|
King's Pawn Game
The King's Pawn Game is any chess opening starting with the move: :1. e4 It is the most popular opening move in chess, followed by the Queen's Pawn Game. Details about the move and the game plan White opens with the most popular of the twenty possible opening moves. Although effective in winning for White (54.25%), it is not quite as successful as the four next most common openings for White: 1.d4 (55.95%), 1.Nf3 (55.8%), 1.c4 (56.3%), and 1.g3 (55.8%). Since nearly all openings beginning 1.e4 have names of their own, the term ''King's Pawn Game,'' unlike Queen's Pawn Game, is rarely used to describe the opening of the game. Advancing the king's pawn two squares is highly useful because it occupies a square, attacks the center square d5, and allows the of White's and queen. Chess grandmaster Bobby Fischer said that the King's Pawn Game is "Best by test", and proclaimed that "With 1.e4! I win." Opening categorization and continuations King's Pawn Games are further cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess Opening
A chess opening or simply an opening is the initial stage of a chess game. It usually consists of established theory; the other phases are the middlegame and the endgame. Many opening sequences have standard names such as the " Sicilian Defense". '' The Oxford Companion to Chess'' lists 1,327 named openings and variants, and there are many others with varying degrees of common usage. Opening moves that are considered standard are referred to as "book moves", or simply "book". When a game begins to deviate from known opening theory, the players are said to be "out of book". In some openings, "book" lines have been worked out for over 30 moves, as in the classical King's Indian Defense and in the Najdorf variation of the Sicilian Defense. Professional chess players spend years studying openings, and continue doing so throughout their careers, as opening theory continues to evolve. Players at the club level also study openings but the importance of the opening phase is smalle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Defence
The Hungarian Defense is a chess opening that begins with the moves: :1. e4 e5 :2. Nf3 Nc6 :3. Bc4 Be7 The Hungarian Defense is a line in the Italian Game typically chosen as a response to the aggressive 3.Bc4. With the move 3...Be7, Black avoids the complexities of the Giuoco Piano (3...Bc5), Evans Gambit (3...Bc5 4.b4), and Two Knights Defense (3...Nf6). White has an advantage in and freer , so Black must be prepared to defend a cramped position. According to Harding and Botterill, "The Hungarian Defence can only be played for a draw. White should have an edge in most lines." The opening is seldom seen in modern play. It has been played on occasion by some grandmasters with strong defensive-, including Reshevsky, Hort, and former world champions Petrosian and Smyslov. The variation takes its name from a correspondence game between Paris and Pest, Hungary, played from 1842 to 1845, but was first analyzed by Cozio in the 18th century.Harding & Botterill (1977) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pirc Defence
The Pirc Defence (pronounced ) is a chess opening characterised by the response of Black to 1.e4 with 1...d6 and 2...Nf6, followed by ...g6 and ...Bg7, while allowing White to establish a with pawns on d4 and e4. It is named after the Slovenian grandmaster Vasja Pirc. The Pirc Defence is usually defined by the opening sequence :1. e4 d6 :2. d4 Nf6 :3. Nc3 g6 This is the most commonly played line after Black responds to 1.e4 with 1...d6. It has been claimed to give rise to somewhat interesting and exciting games, where Black will have but has to be cautious about playing too passively. According to Garry Kasparov, the Pirc Defence is "hardly worth using in the tournaments of the highest category", as it gives White "too many opportunities for anybody's liking". Description The Pirc Defence is a relatively new opening; while it was seen on occasion in the late nineteenth century, it was considered irregular, thus remaining a sideline. The opening began gaining some p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Defence
The Modern Defense (also known as the Robatsch Defence after Karl Robatsch) is a hypermodern chess opening in which Black allows White to occupy the with pawns on d4 and e4, then proceeds to attack and undermine this "ideal" center without attempting to occupy it. The opening has been most notably used by British grandmasters Nigel Davies and Colin McNab. The Modern Defense is closely related to the Pirc Defence, the primary difference being that in the Modern, Black delays developing the knight to f6. The delay of ...Nf6 attacking White's pawn on e4 gives White the option of blunting the g7-bishop with c2–c3. There are numerous transpositional possibilities between the two openings. The ''Encyclopaedia of Chess Openings'' (''ECO'') classifies the Modern Defense as code B06, while codes B07 to B09 are assigned to the Pirc. The tenth edition of '' Modern Chess Openings'' (1965) grouped the Pirc and Robatsch together as the "Pirc–Robatsch Defense". 2.d4 Main line: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pirc Defence
The Pirc Defence (pronounced ) is a chess opening characterised by the response of Black to 1.e4 with 1...d6 and 2...Nf6, followed by ...g6 and ...Bg7, while allowing White to establish a with pawns on d4 and e4. It is named after the Slovenian grandmaster Vasja Pirc. The Pirc Defence is usually defined by the opening sequence :1. e4 d6 :2. d4 Nf6 :3. Nc3 g6 This is the most commonly played line after Black responds to 1.e4 with 1...d6. It has been claimed to give rise to somewhat interesting and exciting games, where Black will have but has to be cautious about playing too passively. According to Garry Kasparov, the Pirc Defence is "hardly worth using in the tournaments of the highest category", as it gives White "too many opportunities for anybody's liking". Description The Pirc Defence is a relatively new opening; while it was seen on occasion in the late nineteenth century, it was considered irregular, thus remaining a sideline. The opening began gaining some p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
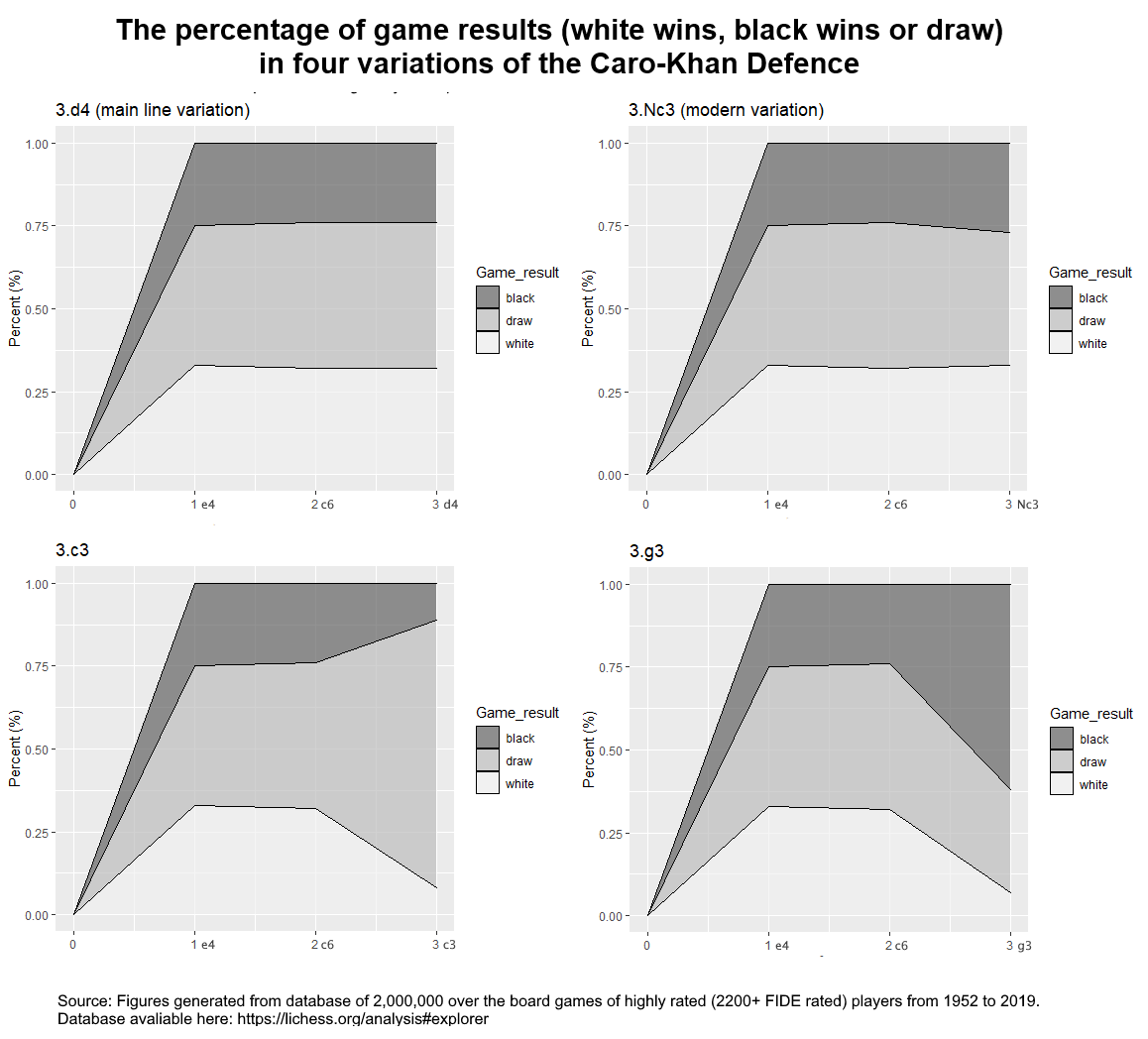
Caro–Kann Defence
The Caro–Kann Defence is a chess opening characterised by the moves: :1. e4 c6 The Caro–Kann is a common defence against the King's Pawn Opening. It is classified as a Semi-Open Game, like the Sicilian Defence and French Defence, although it is thought to be more solid and less dynamic than either of those openings. It often leads to good endgames for Black, who has the better pawn structure. It allows Black to circumvent enormous bodies of theory in 1.e4 openings such as the Ruy Lopez and the Sicilian Defence. Unlike its sister opening, the French Defence, the Caro–Kann does not hinder the development of Black's light-squared bishop. However, it comes at the cost of a tempo because Black has to play 1...c6 before pushing the pawn to c5, whereas Black can push c7–c5 in one move in the French Defence. White can combat the Caro–Kann in several different ways, often gaining a space advantage; additionally, Black has less mobility and can lag in development. In the 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrov's Defence
Petrov's Defence or the Petrov Defence (also called Petroff Defence, Petrov's Game, Russian Defence, or Russian Game – russian: Русская партия) is a chess opening characterised by the following moves: :1. e4 e5 :2. Nf3 Nf6 Though this response has a long history, it was first popularised by Alexander Petrov, a Russian chess player in the mid-19th century. In recognition of the early investigations by the Russian masters Petrov and Carl Jaenisch, this opening is called the Russian Game in some countries. The Petrov has a drawish reputation; however, it offers attacking opportunities for both sides, and a few lines are quite . Often a trade occurs and Black, after gaining a tempo, has a well-placed knight. Pillsbury's game in 1895 against Emanuel Lasker testifies to this. The Black counterattack in the centre also avoids the Ruy Lopez, Giuoco Piano (and other lines of the Italian Game), and the Scotch Game. The Petrov has been adopted by many of the world's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotch Game
The Scotch Game, or Scotch Opening, is a chess opening that begins with the moves: :1. e4 e5 :2. Nf3 Nc6 :3. d4 Ercole del Rio, in his 1750 treatise ''Sopra il giuoco degli Scacchi, Osservazioni pratiche d’anonimo Autore Modenese'' ("On the game of Chess, practical Observations by an anonymous Modenese Author"), was the first author to mention what is now called the Scotch Game. The opening received its name from a correspondence match in 1824 between Edinburgh and London. Popular in the 19th century, by 1900 the Scotch had lost favour among top players because it was thought to release the central tension too early and allow Black to without difficulty. More recently, grandmasters Garry Kasparov and Jan Timman helped to repopularise the Scotch when they used it as a surprise weapon to avoid the well-analysed Ruy Lopez. Analysis White aims to dominate the by exchanging their d-pawn for Black's e-pawn. Black usually plays 3...exd4, as they have no good way of main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Game
The Italian Game is a family of chess openings beginning with the moves: :1. e4 e5 :2. Nf3 Nc6 :3. Bc4 This opening is defined by the of the white bishop to c4 (the so-called ""), where it attacks Black's vulnerable f7-square. It is part of the large family of Open Games or Double King's Pawn Games. The Italian Game is one of the oldest recorded chess openings; it occurs in the Göttingen manuscript and was developed by players such as Damiano and Polerio in the 16th century, and later by Greco in 1620, who gave the game its main line. It has been extensively analyzed for more than 300 years. The term ''Italian Game'' is sometimes used interchangeably with Giuoco Piano, although the latter also refers particularly to play after 3...Bc5. The '' Encyclopaedia of Chess Openings'' gives the Italian Game ten codes: C50–C54 for the Giuoco Piano, and C55–C59 for the Two Knights Defense. Side lines are covered under C50. Main variations Black's two main options are 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King's Gambit
The King's Gambit is a chess opening that begins with the moves: :1. e4 e5 :2. f4 White offers a pawn to divert the black e-pawn. If Black accepts the gambit, White has two main plans. The first is to play d4 and Bxf4, regaining the gambit pawn with domination. The alternative plan is to play Nf3 and Bc4 followed by 0-0, when the semi-open f-file created after a pawn push to g3 allows White to attack the weakest point in Black's position, the pawn on f7. Theory has shown that, in order to maintain the gambit pawn, Black may well be forced to weaken the with moves such as ...g5 or odd piece placement (e.g. ). A downside to the King's Gambit is that it weakens White's king's position, exposing it to the latent threat of ...Qh4+ (or ). With a black pawn on f4, it is not usually viable for White to respond to the check with g2-g3, but if the king moves then it also loses the right to castle. The King's Gambit is one of the oldest documented openings, appearing in one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruy Lopez
The Ruy Lopez (; ), also called the Spanish Opening or Spanish Game, is a chess opening characterised by the moves: :1. e4 e5 :2. Nf3 Nc6 :3. Bb5 The Ruy Lopez is named after 16th-century Spanish priest Ruy López de Segura. It is one of the most popular openings, with many variations. In the '' Encyclopaedia of Chess Openings'' (''ECO''), all codes from C60 to C99 are assigned to the Ruy Lopez. History The opening is named after the 16th-century Spanish priest Ruy López de Segura, who made a systematic study of this and other openings in the 150-page book on chess ''Libro del Ajedrez'', written in 1561. Although it bears his name, this particular opening was included in the Göttingen manuscript, which dates from c.1490. Popular use of the Ruy Lopez opening did not develop, however, until the mid-19th century, when the Russian theoretician Carl Jaenisch "rediscovered" its potential. The opening remains the most commonly used amongst the open games in master play ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Game
An Open Game (or Double King's Pawn Opening) is a chess opening that begins with the following moves: :1. e4 e5 White has moved the king's pawn two squares and Black has replied in kind. The result is an Open Game. Other responses to 1.e4 are termed Semi-Open Games or Single King's Pawn Games. It should not be confused with the term "" (lowercase o and g), referring to a chess position where ranks, files and diagonals are open, and tending to more tactical gameplay. Analysis White opens by playing 1.e4, which is the most popular opening move and has many strengths—it immediately stakes a claim in the center, and frees two pieces (the queen and king's bishop) for action. The oldest openings in chess follow 1.e4. Bobby Fischer wrote that 1.e4 was "Best by test." On the negative side, 1.e4 places a pawn on an undefended square and weakens the squares d4 and f4. If Black keeps the symmetry by replying 1...e5, the result is an Open Game . Variations The most popular sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |