|
Kharshedji Rustomji Cama
Kharshedji Rustomji Cama (1831–1909), often known as K. R. Cama, was an Indian Parsi scholar and reformer from Bombay. Early life Born in a privileged family, Cama gained a reputation as a scholar. He had a traditional Parsi education, and then went to Elphinstone School in Bombay. Leaving in 1849, he joined a trading house in Calcutta, and then travelled in 1850 to London, returning in 1854 to Bombay. He went into business with Dadabhai Naoroji, and again visited Europe in 1855, and studied with orientalists there: Julius Mohl and Julius Oppert in Paris, and Friedrich von Spiegel at the University of Erlangen. Naoroji with Cama and his cousin Muncherjee Hormusji Cama set up the first Indian trading firm in Europe, based in London and Liverpool. Cama and Naoroji then dropped out, however, because of the firm's dealings in alcohol and opium. Reformer There was an identifiable group of Bombay Parsi reformers, including Naoroji, Cama and Manockjee Cursetjee who were concerne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
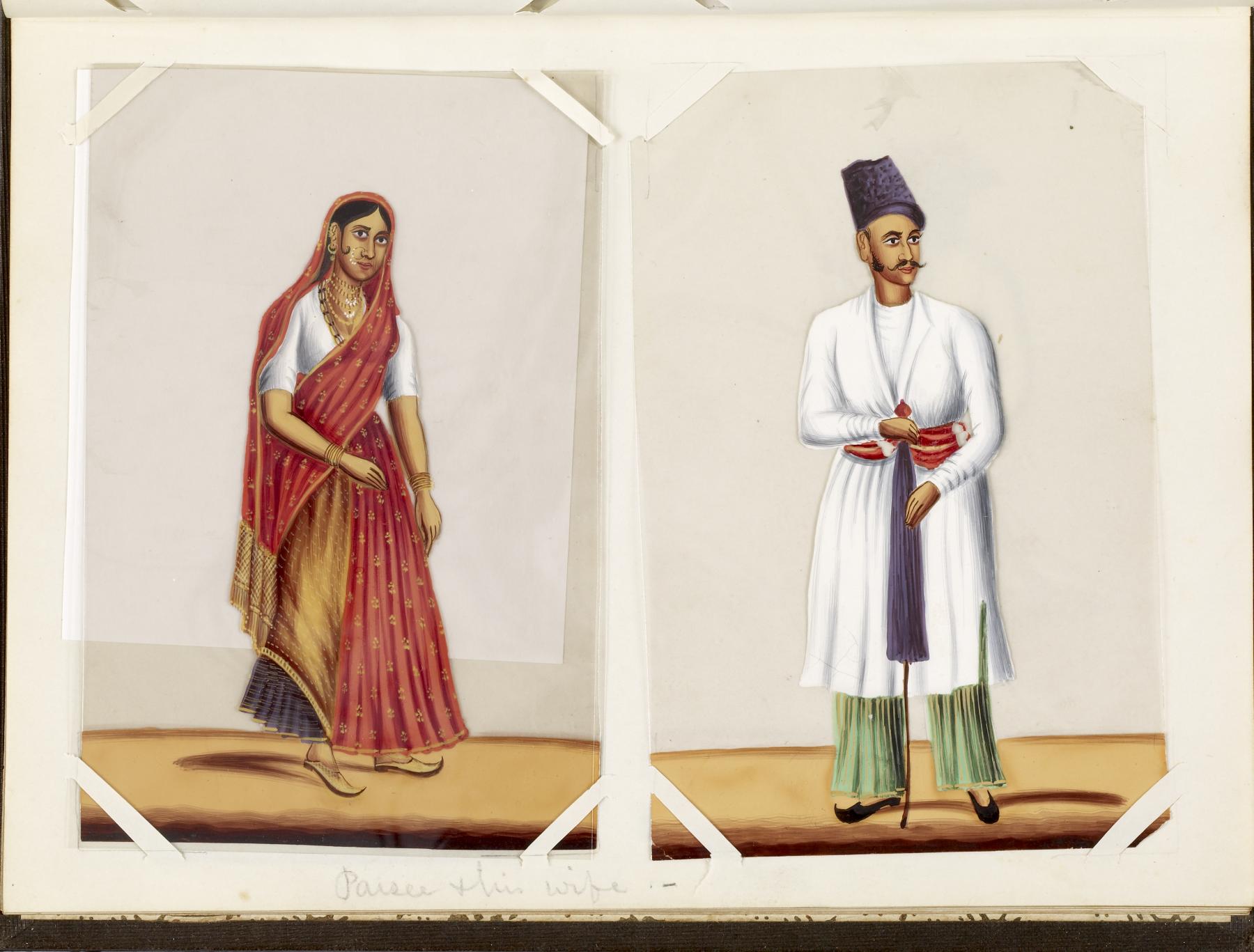
Parsi
Parsis () or Parsees are an ethnoreligious group of the Indian subcontinent adhering to Zoroastrianism. They are descended from Persians who migrated to Medieval India during and after the Arab conquest of Iran (part of the early Muslim conquests) in order to preserve their Zoroastrian identity. The Parsi people comprise the older of the Indian subcontinent's two Zoroastrian communities vis-à-vis the Iranis, whose ancestors migrated to British-ruled India from Qajar-era Iran. According to a 16th-century Parsi epic, ''Qissa-i Sanjan'', Zoroastrian Persians continued to migrate to the Indian subcontinent from Greater Iran in between the 8th and 10th centuries, and ultimately settled in present-day Gujarat after being granted refuge by a local Hindu king. Prior to the 7th-century fall of the Sassanid Empire to the Rashidun Caliphate, the Iranian mainland (historically known as 'Persia') had a Zoroastrian majority, and Zoroastrianism had served as the Iranian state religion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandra Native Girls' English Institution
The Alexandra Girls’ English Institution (commonly abbreviated as the AGEI), formerly known as the Alexandra Native Girls' English Institution, is a girls-only school in Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. Established on 1 September 1863 by Manockjee Cursetjee at his residence Villa Byculla, the institution is named after Princess Alexandra, who became the Princess of Wales upon her marriage to Albert Edward, Prince of Wales on 10 March 1863. The school was later moved to its present location at Hazarimal Somani Marg. Imparting education from nursery to tenth grade, the school is affiliated with the Indian Certificate of Secondary Education for all the grades up to fourth grade and with the Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education from fifth to tenth grade. Its student–teacher ratio, 1:17, is better than the national ratio of 1:24. Foundation The school was founded by Parsi businessman and judge Manockjee Cursetjee as the Alexandra Native Girls' Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
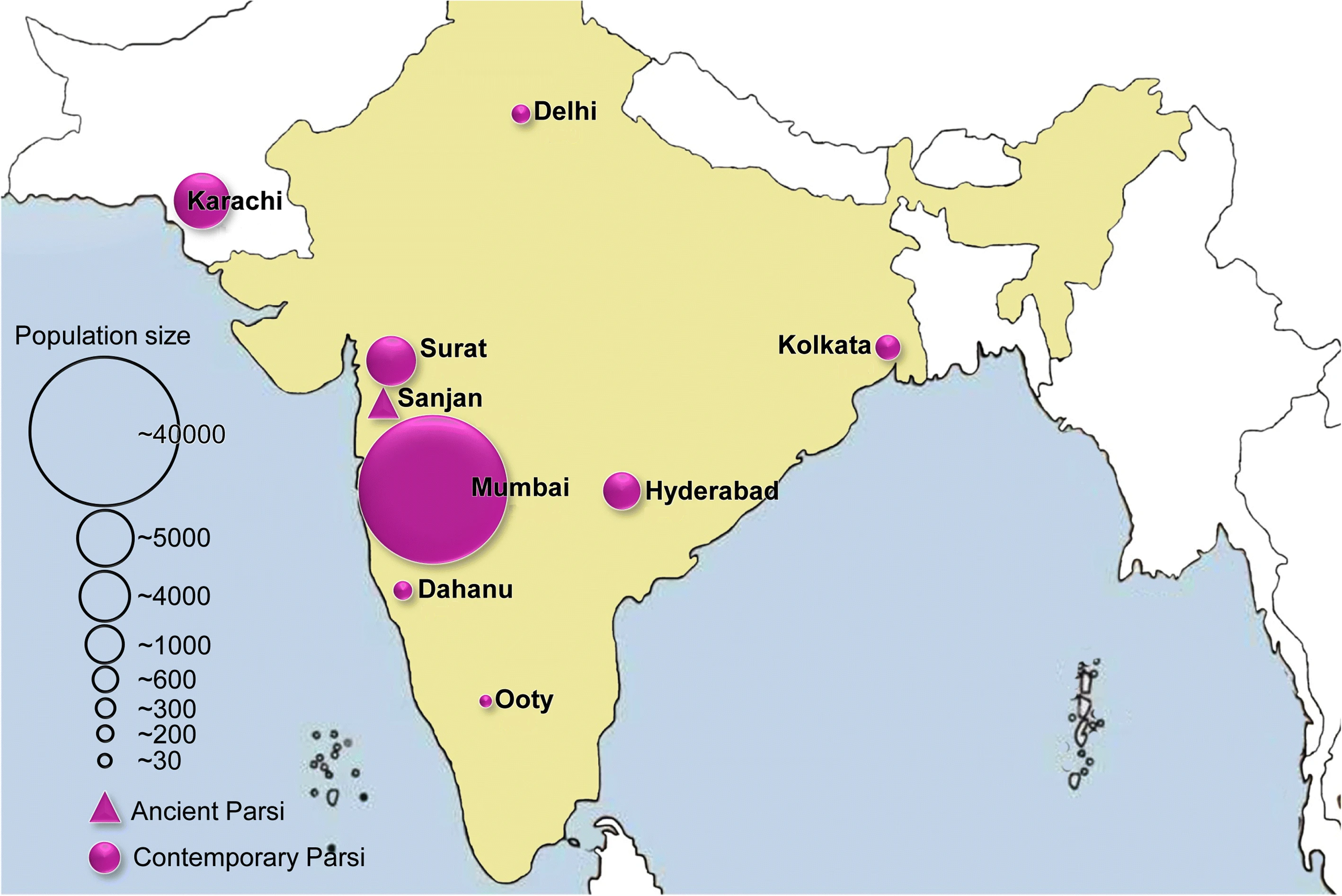
Parsi People From Mumbai
Parsis () or Parsees are an ethnoreligious group of the Indian subcontinent adhering to Zoroastrianism. They are descended from Persians who migrated to Medieval India during and after the Arab conquest of Iran (part of the early Muslim conquests) in order to preserve their Zoroastrian identity. The Parsi people comprise the older of the Indian subcontinent's two Zoroastrian communities vis-à-vis the Iranis, whose ancestors migrated to British-ruled India from Qajar-era Iran. According to a 16th-century Parsi epic, ''Qissa-i Sanjan'', Zoroastrian Persians continued to migrate to the Indian subcontinent from Greater Iran in between the 8th and 10th centuries, and ultimately settled in present-day Gujarat after being granted refuge by a local Hindu king. Prior to the 7th-century fall of the Sassanid Empire to the Rashidun Caliphate, the Iranian mainland (historically known as 'Persia') had a Zoroastrian majority, and Zoroastrianism had served as the Iranian state religion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1909 Deaths
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album ''63/19'' by Kool A.D. * ''Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album '' Refugee'' * "Nineteen", a song by Karma to Burn from the 2001 album ''Almost Heathen''. * "Nineteen" (song), a 2007 song by American singer Billy Ray Cyrus. * "Nineteen", a song by Tegan and Sara from the 2007 album '' The Con''. * "XIX" (song), a 2014 song by Slipk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1831 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – William Lloyd Garrison begins publishing '' The Liberator'', an anti-slavery newspaper, in Boston, Massachusetts. * January 10 – Japanese department store, Takashimaya in Kyoto established. * February–March – Revolts in Modena, Parma and the Papal States are put down by Austrian troops. * February 2 – Pope Gregory XVI succeeds Pope Pius VIII, as the 254th pope. * February 5 – Dutch naval lieutenant Jan van Speyk blows up his own gunboat in Antwerp rather than strike his colours on the demand of supporters of the Belgian Revolution. * February 7 – The Belgian Constitution of 1831 is approved by the National Congress. *February 8 - Aimé Bonpland leaves Paraguay. * February 14 – Battle of Debre Abbay: Ras Marye of Yejju marches into Tigray, and defeats and kills the warlord Sabagadis. * February 25 – Battle of Olszynka Grochowska (Grochów): Polish rebel forces divide a Ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhikaiji Cama
Bhikaiji Rustom CamaBhi''ai''- (with aspirated ''-kh-'') is the name as it appears in the biographies. Another common form is Bhi''ai''- (with unaspirated ''-k-''), as it appears on the postage stamp. The name is also frequently misspelled 'Bhikh''''-' (with missing ''-i-''), which is a male name (unlike the feminine Bhikh''''-). (24 September 1861 – 13 August 1936) or simply as, Madam Cama, was one of the prominent figures in the Indian independence movement. Bhikaiji Cama was born in Bombay (now Mumbai) in a large, affluent Parsi Zoroastrian family. Her parents, Sorabji Framji Patel and Jaijibai Sorabji Patel, were well known in the city, where her father Sorabji—a lawyer by training and a merchant by profession—was an influential member of the Parsi community. She unfurled the first version of flag of independent India on August 21, 1907, when an International Socialist Conference was being held at Stuttgart, a city in Germany. Like many Parsi girls of the time, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Willingdon
Freeman Freeman-Thomas, 1st Marquess of Willingdon (12 September 1866 – 12 August 1941), was a British Liberal politician and administrator who served as Governor General of Canada, the 13th since Canadian Confederation, and as Viceroy and Governor-General of India, the country's 22nd. Freeman-Thomas was born in England and educated at Eton College and then the University of Cambridge before serving for 15 years in the Sussex Artillery. He then entered the diplomatic and political fields, acting as aide-de-camp to his father-in-law when the latter was Governor of Victoria and, in 1900, was elected to the British House of Commons. He thereafter occupied a variety of government posts, including secretary to the British prime minister and, after being raised to the peerage as Lord Willingdon, as Lord-in-waiting to King George V. From 1913, Willingdon held gubernatorial and viceregal offices throughout the British Empire, starting with the governorship of Bombay and then the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilson College, Mumbai
The Wilson College, established in 1832 in Mumbai, is one of India's oldest colleges; its foundation precedes that of the University of Mumbai, to which it is affiliated, by 25 years. Wilson College was granted autonomy by Mumbai University in November 2021. It was awarded an A rating by the National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC) in 2005. Located opposite Mumbai's Girgaon Chowpatty, the college building was constructed in 1889 and designed by John Adams in the domestic Victorian Gothic style. It is listed as a Grade III heritage structure in the city. , the college offered a variety of subjects for both higher secondary and undergraduate students which include University Aided courses for the Arts and the Sciences as well as self-financed courses such as Mass Media, Information Technology, Management Studies, Biotechnology, Electronics & Computer Science. History The Wilson College was founded by the Scottish missionary Rev. John Wilson, in 1832. Beginning as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freemasonry
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities and clients. Modern Freemasonry broadly consists of two main recognition groups: * Regular Freemasonry insists that a volume of scripture be open in a working lodge, that every member profess belief in a Supreme Being, that no women be admitted, and that the discussion of religion and politics be banned. * Continental Freemasonry consists of the jurisdictions that have removed some, or all, of these restrictions. The basic, local organisational unit of Freemasonry is the Lodge. These private Lodges are usually supervised at the regional level (usually coterminous with a state, province, or national border) by a Grand Lodge or Grand Orient. There is no international, worldwide Grand Lodge that supervises all of Freemasonry; each Grand Lod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mithraism
Mithraism, also known as the Mithraic mysteries or the Cult of Mithras, was a Roman mystery religion centered on the god Mithras. Although inspired by Iranian worship of the Zoroastrian divinity (''yazata'') Mithra, the Roman Mithras is linked to a new and distinctive imagery, with the level of continuity between Persian and Greco-Roman practice debated. The mysteries were popular among the Imperial Roman army from about the 1st to the 4th-century CE. Worshippers of Mithras had a complex system of seven grades of initiation and communal ritual meals. Initiates called themselves ''syndexioi'', those "united by the handshake". They met in underground temples, now called ''mithraea'' (singular ''mithraeum''), which survive in large numbers. The cult appears to have had its center in Rome, and was popular throughout the western half of the empire, as far south as Roman Africa and Numidia, as far as Roman Dacia, as far north as Roman Britain, and to a lesser extent in Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoroastrian Calendar
Adherents of Zoroastrianism use three distinct versions of traditional calendars for liturgical purposes, all derived from medieval Iranian calendars and ultimately based on the Babylonian calendar as used in the Achaemenid empire. ''Qadimi'' ("ancient") is a traditional reckoning introduced in 1006. ''Shahanshahi'' ("imperial") is a calendar reconstructed from the 10th century text ''Denkard''. ''Fasli'' is a term for a 1906 adaptation of the 11th century Jalali calendar following a proposal by Kharshedji Rustomji Cama made in the 1860s. A number of Calendar eras are in use: *A tradition of counting years from the birth of Zoroaster was reported from India in the 19th century. There was a dispute between factions variously preferring an era of 389 BCE, 538 BCE, or 637 BCE. *The "Yazdegerdi era" (also ''Yazdegirdi'') counts from the accession of the last Sassanid ruler, Yazdegerd III (16 June 632 CE). This convention was proposed by Cama in the 1860s but has since also been u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calendar Reform
Calendar reform or calendrical reform is any significant revision of a calendar system. The term sometimes is used instead for a proposal to switch to a different calendar design. Principles The prime objective of a calendar is to unambiguously identify any day in past, present and future by a specific date in order to record or organize social, religious, commercial or administrative events. Recurring periods that contain multiple days, like weeks, months and even years, are secondary, convenient features of a calendar. Most cultures adopt a primary dating system, but different cultures have always needed to align multiple calendars with each other, because they coexisted in the same space (e.g. secular and religious groups with different demands) or had established trading relations. Once specified, a ''calendar design'' cannot be altered without becoming a new design. If a proposed design is sufficiently close to the legacy one, i.e. compatible with it, a ''reform'' of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |