|
Kinnaru
Kinnaru ( uga, 𐎋𐎐𐎗, ''knr'') was an Ugaritic god who functioned as the deification of a string instrument, most likely the lyre. He is sparsely attested in the Ugaritic texts, appearing only in a handful of god lists and offering lists. He is entirely absent from known myths. It is sometimes assumed that a mythical king of Cyprus mentioned in the ''Iliad'', Cinyras, was derived from him. Name and character The Ugaritic word ''knr'', as of 1999 attested six times in known Ugaritic texts, functioned both as an ordinary noun referring to a string instrument and as the name of the god Kinnaru, its deification. It is likely that the sound of the instrument was imagined to be the voice of the corresponding god. It is sometimes considered uncertain if ''kinnaru'' was a harp or a lyre, but Dennis Pardee considers the latter option to be correct, as does Gabriele Theuer. Cognates of its name are also attested in other Semitic languages, for example in Eblaite (''kinnārum'') and H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ugaritic God
The Ugaritic pantheon included deities of local origin, many of whom are also known from Eblaite sources from the third millennium BCE or Amorite ones from the early second millennium BCE, as well as Hurrian and Mesopotamian ones. The Ugaritic pantheon is considered better documented than other aspects of Ugaritic religion, such as the life of the clergy or the social context of various offerings. Over two hundred names of deities are known from Ugaritic texts, though it has been argued the number of these who were an object of active worship was lower. Many of the names are binomial, and as such may refer either to a single deity and their epithet, to two deities syncretized into one, or to a closely associated pair. The presence of Hurrian deities in the pantheon is considered one of the main differences between the religion of the inhabitants of Ugarit and those known from other areas inhabited by speakers of Northwest Semitic languages, for example Canaan, understood by researc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinyras
In Greek mythology, Cinyras (; grc, Κινύρας – ''Kinyras'') was a famous hero and king of Cyprus. Accounts vary significantly as to his genealogy and provide a variety of stories concerning him; in many sources he is associated with the cult of Aphrodite on Cyprus, and Adonis, a consort of Aphrodite, is mentioned as his son. Some scholars have proposed a connection with the minor Ugaritic deity Kinnaru, the god of the lyre. The city Cinyreia on Cyprus was believed to have taken its name from Cinyras. According to Strabo, he had previously ruled in the city of Byblos in Phoenicia. Biography The name Cinyras does not appear again until he is mentioned by Pindar as "beloved of Apollo," and the priest of Aphrodite. Pindar mentions Cinyras as being fabulously rich in ''Nemean Ode 8'' line 18. Later, in Greek and Roman literature and in the Christian fathers such as Clement of Alexandria, the story of Cinyras is elaborated. They say that on Cyprus, Cinyras was revered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ugarit
) , image =Ugarit Corbel.jpg , image_size=300 , alt = , caption = Entrance to the Royal Palace of Ugarit , map_type = Near East#Syria , map_alt = , map_size = 300 , relief=yes , location = Latakia Governorate, Syria , region = Fertile Crescent , coordinates = , type = settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , height = , builder = , material = , built = c. 6000 BC , abandoned = c. 1185 BC , epochs =Neolithic–Late Bronze Age , cultures = Canaanite , dependency_of = , occupants = , event = Bronze Age Collapse , excavations = 1928–present , archaeologists = Claude F. A. Schaeffer , condition = ruins , ownership = Public , public_access = Yes , website = , notes = Ugarit (; uga, 𐎜𐎂𐎗𐎚, ''ʾUgarītu''; ar, أُوغَارِيت ''Ūġārīt'' or ''Ūǧārīt'') was an ancient port city in northern Syria, in the outskirts of modern Latakia, discovered by accident in 1928 together with the Ugar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alashiya
Alashiya ( akk, 𒀀𒆷𒅆𒅀 ''Alašiya'' -la-ši-ia uga, 𐎀𐎍𐎘𐎊 ''ẢLṮY''; Linear B: 𐀀𐀨𐀯𐀍 ''Alasios'' -ra-si-jo, also spelled Alasiya, also known as the Kingdom of Alashiya, was a state which existed in the Middle and Late Bronze Ages, and was situated somewhere in the Eastern Mediterranean. It was a major source of goods, especially copper, for ancient Egypt and other states in the Ancient Near East. It is referred to in a number of the surviving texts and is now thought to be the ancient name of Cyprus, or an area of Cyprus. This was confirmed by the scientific analysis performed in the Tel Aviv University of the clay tablets which were sent from Alashiya to other rulers. Texts The name of the state, rendered as ''Alashiya'', is found on texts written in Egyptian, Hittite, Akkadian, Mycenean (Linear B) and Ugaritic. It corresponds to the Biblical Elishah, thus meaning something like "under the god's protection" or "god's country", Some of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eustathius Of Thessalonica
Eustathius of Thessalonica (or Eustathios of Thessalonike; el, Εὐστάθιος Θεσσαλονίκης; c. 1115 – 1195/6) was a Byzantine Greek scholar and Archbishop of Thessalonica. He is most noted for his contemporary account of the sack of Thessalonica by the Normans in 1185, for his orations and for his commentaries on Homer, which incorporate many remarks by much earlier researchers. He was officially canonized on June 10, 1988, and his feast day is on September 20.Great Synaxaristes: Ὁ Ἅγιος Εὐστάθιος ὁ Κατάφλωρος Ἀρχιεπίσκοπος Θεσσαλονίκης'' 20 Σεπτεμβρίου. ΜΕΓΑΣ ΣΥΝΑΞΑΡΙΣΤΗΣ. Life A pupil of Nicholas Kataphloron, Eustathius was appointed to the offices of superintendent of petitions (, ''epi ton deeseon''), professor of rhetoric (), and was ordained a deacon in Constantinople. He was ordained bishop of Myra. Around the year 1178, he was appointed to the archbishopric of Thess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cymbal
A cymbal is a common percussion instrument. Often used in pairs, cymbals consist of thin, normally round plates of various alloys. The majority of cymbals are of indefinite pitch, although small disc-shaped cymbals based on ancient designs sound a definite note (such as crotales). Cymbals are used in many ensembles ranging from the orchestra, percussion ensembles, jazz bands, heavy metal bands, and marching groups. Drum kits usually incorporate at least a crash, ride, or crash/ride, and a pair of hi-hat cymbals. A player of cymbals is known as a cymbalist. Etymology and names The word cymbal is derived from the Latin ''cymbalum'', which is the latinisation of the Greek word ''kymbalon'', "cymbal", which in turn derives from ''kymbē'', "cup, bowl". In orchestral scores, cymbals may be indicated by the French ''cymbales''; German ''Becken'', ''Schellbecken'', ''Teller'', or ''Tschinellen''; Italian ''piatti'' or ''cinelli''; and Spanish ''platillos''. Many of these deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baal
Baal (), or Baal,; phn, , baʿl; hbo, , baʿal, ). ( ''baʿal'') was a title and honorific meaning "owner", "lord" in the Northwest Semitic languages spoken in the Levant during Ancient Near East, antiquity. From its use among people, it came to be applied to gods. Scholars previously associated the theonym with solar god, solar cults and with a variety of unrelated patron deity, patron deities but inscriptions have shown that the name Ba'al was particularly associated with the storm god, storm and fertility god Hadad and his local manifestations. The Hebrew Bible includes use of the term in reference to various Levantine mythology, Levantine deities, often with application towards Hadad, who was decried as a false god. That use was taken over into Christianity and Islam, sometimes under the form Beelzebub in demonology. Etymology The spelling of the English term "Baal" derives from the Koine Greek, Greek ''Báal'' ( which appears in the New Testament and Septuagint, and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baal Cycle
The Baal Cycle is an Ugaritic cycle of stories about the Canaanite god Baʿal ( "Owner", "Lord"), a storm god associated with fertility. It is one of the Ugarit texts, dated to c. 1500-1300 BCE. The text identifies Baal as the god Hadad, the Northwest Semitic form of Adad. The stories are written in Ugaritic, a Northwest Semitic language, and written in a cuneiform consonantal alphabet. It was discovered on a series of clay tablets found in the 1920s in the Tell of Ugarit (modern Ras Shamra), situated on the Mediterranean coast of northern Syria, a few kilometers north of the modern city of Latakia and far ahead of the current coastline. The stories include ''The Myth of Baʿal Aliyan'' and ''The Death of Baʿal''. Basic synopsis The Baʿal Cycle series of stories are summarized as: * Yam wants to rule over the other gods and be the most powerful of all * Baʿal Hadad opposes Yam and slays him * Baʿal Hadad, with the help of Anat and Athirat, persuades El to allow him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Censer
A censer, incense burner, perfume burner or pastille burner is a vessel made for burning incense or perfume in some solid form. They vary greatly in size, form, and material of construction, and have been in use since ancient times throughout the world. They may consist of simple earthenware bowls or fire pots to intricately carved silver or gold vessels, small table top objects a few centimetres tall to as many as several metres high. Many designs use openwork to allow a flow of air. In many cultures, burning incense has spiritual and religious connotations, and this influences the design and decoration of the censer. Often, especially in Western contexts, "censer" is used for pieces made for religious use, especially those on chains that are swung through the air to spread the incense smoke widely, while "perfume burner" is used for objects made for secular use. The original meaning of pastille was a small compressed mixture of aromatic plant material and charcoal that was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yam (god)
Yam (also ''Yamm''; Semitic: ) is the god of the sea in the Canaanite pantheon. He takes the role of the adversary of Baal in the Ugaritic ''Baal Cycle''. The deity's name derives from the Canaanite word for "Sea", and is one name of the Ugaritic god of Rivers and Sea. Also titled ''ṯpṭ nhr'' (" the Judge of the River"), he is also one of the '' 'ilhm'', or sons of El, the name given to the Levantine pantheon. Of all the gods, despite being the champion of El, Yam holds special hostility against Baal Hadad, son of Dagon. He is a deity of the sea and his palace is in the abyss associated with the depths, or Biblical tehom, of the oceans. Yam is the deity of the primordial chaos and represents the power of the sea, untamed and raging; he is seen as ruling storms and the disasters they wreak, and was an important divinity to the maritime Phoenicians. The gods cast out Yam from the heavenly mountain Sappan (modern Jebel Aqra; ''Sappan'' is cognate to '' Tsephon''). The fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
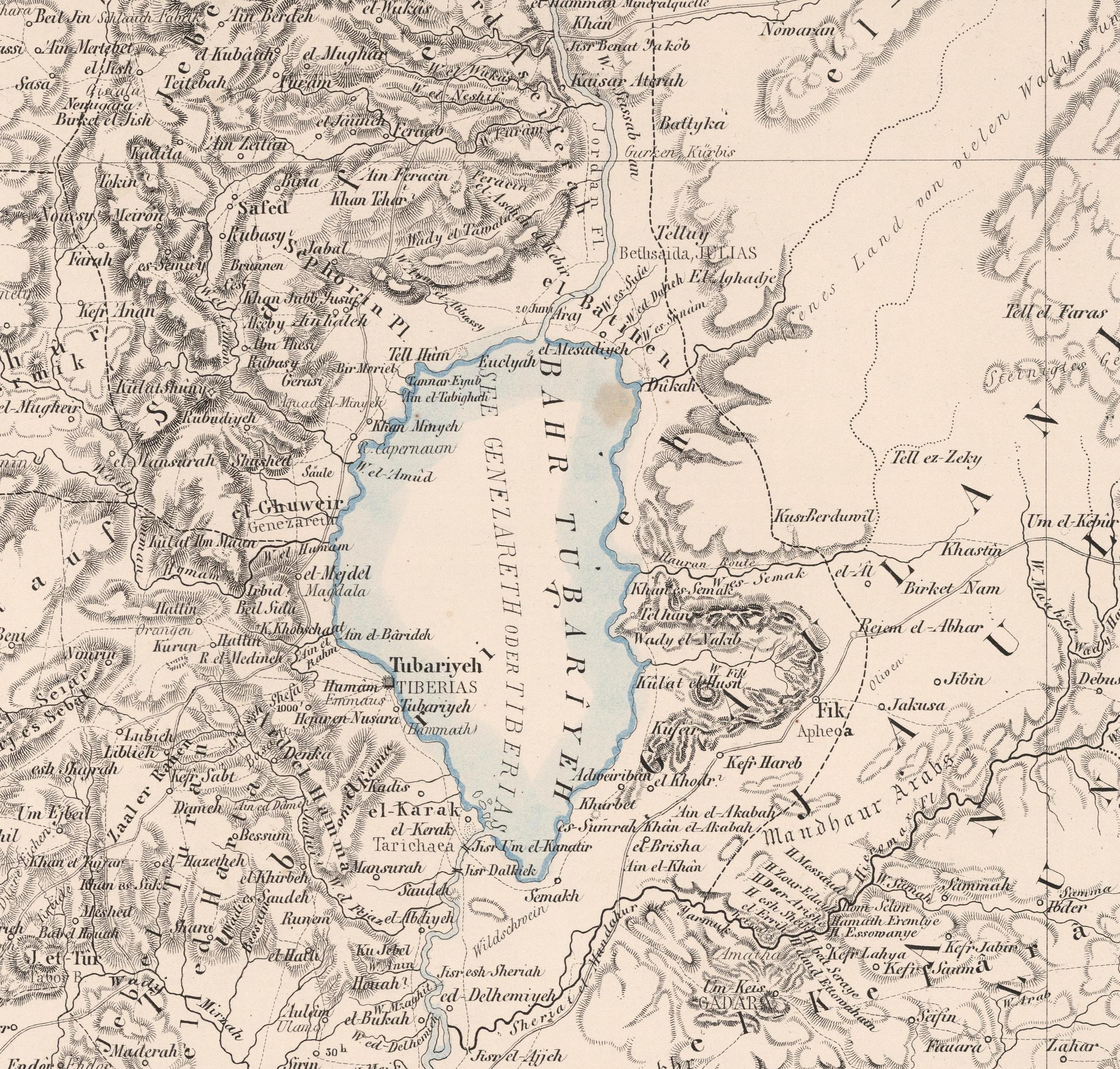
Kinneret (archaeological Site)
Kinneret () is the name of an important Bronze and Iron Age city situated on the northwestern shore of the Sea of Galilee, mentioned in the 14th century BC Aqhat Epic of Ugarit, and in the Old Testament and New Testament. Older Bible translations spell the name alternatively Kinnereth or Chinnereth, and sometimes in the plural as Chinneroth. In time the name became Gennesaret and Ginosar (). The remains of Kinneret have been excavated at a site called Tell el-'Oreimeh (Tell el-‘Orēme) in Arabic and Tel Kinrot in Modern Hebrew. Etymology "Kinneret" Talmud According to the Jerusalem Talmud (Megillah 1:1), the name Kinneret is derived from the name of the ''kinnar'' trees which grow in its vicinity, explained by lexicographer M. Jastrow to mean the Christ's thorn jujube (Ziziphus spina-christi), and by Moses Margolies to mean cane reeds. Another Talmud passage says that it is so-called because its fruits are as sweet as those of the ''kinnara'' (Ziziphus spina-christi). "Gennes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ninigizibara
Ningizibara, also known as Igizibara and Ningizippara, was a Mesopotamian goddess associated with the ''balaĝ'' instrument, usually assumed to be a type of lyre. She could be regarded both as a physical instrument and as a minor deity. In both cases, she was associated with the goddess Inanna. A connection between her and the medicine goddess Gula is also attested, and it is possible she could serve as a minor healing deity herself. Character Ninigizibarra's name most likely means "well regarded lady" in Sumerian. In Umma, the name was written without the NIN sign, and the goddess was called Igizibara, "well regarded." In documents from Mari the usual spelling is Ningizippara. Ninigizibarra was both the name of a goddess and of individual instruments placed in a number of temples of Inanna. The instrument represented by her was the ''balaĝ''. The precise meaning of this Sumerian term is a matter of scholarly debate, though it is generally accepted that it referred first and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |