|
Kielce Cemetery Massacre
The Kielce cemetery massacre refers to the shooting action by the Nazi German police that took place on May 23, 1943 in occupied Poland during World War II, in which 45 Jewish children who had survived the Kielce Ghetto liquidation, and remained with their working parents at the Kielce forced-labour camps, were rounded up and brought to the Pakosz cemetery in Kielce, Poland, where they were murdered by the German paramilitary police. The children ranged in age from 15 months to 15 years old. During the ghetto liquidation action which began on 20 August 1942 approximately 20,000-21,000 Jews were led to awaiting Holocaust trains and sent to Treblinka extermination camp. By the end of 24 August 1942, there were only 2,000 skilled workers left alive in the labour camp at Stolarska-and-Jasna Streets '' (pl)'' within the small ghetto, including members of the ''Judenrat'' and the Jewish policemen. In May 1943, most Jewish prisoners from Kielce were transported to forced-labour camps i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
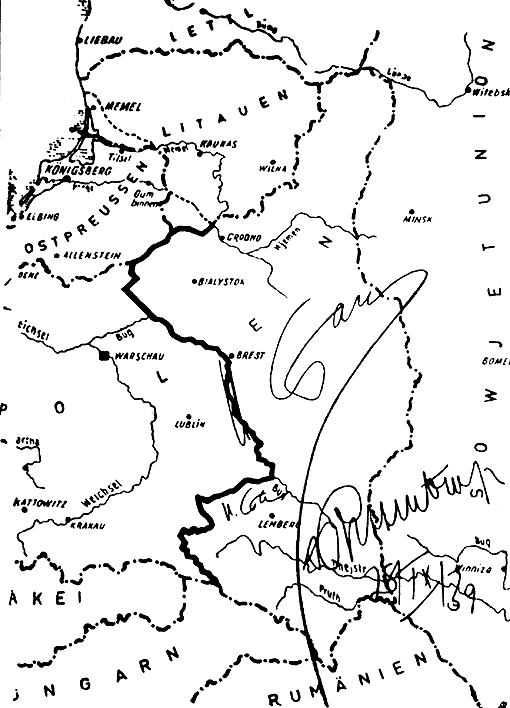
General Government
The General Government (german: Generalgouvernement, pl, Generalne Gubernatorstwo, uk, Генеральна губернія), also referred to as the General Governorate for the Occupied Polish Region (german: Generalgouvernement für die besetzten polnischen Gebiete), was a German zone of occupation established after the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany, Slovakia and the Soviet Union in 1939 at the onset of World War II. The newly occupied Second Polish Republic was split into three zones: the General Government in its centre, Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany in the west, and Polish areas annexed by the Soviet Union in the east. The territory was expanded substantially in 1941, after the German Invasion of the Soviet Union, to include the new District of Galicia. The area of the ''Generalgouvernement'' roughly corresponded with the Austrian part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth after the Third Partition of Poland in 1795. The basis for the formation of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocaust Massacres And Pogroms In Poland
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; around two-thirds of Europe's Jewish population. The murders were carried out in pogroms and mass shootings; by a policy of extermination through labor in concentration camps; and in gas chambers and gas vans in German extermination camps, chiefly Auschwitz-Birkenau, Bełżec, Chełmno, Majdanek, Sobibór, and Treblinka in occupied Poland. Germany implemented the persecution in stages. Following Adolf Hitler's appointment as chancellor on 30 January 1933, the regime built a network of concentration camps in Germany for political opponents and those deemed "undesirable", starting with Dachau on 22 March 1933. After the passing of the Enabling Act on 24 March, which gave Hitler dictatorial plenary powers, the government began isolating Jews fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1943 Crimes In Poland
Events Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix. January * January 1 – WWII: The Soviet Union announces that 22 German divisions have been encircled at Stalingrad, with 175,000 killed and 137,650 captured. * January 4 – WWII: Greek-Polish athlete and saboteur Jerzy Iwanow-Szajnowicz is executed by the Germans at Kaisariani. * January 11 ** The United States and United Kingdom revise previously unequal treaty relationships with the Republic of China. ** Italian-American anarchist Carlo Tresca is assassinated in New York City. * January 13 – Anti-Nazi protests in Sofia result in 200 arrests and 36 executions. * January 14 – 24 – WWII: Casablanca Conference: Franklin D. Roosevelt, President of the United States; Winston Churchill, Prime Minister of the United Kingdom; and Generals Charles de Gaulle and Henri Giraud of the Free French forces meet secretly at the Anfa Hotel in Casablanca, Morocco, to plan the Allied European strategy for the next stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bliżyn
Bliżyn is a village in Skarżysko County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, in south-central Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Bliżyn. It lies on the Kamienna river and Bliżyn Reservoir, approximately west of Skarżysko-Kamienna and north of the regional capital Kielce. The village has a population of 2,000. The village was first mentioned in 1410, when King Władysław II Jagiełło spent a night there on his way to the battle of Grunwald. In 19th century Stanisław Staszic founded several minor manufactories and factories there, as part of his plan of creation of the "Old Polish Industrial Area". During World War II the forests around Bliżyn were a mass murder site of Polish intelligentsia during the so-called AB Action. After the war the forests were made into the Suchedniów-Oblęgorek Landscape Park. There are also two forest nature reserves: Świnia Góra and Dalejów located south of Bliżyn in ''Puszcza Świetokrzyska'' (Holy Cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pionki
Pionki is a town in Radom County, Masovian Voivodeship, central Poland with 18 846 inhabitants (2016). Surrounded by the ''Kozienice'' Wilderness, Pionki is located in northern part of historic province of Lesser Poland, from Radom, and from Warsaw. History The mills of Pionki and Zagożdżon were first mentioned in medieval documents in 1391. Both settlements were royal villages, administratively located in the Radom County in the Sandomierz Voivodeship in the Lesser Poland Province, Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Lesser Poland Province of the Kingdom of Poland. Until 1932, the settlement was a village named Zagożdżon. Its development was closely associated with ''Chemical Plant Pronit'' (''Zakłady Tworzyw Sztucznych ZTS Pronit''), founded in 1923 as ''State Manufacturer of Gunpowder and Explosives'' (''Państwowa Wytwórnia Prochu i Materiałów Kruszących PWPiMK''). Originally, it was an arms factory, which manufactured explosives, and its location was deliberate - ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skarżysko-Kamienna
Skarżysko-Kamienna is a city in northern Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship in south-central Poland by Kamienna river, to the north of Świętokrzyskie Mountains; one of the voivodship's major cities. Prior to 1928, it bore the name of ''Kamienna''; in less formal contexts usually only the first part of the name (''Skarżysko'') is used. It belongs to historic Polish province of Lesser Poland. Skarżysko-Kamienna is an important railroad junction, with two main lines (Kraków – Warsaw and Sandomierz – Koluszki) crossing there. History The present-day districts of Łyżwy and Nowy Młyn were the locations of Paleolithic industrial settlements, which are now archaeological sites, part of the Rydno Archaeological Reserve, consisting of several hundred former Paleolithic sites stretching from Skarżysko-Kamienna to Wąchock. The sites were discovered in 1923–1925. In 1173, the knights' congress gathered in Milica village (now the town's district) led by Casimir II The Just. Within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starachowice
Starachowice is a city in southeastern Poland (historic Lesser Poland), with 49,513 inhabitants (31.12.2017). Starachowice is situated in the Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship (since 1999); it was formerly in the Kielce Voivodeship (1975–1998). It is the capital of Starachowice County. It is situated upon the River Kamienna, a tributary of the Vistula River, among hills and forests. History In the location of present-day Starachowice, a forge existed, which in the 16th century belonged to the Starzechowski family (most probably, the name of the town comes from this family). The oldest known mention of Starachowice comes from 1547. The settlement, which was built around the forge, belonged until 1817 to the Cistercians from Wąchock Abbey, located nearby. It was the monks who in 1789 initiated construction of a blast furnace (see also Old-Polish Industrial Region). In the meantime Polish bishop Bogusław Radoszewski founded the town of Wierzbnik in 1624, which was granted town righ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Shtetl
The Virtual Shtetl ( pl, Wirtualny Sztetl) is a bilingual Polish-English portal of the Museum of the History of Polish Jews in Warsaw, devoted to the Jewish history of Poland. History The Virtual Shtetl website was officially launched on June 16, 2009 by founder Albert Stankowski. The portal lists over 1,900 towns with maps, statistics and picture galleries. In the future, it will also include an interactive system by which Internet users will interact with each other. It creates a link between Polish-Jewish history and the contemporary, multi-cultural world. The Virtual Shtetl is an extension of the real Museum scheduled to open in 2011 on the site of the Warsaw ghetto. Its main objective is to provide a unique social forum for everyone interested in Polish-Jewish life. The "Virtual Shtetl" re-tells the history of Polish Jews which existed, to a great extent, in a town or a village (Yiddish: shtetl). But besides that, it also provides information about German Jews and the Jew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occupied Poland
' (Norwegian: ') is a Norwegian political thriller TV series that premiered on TV2 on 5 October 2015. Based on an original idea by Jo Nesbø, the series is co-created with Karianne Lund and Erik Skjoldbjærg. Season 2 premiered on 10 October 2017. The third and final season started airing in Scandinavia on 5 December 2019, and was released in many countries via Netflix on 31 December 2019. With a budget of 90 million kr (US$11 million), the series is the most expensive Norwegian production to date and has been sold to the UK, Germany, France, Sweden, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Serbia, Estonia, Poland, Czech Republic, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Spain, Portugal, and Canada. It is also streamed by Netflix in the United States, Australia, New Zealand, Israel, Ireland, the United Kingdom, India, Singapore, Canada, Belgium, Italy, South Africa and the Netherlands. The series depicts a fictional near future in which, due to catastrophic environmental events, Norway's Prime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
POLIN Museum Of The History Of Polish Jews
POLIN Museum of the History of Polish Jews ( pl, Muzeum Historii Żydów Polskich) is a museum on the site of the former Warsaw Ghetto. The Hebrew word ''Polin'' in the museum's English name means either "Poland" or "rest here" and relates to a legend about the arrival of the first Jews to Poland. The museum's cornerstone was laid in 2007, and the museum opened on 19 April 2013. The core exhibition opened in October 2014 The building, a postmodern structure in glass, copper, and concrete, was designed by Finnish architects Rainer Mahlamäki and Ilmari Lahdelma. History The idea for creating a major new museum in Warsaw dedicated to the history of Polish Jews was initiated in 1995 by the Association of the Jewish Historical Institute of Poland.A.J. Goldmann "Polish Museum Set To Open Spectacular Window on Jewish Past"The Jewish Daily Forward, April 01, 2013. In the same year, the Warsaw City Council allocated the land for this purpose in Muranów, Warsaw's prewar Jewish qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
