|
King Jing Of Zhou (Gai)
King Jìng of Zhou, (), personal name Ji Gai, was the twenty-sixth king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty and the fourteenth of Eastern Zhou. He ruled from 519 BC to 477 BC. He was succeeded by his son, Prince Ren (), who ruled as King Yuan of Zhou King Yuan of Zhou (,) personal name Ji Ren, was the twenty-seventh king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty and the fifteenth of Eastern Zhou.''Records of the Grand Historian'' by Sima Qian He ruled from 476 BC to 469 BC. He was succeeded by his son, Pri ... from 476 BC to 469 BC. Ancestry See also # Family tree of ancient Chinese emperors 477 BC deaths Zhou dynasty kings 5th-century BC Chinese monarchs 6th-century BC Chinese monarchs Year of birth unknown {{China-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Dao Of Zhou
King Dao of Zhou (; died 520 BC), personal name Ji Meng, was the twenty-fifth king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty The Zhou dynasty ( ; Old Chinese ( B&S): *''tiw'') was a royal dynasty of China that followed the Shang dynasty. Having lasted 789 years, the Zhou dynasty was the longest dynastic regime in Chinese history. The military control of China by ... and the thirteenth of Eastern Zhou. His given name was Měng. Dao succeeded his father, King Jĭng of Zhou. After a reign of less than a year, he was killed by his brother Prince Chao. Following his death, the throne passed onto his brother King Jìng of Zhou. Ancestry See also * Family tree of ancient Chinese emperors Notes 520 BC deaths Zhou dynasty kings 6th-century BC Chinese monarchs Year of birth unknown 6th-century BC murdered monarchs Assassinated Chinese politicians {{China-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Ding Of Zhou
King Ding of Zhou (), personal name Ji Yu, was the twenty-first king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty and the ninth of Eastern Zhou. He was a son of King Qing of Zhou and brother of King Kuang of Zhou. He sent an official named Wangsun Man to present gifts to the Chu army. He met Prince Zhuang.Constance A. Cook: ''Defining Chu: Image And Reality In Ancient China'' Family Spouse: * Queen Ding of Zhou, of the Jiang clan of Qi (), possibly a daughter of Duke Hui of Qi; married in 603 BC Sons: * Prince Yi (; d. 572 BC), ruled as King Jian of Zhou King Jian of Zhou (), personal name Ji Yi, was the twenty-second king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty and the tenth of the Eastern Zhou. Family Sons: * Prince Xiexin (; d. 545 BC), ruled as King Ling of Zhou from 571 to 545 BC * A son (d. 545 BC) who ... from 585–572 BC Ancestry See also # Family tree of ancient Chinese emperors Sources 586 BC deaths Zhou dynasty kings 6th-century BC Chinese monarchs 7th-century BC Chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th-century BC Chinese Monarchs
The 5th century is the time period from 401 ( CDI) through 500 ( D) ''Anno Domini'' (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar. The 5th century is noted for being a period of migration and political instability throughout Eurasia. It saw the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, which came to an end in 476 AD. This empire had been ruled by a succession of weak emperors, with the real political might being increasingly concentrated among military leaders. Internal instability allowed a Visigoth army to reach and ransack Rome in 410. Some recovery took place during the following decades, but the Western Empire received another serious blow when a second foreign group, the Vandals, occupied Carthage, capital of an extremely important province in Africa. Attempts to retake the province were interrupted by the invasion of the Huns under Attila. After Attila's defeat, both Eastern and Western empires joined forces for a final assault on Vandal North Africa, but this campaign was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhou Dynasty Kings
Zhou may refer to: Chinese history * King Zhou of Shang () (1105 BC–1046 BC), the last king of the Shang dynasty * Predynastic Zhou (), 11th-century BC precursor to the Zhou dynasty * Zhou dynasty () (1046 BC–256 BC), a dynasty of China ** Western Zhou () (1046 BC–771 BC) ** Eastern Zhou () (770 BC–256 BC) * Western Zhou (state) () (440 BC–256 BC) * Eastern Zhou (state) () (367 BC–249 BC) * Northern Zhou () (557–581), one of the Northern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period * Wu Zhou () (690–705), an imperial dynasty established by Wu Zetian * Later Zhou () (951–960), the last of the Five dynasties during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period * Zhou (Zhang Shicheng's kingdom) () (1354–1367), a state founded by Zhang Shicheng during the Red Turban Rebellion * Zhou (Qing period state) () (1678–1681), a state founded by Wu Sangui during the Qing dynasty Other uses *Zhou (surname) (), Chinese surname *Zhou (country subdivision) (), a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
477 BC Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 477 ( CDLXXVII) was a common year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year after the Consulship of Basiliscus and Armatus (or, less frequently, year 1230 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 477 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Africa * January 25 – Genseric, ruler of the Vandal Kingdom, dies a natural death at Carthage, and is succeeded by his eldest son Huneric. He maintains control over the islands in the western Mediterranean Sea with his Vandal fleet, and rescinds his father's policy of persecuting the Roman Catholics in Africa. * The independent Mauro-Roman Kingdom (Kingdom of the Moors and Romans) is formed by Christian Berbers in the Roman province of Mauretania Caesariensis (present-day northern Algeria), bordering the Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Chinese Monarchs
This list of Chinese monarchs includes rulers of China with various titles prior to the establishment of the Republic in 1912. From the Zhou dynasty until the Qin dynasty, rulers usually held the title "king" (). With the separation of China into different Warring States, this title had become so common that the unifier of China, the first Qin Emperor Qin Shihuang created a new title for himself, that of "emperor" (). The title of Emperor of China continued to be used for the remainder of China's imperial history, right down to the fall of the Qing dynasty in 1912. While many other monarchs existed in and around China throughout its history, this list covers only those with a quasi-legitimate claim to the majority of China, or those who have traditionally been named in king-lists. The following list of Chinese monarchs is in no way comprehensive. Chinese sovereigns were known by many different names, and how they should be identified is often confusing. Sometimes the same empero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
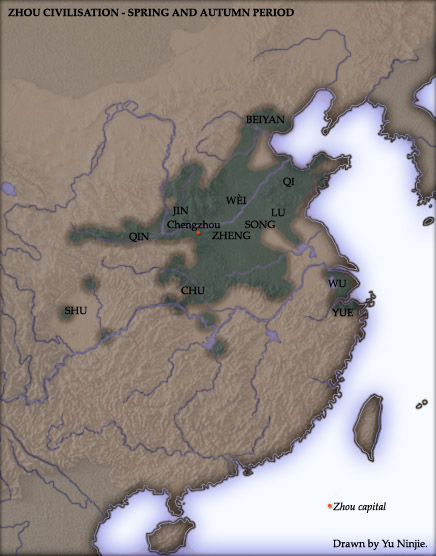
Zhou Dynasty
The Zhou dynasty ( ; Old Chinese ( B&S): *''tiw'') was a royal dynasty of China that followed the Shang dynasty. Having lasted 789 years, the Zhou dynasty was the longest dynastic regime in Chinese history. The military control of China by the royal house, surnamed Ji, lasted initially from 1046 until 771 BC for a period known as the Western Zhou, and the political sphere of influence it created continued well into the Eastern Zhou period for another 500 years. The establishment date of 1046 BC is supported by the Xia–Shang–Zhou Chronology Project and David Pankenier, but David Nivison and Edward L. Shaughnessy date the establishment to 1045 BC. During the Zhou dynasty, centralized power decreased throughout the Spring and Autumn period until the Warring States period in the last two centuries of the dynasty. In the latter period, the Zhou court had little control over its constituent states that were at war with each other until the Qin state consolidated power and forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family Tree Of Ancient Chinese Emperors
This is a family tree of Chinese monarchs covering the period of the Five Emperors up through the end of the Spring and Autumn period. Five Emperors The legendary Five Emperors were traditionally regarded as the founders of the Chinese state. The ''Records of the Grand Historian'' states that Shaohao did not accede to the throne while Emperor Zhi’s ephemeral and uneventful rule disqualify him from the Five Emperors in all sources. Other sources name Yu the Great, the founder of the Xia dynasty, as the last of the Five. Pretenders are ''italicized''. Xia dynasty This is a family tree for the Xia dynasty which ruled circa 2000–1750 BC. The historicity of the dynasty has sometimes been questioned, but circumstantial archaeological evidence supports its existence. Shang dynasty This is a family tree for the Shang dynasty, which ruled China proper between circa 1750 BC and 1046 BC.'' Bamboo Annals'' The Shang rulers bore the title Di ( 帝) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Jian Of Zhou
King Jian of Zhou (), personal name Ji Yi, was the twenty-second king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty and the tenth of the Eastern Zhou. Family Sons: * Prince Xiexin (; d. 545 BC), ruled as King Ling of Zhou from 571 to 545 BC * A son (d. 545 BC) who was the progenitor of the Dan lineage and the father of Dan Kuo () ** Known as Dan Ji () Ancestry See also *Family tree of ancient Chinese emperors This is a family tree of Chinese monarchs covering the period of the Five Emperors up through the end of the Spring and Autumn period. Five Emperors The legendary Five Emperors were traditionally regarded as the founders of the Chinese state. ... Sources 572 BC deaths Zhou dynasty kings 6th-century BC Chinese monarchs Year of birth unknown {{China-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Yuan Of Zhou
King Yuan of Zhou (,) personal name Ji Ren, was the twenty-seventh king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty and the fifteenth of Eastern Zhou.''Records of the Grand Historian'' by Sima Qian He ruled from 476 BC to 469 BC. He was succeeded by his son, Prince Jie (), who ruled as King Zhending of Zhou from 468 BC to 441 BC. Ancestry See also * Family tree of ancient Chinese emperors This is a family tree of Chinese monarchs covering the period of the Five Emperors up through the end of the Spring and Autumn period. Five Emperors The legendary Five Emperors were traditionally regarded as the founders of the Chinese state. ... Sources 469 BC deaths Zhou dynasty kings 5th-century BC Chinese monarchs Year of birth unknown {{China-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Ling Of Zhou
King Ling of Zhou (), personal name Ji Xiexin, was the twenty-third king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty and the eleventh of Eastern Zhou. He died in 545 BC. In the twenty-first year of his reign, Confucius was born. His successor was his son King Jĭng of Zhou. His other son was the Crown prince Ji Jin (姬晉). Empress Wu Zetian claimed that her lover Zhang Changzong was a reincarnation of Ji Jin. Ancestor of the Taiyuan Wang During the Tang dynasty the Li family of Zhaojun 赵郡李氏, the Cui family of Boling 博陵崔氏, the Cui family of Qinghe 清河崔氏, the Lu family of Fanyang 范陽盧氏, the Zheng family of Xingyang 荥阳郑氏, the Wang family of Taiyuan 太原王氏, and the Li family of Longxi 隴西李氏 were the seven noble families among whom marriage was banned by law. Moriya Mitsuo wrote a history of the Later Han-Tang period of the Taiyuan Wang. Among the strongest families was the Taiyuan Wang. The prohibition on marriage between the clans i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Zhou
The Eastern Zhou (; zh, c=, p=Dōngzhōu, w=Tung1-chou1, t= ; 771–256 BC) was a royal dynasty of China and the second half of the Zhou dynasty. It was divided into two periods: the Spring and Autumn and the Warring States. History In 770 BCE, the capital of the Zhou Kingdom was moved from Haojing (Chang'an County in Xi'an City) to Luoyi (known today as Luoyang, Henan Province). This brought about the beginning of the Eastern Zhou dynasty (as opposed to Western Zhou dynasty), so named due to Luoyi being situated to the east of Haojing. Over 25 kings reigned over the Eastern Zhou Dynasty, lasting 515 years in all. With the death of King You of Zhou, the last king of the Western Zhou Dynasty, ascended Crown Prince Yijiu was proclaimed the new king by the nobles from the states of Zheng, Lü, Qin and the Marquess of Shen. He was King Ping of Zhou. In the second year of his reign, he moved the capital east to Luoyi as Quanrong invaded Haojing, indicating the end of the Weste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |