|
Kidnapping Into Slavery In The United States
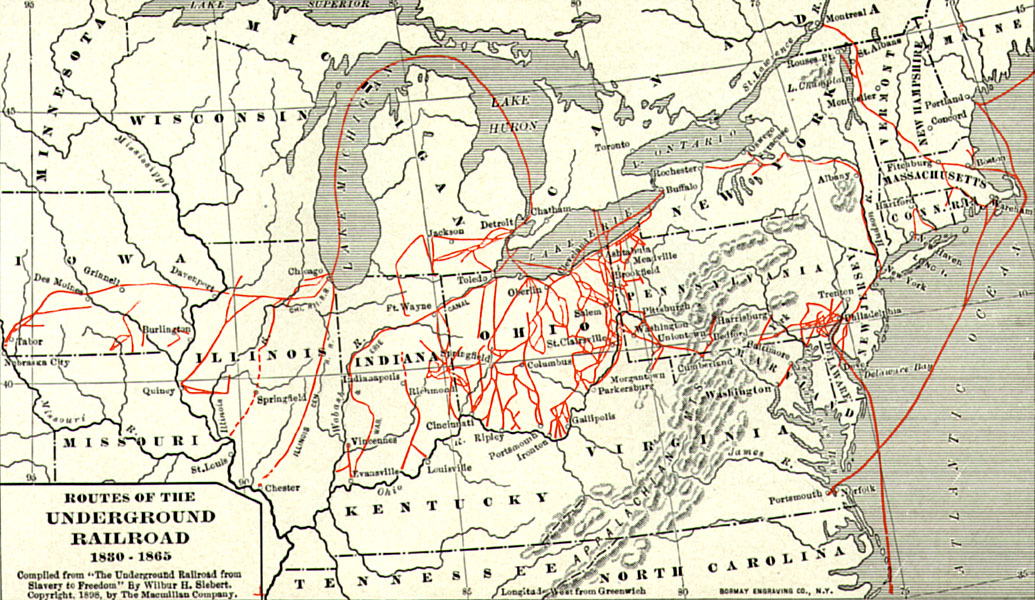
The pre- American Civil War practice of kidnapping into slavery in the United States occurred in both free and slave states, and both fugitive slaves and free negroes were transported to slave markets and sold, often multiple times. There were also rewards for the return of fugitives. Three types of kidnapping methods were employed: physical abduction, inveiglement (kidnapping through trickery) of free blacks, and apprehension of fugitives. The enslavement, or re-enslavement, of free blacks occurred for 85 years, from 1780 to 1865. Those who used the term ''Reverse Underground Railroad'' were angered at an " underground railroad" helping slaves escape. Rescues of blacks who had been kidnapped were unusual. The name is a reference to the Underground Railroad, the informal network of abolitionists and sympathizers who helped smuggle escaped slaves to freedom, generally in Canada but also in Mexico where slavery had been abolished. Prevalence Free African Americans were oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manumission
Manumission, or enfranchisement, is the act of freeing enslaved people by their enslavers. Different approaches to manumission were developed, each specific to the time and place of a particular society. Historian Verene Shepherd states that the most widely used term is gratuitous manumission, "the conferment of freedom on the enslaved by enslavers before the end of the slave system". The motivations for manumission were complex and varied. Firstly, it may present itself as a sentimental and benevolent gesture. One typical scenario was the freeing in the master's will of a devoted servant after long years of service. A trusted bailiff might be manumitted as a gesture of gratitude. For those working as agricultural laborers or in workshops, there was little likelihood of being so noticed. In general, it was more common for older slaves to be given freedom. Legislation under the early Roman Empire put limits on the number of slaves that could be freed in wills (''lex Fufia Can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, Maryland to its south, West Virginia to its southwest, Ohio to its west, Lake Erie and the Canadian province of Ontario to its northwest, New York to its north, and the Delaware River and New Jersey to its east. Pennsylvania is the fifth-most populous state in the nation with over 13 million residents as of 2020. It is the 33rd-largest state by area and ranks ninth among all states in population density. The southeastern Delaware Valley metropolitan area comprises and surrounds Philadelphia, the state's largest and nation's sixth most populous city. Another 2.37 million reside in Greater Pittsburgh in the southwest, centered around Pittsburgh, the state's second-largest and Western Pennsylvania's largest city. The state's su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Crenshaw
John Hart Crenshaw (November 19, 1797 – December 4, 1871) was an American landowner, salt maker, kidnapper and slave trader, based out of Gallatin County, Illinois. He is also the great-great grandfather of killer and suspected serial killer Joe Ball, also known as "The Alligator Man". Slave trader Although Illinois was a free state, Crenshaw leased the salt works in nearby Equality, Illinois from the government, which permitted the use of slaves for the arduous labor of hauling and boiling brackish water to produce salt. Crenshaw was widely believed to be involved in the kidnapping and sale of free black citizens in free states as slaves in the south, an enormously profitable trade later known as the Reverse Underground Railroad. Crenshaw was twice prosecuted for kidnapping, but never convicted. Due to Crenshaw's keeping slaves and kidnapping free blacks, who were then pressed into slavery, his house became popularly known as The Old Slave House and is alleged to be hau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poison
Poison is a chemical substance that has a detrimental effect to life. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figuratively, with a broad sense. Whether something is considered a poison may change depending on the amount, the circumstances, and what living things are present. Poisoning could be accidental or deliberate, and if the cause can be identified there may be ways to neutralise the effects or minimise the symptoms. In biology, a poison is a chemical substance causing death, injury or harm to organisms or their parts. In medicine, poisons are a kind of toxin that are delivered passively, not actively. In industry the term may be negative, something to be removed to make a thing safe, or positive, an agent to limit unwanted pests. In ecological terms, poisons introduced into the environment can later cause unwanted effects elsewhere, or in other parts of the food ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but only the gray form, which has a metallic appearance, is important to industry. The primary use of arsenic is in alloys of lead (for example, in car batteries and ammunition). Arsenic is a common n-type dopant in semiconductor electronic devices. It is also a component of the III-V compound semiconductor gallium arsenide. Arsenic and its compounds, especially the trioxide, are used in the production of pesticides, treated wood products, herbicides, and insecticides. These applications are declining with the increasing recognition of the toxicity of arsenic and its compounds. A few species of bacteria are able to use arsenic compounds as respiratory metabolites. Trace quantities of arsenic are an essential dietary element in rats, ham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murders
Murder is the unlawful killing of another human without justification or valid excuse, especially the unlawful killing of another human with malice aforethought. ("The killing of another person without justification or excuse, especially the crime of killing a person with malice aforethought or with recklessness manifesting extreme indifference to the value of human life.") This state of mind may, depending upon the jurisdiction, distinguish murder from other forms of unlawful homicide, such as manslaughter. Manslaughter is killing committed in the absence of ''malice'',This is "malice" in a technical legal sense, not the more usual English sense denoting an emotional state. See malice (law). brought about by reasonable provocation, or diminished capacity. ''Involuntary'' manslaughter, where it is recognized, is a killing that lacks all but the most attenuated guilty intent, recklessness. Most societies consider murder to be an extremely serious crime, and thus that a pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantations In The American South
A plantation complex in the Southern United States is the built environment (or complex) that was common on agricultural plantations in the American South from the 17th into the 20th century. The complex included everything from the main residence down to the pens for livestock. Until the abolition of slavery, such plantations were generally self-sufficient settlements that relied on the forced labor of enslaved people. Plantations are an important aspect of the history of the Southern United States, particularly the antebellum era (pre-American Civil War). The mild temperate climate, plentiful rainfall, and fertile soils of the southeastern United States allowed the flourishing of large plantations, where large numbers of enslaved Africans or African Americans were held captive and forced to produce crops to create wealth for a white elite. Today, as was also true in the past, there is a wide range of opinion as to what differentiated a plantation from a farm. Typically, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / Eastern Shore of Virginia and the state of Delaware) with its mouth of the Bay at the south end located between Cape Henry and Cape Charles (headland), Cape Charles. With its northern portion in Maryland and the southern part in Virginia, the Chesapeake Bay is a very important feature for the ecology and economy of those two states, as well as others surrounding within its watershed. More than 150 major rivers and streams flow into the Bay's drainage basin, which covers parts of six states (New York, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia and West Virginia) and all of District of Columbia. The Bay is approximately long from its northern headwaters in the Susquehanna River to its outlet in the Atlantic Ocea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
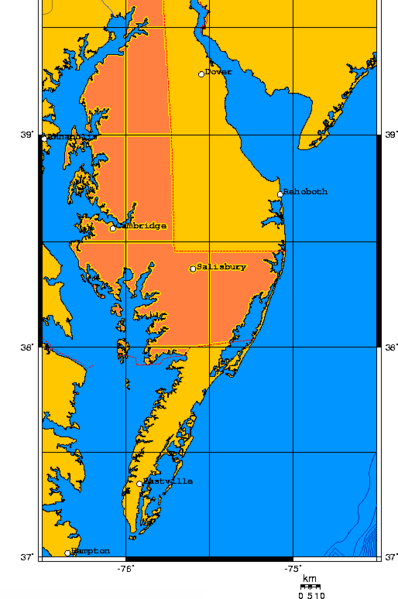
Delmarva Peninsula
The Delmarva Peninsula, or simply Delmarva, is a large peninsula and proposed state on the East Coast of the United States, occupied by the vast majority of the state of Delaware and parts of the Eastern Shore regions of Maryland and Virginia. The peninsula is long. In width, it ranges from near its center, to at the isthmus on its northern edge, to less near its southern tip of Cape Charles. It is bordered by the Chesapeake Bay on the west, Pocomoke Sound on the southwest, and the Delaware River, Delaware Bay, and the Atlantic Ocean on the east. Etymology In older sources, the peninsula between Delaware Bay and Chesapeake Bay was referred to variously as the Delaware and Chesapeake Peninsula or simply the Chesapeake Peninsula. The toponym ''Delmarva'' is a clipped compound of Delaware, Maryland, and Virginia ( official abbreviation ''VA''), which in turn was modeled after Delmar, a border town named after two of those states. While Delmar was founded and named in 1859, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patty Cannon
Patty Cannon, whose birth name may have been Lucretia Patricia Hanly (c. 1759/1760 or 1769 – May 11, 1829), was an illegal slave trader, murderer and the co-leader of the Cannon–Johnson Gang of Maryland–Delaware. The group operated for about a decade in the early 19th century and abducted hundreds of free Black people and fugitive slaves, along the Delmarva Peninsula, across multiple state lines to sell into slavery in southern states such as Alabama and Mississippi. The activity became known as the Reverse Underground Railroad. Mayor Joseph Watson of Philadelphia and Governor John Andrew Shulze of Pennsylvania worked to recover young free Black people kidnapped by the gang in the summer of 1825 and to prosecute the gang members. They did not succeed in trying any of the white members. The only time any real efforts to arrest and convict the gang is when authorities found the bodies of several white slave traders, a child and a baby. After being acquitted in Mayor's Cour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackbirding
Blackbirding involves the coercion of people through deception or kidnapping to work as slaves or poorly paid labourers in countries distant from their native land. The term has been most commonly applied to the large-scale taking of people indigenous to the numerous islands in the Pacific Ocean during the 19th and 20th centuries. These blackbirded people were called Kanakas or South Sea Islanders. They were taken from places such as Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Niue, Easter Island, the Gilbert Islands, Tuvalu, the Fiji islands and the islands of the Bismarck Archipelago amongst others. The owners, captains, and crews of the ships involved in the acquisition of these labourers were termed ''blackbirders''. The demand for this kind of cheap labour principally came from European colonists in New South Wales, Queensland, Samoa, New Caledonia, Fiji, Tahiti and Hawaii, as well as plantations in Peru, Mexico and Guatemala. Labouring on sugar cane, cotton, and coffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |