|
Kilmallock
Kilmallock () is a town in south County Limerick, Ireland, near the border with County Cork. There is a Dominican Priory in the town and King's Castle (or King John's Castle). The remains of medieval walls which encircled the settlement are still visible. History Foundation and development Saint Mocheallóg built a church in the area in the early 7th century, and the town's name derives from the Irish ''Cill Mocheallóg'' meaning "the church of Mocheallóg". The town was of considerable importance in the late medieval period, ranking as one of the main urban areas in Ireland at the time. The Collegiate Church of St Peter and St Paul was built by 1241. Kilmallock was located in a position of some strategic importance, and in consequence the town frequently became a target during times of war. In 1571, the town was burned by the rebel Earl of Desmond during the Desmond Rebellions. Seventy years later, during the Irish Confederate Wars, the Dominican Priory of Kilmallock was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilmallock Priory SW 2007 08 08
Kilmallock () is a town in south County Limerick, Ireland, near the border with County Cork. There is a Dominican Priory in the town and King's Castle (or King John's Castle). The remains of medieval walls which encircled the settlement are still visible. History Foundation and development Saint Mocheallóg built a church in the area in the early 7th century, and the town's name derives from the Irish ''Cill Mocheallóg'' meaning "the church of Mocheallóg". The town was of considerable importance in the late medieval period, ranking as one of the main urban areas in Ireland at the time. The Collegiate Church of St Peter and St Paul was built by 1241. Kilmallock was located in a position of some strategic importance, and in consequence the town frequently became a target during times of war. In 1571, the town was burned by the rebel Earl of Desmond during the Desmond Rebellions. Seventy years later, during the Irish Confederate Wars, the Dominican Priory of Kilmallock was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kilmallock
The Battle of Kilmallock took place between 25 July and 5 August 1922 in County Limerick, Ireland. It was one of the largest engagements of the Irish Civil War. It consisted of ten days of fighting in the countryside round Kilmallock in County Limerick, in which Irish Free State Army forces, advancing south from Limerick city, found their path blocked by anti-Treaty IRA troops, dug into a number of villages at Bruff, Bruree and Patrickswell. The fighting ended with the retreat of the anti-Treaty fighters and the occupation of Kilmallock by Free State forces. Preparations The prelude to the battle was the fall of Limerick city to Free State forces. The Republican forces in the city under Liam Deasy withdrew from their positions after a week's fighting and concentrated in Kilmallock and the nearby towns of Bruff and Bruree. The Free State forces, advancing south from the city, found their path blocked by the Republicans dug in at the three hilltop towns. The National Army's a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilmallock Abbey
Kilmallock Abbey ( ga, Mainistir Chill Mocheallóg) or St. Saviour's Priory is a 13th-century Dominican friary in the town of Kilmallock on the banks of the River Loobagh. History The Abbey was established in 1291 when the Dominicans were invited to build a monastery by Gilbert Fitzgerald of the White Knights. The Fitzgeralds continued to be the main benefactors of the Abbey, including the expansion funded by Maurice Fitzgibbon (Fils de Gilbert) in 1320. The church dates from the 14th century, and was a simple rectangular building. A tower and ornate five-light east window were added to the church in the 15th century. The buildings have extensive carved details, including flower buds and human heads some of whom may represent the benefactors of the abbey. The monastery was dissolved in 1541, with the monks returning in 1622. In 1645 the Papal Legate, Cardinal Giovanni Battista Rinuccini, visited during the Confederate Wars. It was sacked by Cromwellian forces led by Lord In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collegiate Church Of St Peter And St Paul (Kilmallock)
The Collegiate Church of St Peter and St Paul is a medieval collegiate church and a National Monument in Kilmallock, Ireland. The church is believed to have been built on the site of an ancient monastery. Location The church is located on the south bank of the River Loobagh, to the north of Kilmallock's main street. History The church was completed by 1241, on what was probably the site of an earlier monastery, founded by Mocheallóg c. AD 600. A round tower has its foundations here. It was dedicated to Peter and Paul in 1410. The nave and transept were substantially altered in 1420 by Maurice Fitzgerald. It became a collegiate church c. 1500. Carved tombs from the 16th century are visible in the south transept. The building was partly destroyed by Cromwell and was roofless since 1657 according to Samuel Lewis. The church remained in use by the local Church of Ireland until a 1935 fire. Church In the northwest corner of the nave is a tower which incorporates the stump ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King John's Castle (Kilmallock)
King John's Castle or King's Castle is a tower house and National Monument located in Kilmallock, Ireland. Location King John's Castle is located in Kilmallock, west of the Collegiate Church of St Peter and St Paul and southwest of Kilmallock Abbey. History Despite the name, the tower house (or peel tower) was not erected during King John's reign (1177–1216) but some time in the 15th century. The name is probably intended to invite comparison to King John's Castle, Limerick. There are some original mullioned windows still present but most were replaced with 18th-century windows. It was granted to Henry Billingsley in 1588, and to Thomas Browne in 1604. In 1645 it was used as an arsenal by James Tuchet, 3rd Earl of Castlehaven's troops during the Irish Confederate Wars, and was a military hospital in 1651. The tower was renovated in the 18th/19th century and was used as a blacksmith's workshop. Building A four-storey tower house with some original mullioned windows. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limerick City And County Council
Limerick City and County Council ( ga, Comhairle Cathrach agus Contae Luimnigh) is the authority responsible for Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local government in the Limerick, City of Limerick and County Limerick in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It came into operation on 1 June 2014 after the 2014 Irish local elections, 2014 local elections. It was formed by the merger of Limerick City Council and Limerick County Council under the provisions of the Local Government Reform Act 2014. As a city and county council, it is governed by the Local Government Act 2001. The council is responsible for housing and community, roads and transportation, urban planning and development, amenity and culture, and natural environment, environment. The council has 40 elected members. Elections are held every five years and are by single transferable vote. The head of the council has the title of Mayor. The city and county administration is headed by a Chief executive (Irish local gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Limerick
"Remember Limerick" , image_map = Island_of_Ireland_location_map_Limerick.svg , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Ireland , subdivision_type1 = Province , subdivision_name1 = Munster , subdivision_type2 = Region , subdivision_name2 = Southern (Mid-West) , seat_type = County town , seat = Limerick and Newcastle West , leader_title = Local authority , leader_name = Limerick City and County Council , leader_title2 = Dáil constituencies , leader_name2 = Limerick City and Limerick County , leader_title3 = EP constituency , leader_name3 = South , area_total_km2 = 2756 , area_rank = 10th , blank_name_sec1 = Vehicle indexmark code , blank_info_sec1 = L (since 2014)LK (1987–2013) , population = 205444 , population_density_km2 = 74.544 , population_rank = 9th , population_demonym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murrough O'Brien, 1st Earl Of Inchiquin
Murrough MacDermod O'Brien, 1st Earl of Inchiquin (September 1614 – 9 September 1673), was an Irish nobleman and soldier, who came from one of the most powerful families in Munster. Known as "''Murchadh na dTóiteán''" ("Murrough the Burner") he initially trained for war in the Spanish service. He accompanied the Earl of Strafford into Leinster on the outbreak of the Irish Rebellion of 1641 and was appointed governor of Munster in 1642. He had some small success, but was hampered by lack of funds and he was outwitted the Irish leader, Viscount Muskerry, at Cappoquin and Lismore. His forces dispersed at the truce of 1643. Murrough visited Charles I at Oxford in 1644, but found it expedient to submit to the English Parliament the same year as the Parliamentarians being masters of sea, were the only people who could help the Munster Protestants defend themselves against Roman Catholics. He was made President of Munster by Parliament, and sought to enhance his position with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liam Deasy
Liam Deasy (6 May 1896 – 20 August 1974) was an Irish Republican Army officer who fought in the Irish War of Independence and the Irish Civil War. In the latter conflict, he was second-in-command of the Anti-Treaty forces for a period in late 1922 and early 1923. Early life Deasy was born in Kilmacsimon, Bandon in County Cork on 6 May 1896, and educated in the local school at Ballinadee. He was the third son of William and Mary Deasy. Irish War of Independence In the War of Independence (1919–21, he was the Adjutant of the 3rd Cork Brigade (West Cork). He served under Tom Barry in one of the unit's best known action, the Crossbarry Ambush in March 1921. His younger brother, Pat, died in action at the Kilmichael Ambush in November 1920, an engagement which Liam Deasy himself was not present at. He also took part in the Tooreen ambush. Civil War He opposed the Anglo-Irish Treaty which ended the war. In the months that followed, he along with others like Éamon d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmond Rebellions
The Desmond Rebellions occurred in 1569–1573 and 1579–1583 in the Irish province of Munster. They were rebellions by the Earl of Desmond, the head of the Fitzmaurice/FitzGerald Dynasty in Munster, and his followers, the Geraldines and their allies, against the threat of the extension of the English government over the province. The rebellions were motivated primarily by the desire to maintain the independence of feudal lords from their monarch but also had an element of religious antagonism between Catholic Geraldines and the Protestant English state. They culminated in the destruction of the Desmond dynasty and the plantation or colonisation of Munster with English Protestant settlers. 'Desmond' is the Anglicisation of the Irish ''Deasmumhain'', meaning 'South Munster' In addition to the Scorched Earth policy, it might be worth mentioning that, Sir Humphrey Gilbert, Warham St Leger, Perrot and later Nicholas Malby and Lord Grey and William Pelham, deliberately target ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
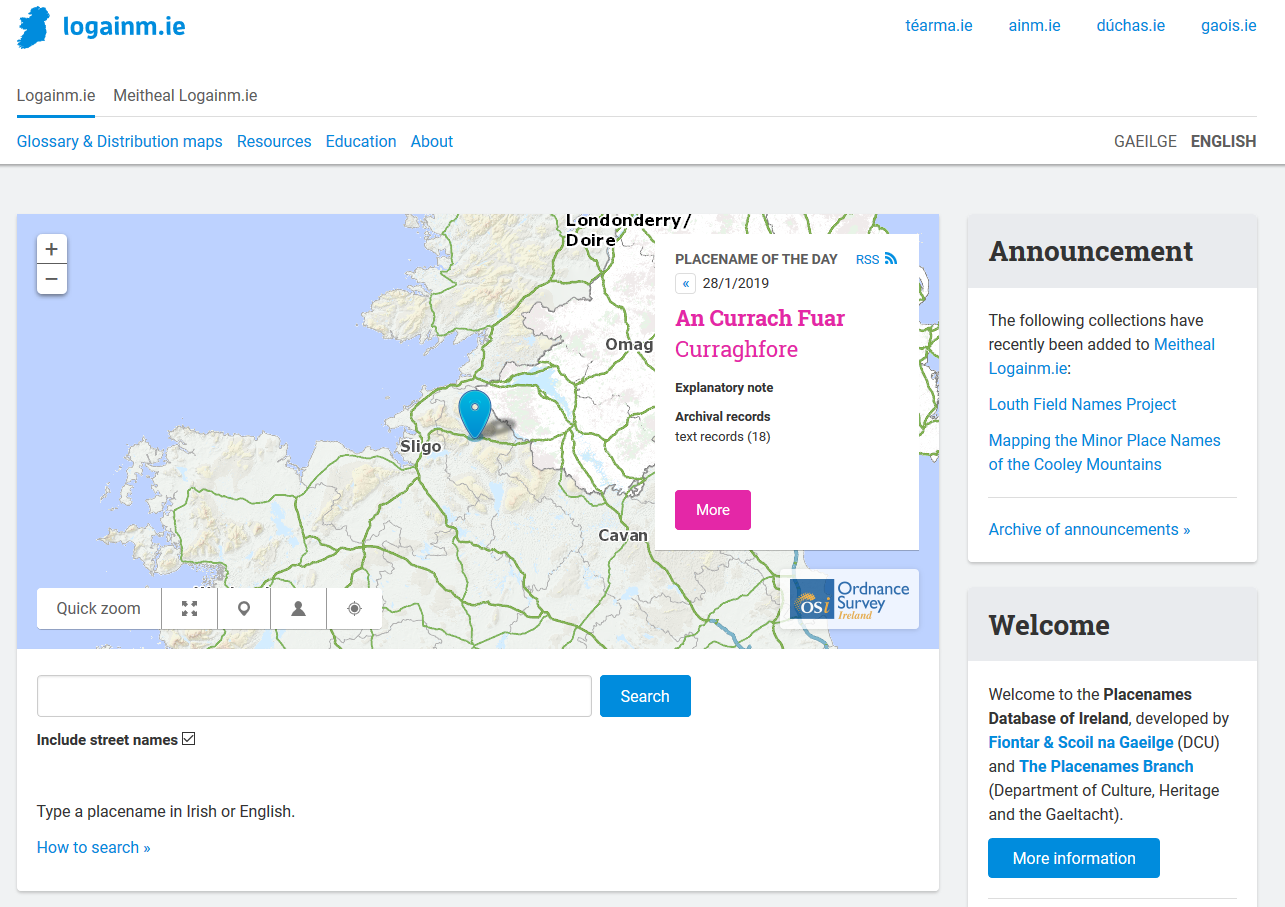
Placenames Database Of Ireland
The Placenames Database of Ireland ( ga, Bunachar Logainmneacha na hÉireann), also known as , is a database and archive of place names in Ireland. It was created by Fiontar, Dublin City University in collaboration with the Placenames Branch of the Department of Tourism, Culture, Arts, Gaeltacht, Sport and Media. The website is a public resource primarily aimed at journalists and translators, students and teachers, historians and researchers in genealogy. Placenames Commission and Placenames Branch The Placenames Commission ( ga, an Coimisiún Logainmneacha) was established by the Department of Finance (Ireland), Department of Finance in 1946 to advise Ordnance Survey Ireland and the government of what the Irish name of places should be. Although both the 1922 Constitution of the Irish Free State and the Constitution of Ireland, current constitution adopted in 1937 recognised Irish as the national language, the law in regard to placenames was carried over from the 19th-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sean Nos Song
Sean, also spelled Seán or Séan in Irish English, is a male given name of Irish origin. It comes from the Irish versions of the Biblical Hebrew name ''Yohanan'' (), Seán (anglicized as ''Shaun/ Shawn/ Shon'') and Séan (Ulster variant; anglicized ''Shane/Shayne''), rendered ''John'' in English and Johannes/Johann/Johan in other Germanic languages. The Norman French ''Jehan'' (see ''Jean'') is another version. For notable people named Sean, refer to List of people named Sean. Origin The name was adopted into the Irish language most likely from ''Jean'', the French variant of the Hebrew name ''Yohanan''. As Gaelic has no letter (derived from ; English also lacked until the late 17th Century, with ''John'' previously been spelt ''Iohn'') so it is substituted by , as was the normal Gaelic practice for adapting Biblical names that contain in other languages (''Sine''/''Siobhàn'' for ''Joan/Jane/Anne/Anna''; ''Seonaid''/''Sinéad'' for ''Janet''; ''Seumas''/''Séamus'' for ''Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

_p_2.168_Ireland_about_1570.jpg)