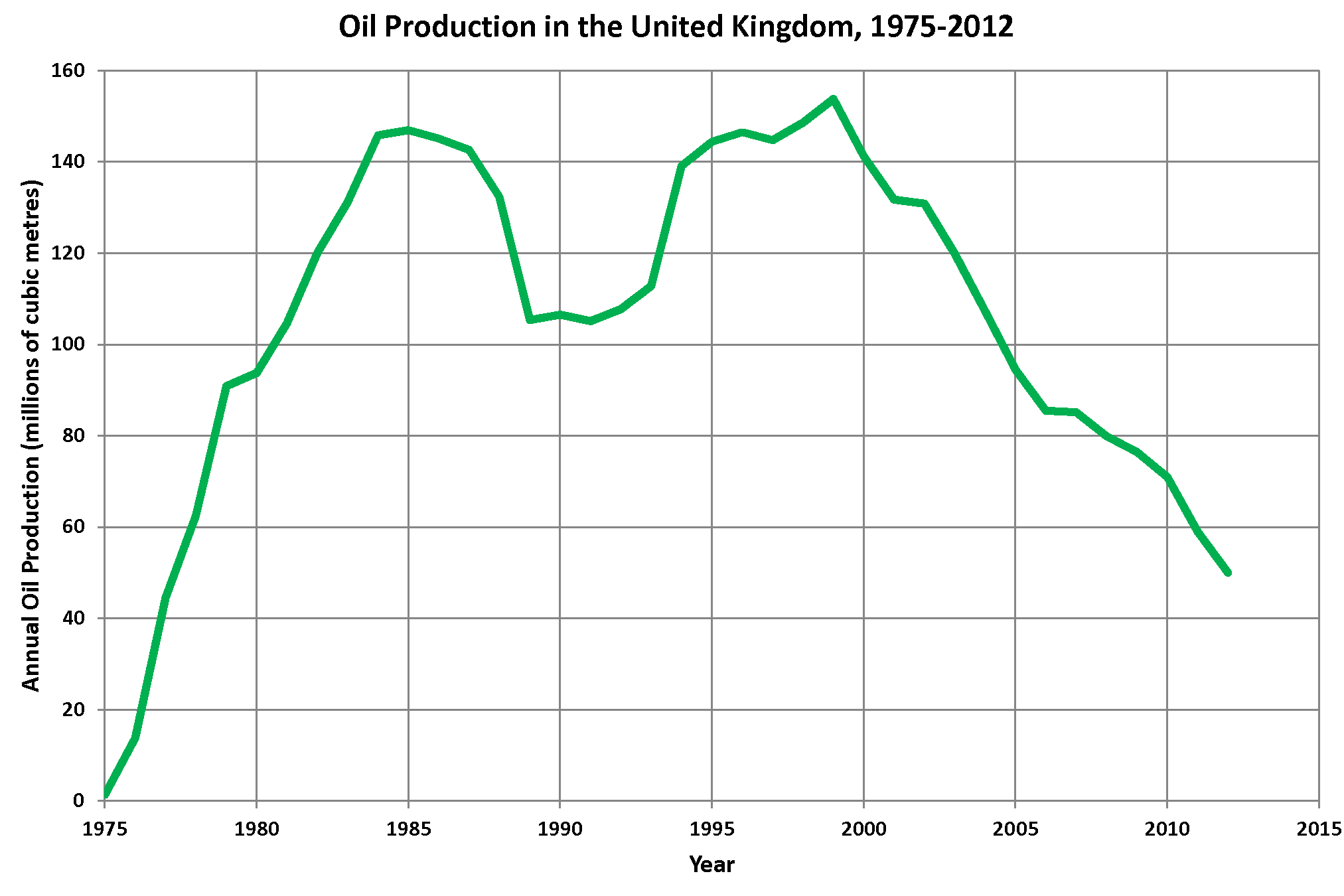
Petroleum Industry In The United Kingdom
The oil and gas industry plays a central role in the economy of the United Kingdom. Oil and gas account for more than three-quarters of the UK's total primary energy needs. Oil provides 97 per cent of the fuel for transport, and gas is a key fuel for heating and electricity generation. Transport, heating and electricity each account for about one-third of the UK's primary energy needs. Oil and gas are also major feedstocks for the petrochemicals industries producing pharmaceuticals, plastics, cosmetics and domestic appliances. Although UK Continental Shelf production peaked in 1999, in 2016 the sector produced 62,906,000 cubic metres of oil and gas, meeting more than half of the UK's oil and gas needs. There could be up to 3.18 billion cubic metres of oil and gas still to recover from the UK's offshore fields. In 2017, capital investment in the UK offshore oil and gas industry was £5.6 billion. Since 1970 the industry has paid almost £330 billion in production tax. About 280,000 j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Science Research Institutes
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More solar energy is rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineering Research Institutes
Engineering is the use of scientific method, scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more specialized List of engineering branches, fields of engineering, each with a more specific emphasis on particular areas of applied mathematics, applied science, and types of application. See glossary of engineering. The term ''engineering'' is derived from the Latin ''ingenium'', meaning "cleverness" and ''ingeniare'', meaning "to contrive, devise". Definition The American Engineers' Council for Professional Development (ECPD, the predecessor of Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology, ABET) has defined "engineering" as: The creative application of scientific principles to design or develop structures, machines, apparatus, or manufacturing processes, or works utilizing them singly or in combination; or to construct o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Research Institutes
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Nottinghamshire
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1957 Disestablishments In England
1957 ( MCMLVII) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Gregorian calendar, the 1957th year of the Common Era (CE) and ''Anno Domini'' (AD) designations, the 957th year of the 2nd millennium, the 57th year of the 20th century, and the 8th year of the 1950s decade. Events January * January 1 – The Saarland joins West Germany. * January 3 – Hamilton Watch Company introduces the first electric watch. * January 5 – South African player Russell Endean becomes the first batsman to be dismissed for having ''handled the ball'', in Test cricket. * January 9 – British Prime Minister Anthony Eden resigns. * January 10 – Harold Macmillan becomes Prime Minister of the United Kingdom. * January 11 – The African Convention is founded in Dakar. * January 14 – Kripalu Maharaj is named fifth Jagadguru (world teacher), after giving seven days of speeches before 500 Hindu scholars. * January 15 – The film ''Throne of Blood'', Akira Kurosawa's reworking of ''Macbeth'', is rele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |