|
Khaemwaset
Prince Khaemweset (also translated as Khamwese, Khaemwese or Khaemwaset or Setne Khamwas) was the fourth son of Ramesses II and the second son by his queen Isetnofret. His contributions to Egyptian society were remembered for centuries after his death.Aidan Dodson & Dyan Hilton, ''The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt'', Thames & Hudson (2004), p. 170-171 Khaemweset has been described as "the first Egyptologist" due to his efforts in identifying and restoring historic buildings, tombs and temples. Life According to historian Miriam Lichtheim: :Here I should like to stress that Prince Setne Khamwas, the hero of the two tales named for him, was a passionate antiquarian. The historical prince Khamwas, was the fourth son of King Ramses II, had been high priest of Ptah at Memphis and administrator of all the Memphite sanctuaries. In that capacity he had examined decayed tombs, restored the names of their owners, and renewed their funerary cults. Posterity had transmitted his r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isetnofret
Isetnofret (or Isis-nofret or Isitnofret) ( Ancient Egyptian: "the beautiful Isis") was one of the Great Royal Wives of Pharaoh Ramesses II and was the mother of his successor, Merneptah. She was one of the most prominent of the royal wives, along with Nefertari, and was the chief queen after Nefertari's death (around the 24th year of the pharaoh's reign). Family The parents of Isetnofret are not known. She must have married Ramesses II even before he came to the throne as her eldest children already appear in scenes from the time of Seti I. She had at least three sons and one daughter. Her children include: * Prince Ramesses, Crown Prince from Year 25 to 50 of Ramesses II * Princess-Queen Bintanath, firstborn daughter and later wife of RamessesDodson & Hilton, p.170 * Prince Khaemwaset, High Priest of Ptah. Crown Prince from Year 50 to 55 of Ramesses II * Pharaoh Merneptah, Ramesses' 13th son and ultimate successor (he outlived the first 12 princes) * Pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramesses (prince)
Ramesses (sometimes referred as Ramesses B) was an ancient Egyptian crown prince during the 19th Dynasty. Family Ramesses was the eldest son of Ramesses II and Queen Isetnofret, and the second son overall after Amunherkhepeshef, the eldest son of the Great Royal Wife Nefertari.Kitchen, Kenneth A., ''Pharaoh Triumphant: The Life and Times of Ramesses II, King of Egypt'', Aris & Phillips. 1983 Born during the reign of his grandfather Sethi I, he had at least one sister and two brothers. His sister Bintanath was elevated to the position of Great Royal Wife later in the reign of Ramesses II and played an important role at court. A possible sister named Isetnofret may have married her brother Merneptah and been his queen, however, it is possible that Merneptah's queen was his niece, not his sister. His known younger brothers are Khaemwaset and Merneptah. Ramesses is listed on several monuments with his younger brothers Khaemwaset and Merenptah. He appears as the second pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Priest Of Ptah
The High Priest of Ptah was sometimes referred to as "the Greatest of the Directors of Craftsmanship" ('' wr-ḫrp-ḥmwt''). This title refers to Ptah as the patron god of the craftsmen.Dodson and Hilton, ''The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt'', 2004 The office of the high priest of Ptah was located in Memphis in Lower Egypt. The temple of Ptah in Memphis was dedicated to Ptah, his consort Sekhmet and their son Nefertem. History High priests of Ptah are mentioned in inscriptions dating back to at least the Fourth Dynasty. In the tomb of the nobleman Debhen, for instance, there is a description of a visit by Pharaoh Menkaure to the construction site for his pyramid "Divine is Menkaure". The pharaoh is accompanied by a naval commander and two high priests of Ptah. There used to be two high priests of Ptah until the Sixth Dynasty. It was probably during the reign of Pepi I Meryre that the two offices were combined into one. In the tomb of Sabu called Thety in Saqqar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramesses II
Ramesses II ( egy, wikt:rꜥ-ms-sw, rꜥ-ms-sw ''Rīʿa-məsī-sū'', , meaning "Ra is the one who bore him"; ), commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was the third pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Along with Thutmose III he is often regarded as the greatest, most celebrated, and most powerful pharaoh of the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom, itself the most powerful period of Ancient Egypt. The name ''Ramesses'' is pronounced variously . Transliteration of Ancient Egyptian, Other spellings include Rameses and Ramses; in grc-koi, Ῥαμέσσης, Rhaméssēs. He is known as Ozymandias in Greek sources ( grc-koi, Ὀσυμανδύας, translit=Osymandýas), from the first part of Ramesses's regnal name, , "The Maat of Ra is powerful, Chosen of Ra". His successors and later Egyptians called him the "Great Ancestor". At age fourteen, he was appointed prince regent by his father, Seti I. Most Egyptologists today believe he assumed the throne on 31 May 1279 BC, bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apis (deity)
In ancient Egyptian religion, Apis or Hapis ( egy, ḥjpw, reconstructed as Old Egyptian with unknown final vowel > Medio-Late Egyptian , cop, ϩⲁⲡⲉ ''ḥapə''), alternatively spelled Hapi-ankh, was a sacred bull worshiped in the Memphis region, identified as the son of Hathor, a primary deity in the pantheon of ancient Egypt. Initially, he was assigned a significant role in her worship, being sacrificed and reborn. Later, Apis also served as an intermediary between humans and other powerful deities (originally Ptah, later Osiris, then Atum). The Apis bull was an important sacred animal to the ancient Egyptians. As with the other sacred beasts, Apis' importance increased over the centuries. During colonization of the conquered Egypt, Greek and Roman authors had much to say about Apis, the markings by which the black calf was recognized, the manner of his conception by a ray from heaven, his house at Memphis (with a court for his deportment), the mode of prognosti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shepseskaf
Shepseskaf (meaning "His Ka is noble") was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt, the sixth and probably last ruler of the fourth dynasty during the Old Kingdom period. He reigned most probably for four but possibly up to seven years in the late 26th to mid-25th century BC. Shepseskaf's relation to his predecessor Menkaure is not entirely certain; he might have been his son or possibly his brother. The identity of his mother is highly uncertain as she could have been one of Menkaure's consorts or queen Khentkaus I or Neferhetepes. Similarly, Shepseskaf's relation to his probable successor on the throne, Userkaf, is not known although in the absence of clear indication of strife at the transition between the fourth and fifth dynasties, Userkaf could well have been his son or his brother. If Shepseskaf was succeeded directly by Userkaf rather than by Thampthis as claimed by some historical sources, then his death marks the end of the fourth dynasty. The transition to the fifth dynasty se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seti I
Menmaatre Seti I (or Sethos I in Greek) was the second pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt during the New Kingdom period, ruling c.1294 or 1290 BC to 1279 BC. He was the son of Ramesses I and Sitre, and the father of Ramesses II. The name 'Seti' means "of Set", which indicates that he was consecrated to the god Set (also termed "Sutekh" or "Seth"). As with most pharaohs, Seti had several names. Upon his ascension, he took the prenomen "mn-m3't-r' ", usually vocalized in Egyptian as ''Menmaatre (''Established is the Justice of Re). His better known nomen, or birth name, is transliterated as "''sty mry-n-ptḥ"'' or ''Sety Merenptah'', meaning "Man of Set, beloved of Ptah". Manetho incorrectly considered him to be the founder of the 19th Dynasty, and gave him a reign length of 55 years, though no evidence has ever been found for so long a reign. Reign After the enormous social upheavals generated by Akhenaten's religious reform, Horemheb, Ramesses I and Seti I's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amun-her-khepeshef
Amun-her-khepeshef (died c. 1254 BC; also Amonhirkhopshef, Amun-her-wenemef and Amun-her-khepeshef A to distinguish him from later people of the same name) was the firstborn son of Pharaoh Ramesses II and Queen Nefertari. Name He was born when his father was still a co-regent with Seti I. He was originally called ''Amun-her-wenemef'' ("Amun Is with His Right Arm"). He changed his name to ''Amun-her- khepeshef'' ("Amun Is with His Strong Arm") early in his father's reign.Aidan Dodson & Dyan Hilton, ''The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt'', Thames & Hudson (2004), p.170 He appears to have changed his name once again to ''Seth-her-khepeshef'' around Year 20 of Ramesses II. Seth-her-khepeshef was formerly thought to be another son of Ramesses II. Biography Amun-her-khepeshef was the crown prince of Egypt for the first 25 years of Ramesses II's reign but eventually predeceased his father in Year 25 of his father's reign.Dodson & Hilton, p.173 Ramesses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gebel El-Silsila
Gebel el-Silsila or Gebel Silsileh ( ar, جبل السلسلة - Jabal al-Silsila or Ǧabal as-Silsila – "Chain of Mountains" or "Series of Mountains"; Egyptian: ẖny, Khenyt,Kitchen (1983). Kheny or Khenu – "The Place of Rowing"; German: Dschabal as-Silsila – "Ruderort", or "Ort des Ruderns" – "Place of Rowing"; Italian: Gebel Silsila – "Monte della Catena" – "Upstream Mountain Chain") is north of Aswan in Upper Egypt, where the cliffs on both sides close to the narrowest point along the length of the entire Nile. The location is between Edfu in the north towards Lower Egypt and Kom Ombo in the south towards Upper Egypt. The name ''Kheny'' (or sometimes ''Khenu'') means "The Place of Rowing". It was used as a major quarry site on both sides of the Nile from at least the 18th Dynasty to Greco-Roman times. Silsila is famous for its New Kingdom stelai and cenotaphs. Sandstone quarry During the 18th Dynasty the Egyptians switched from limestone to sandstone. At thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saqqara
Saqqara ( ar, سقارة, ), also spelled Sakkara or Saccara in English , is an Egyptian village in Giza Governorate, that contains ancient burial grounds of Egyptian royalty, serving as the necropolis for the ancient Egyptian capital, Memphis. Saqqara contains numerous pyramids, including the Step pyramid of Djoser, sometimes referred to as the Step Tomb, and a number of mastaba tombs. Located some south of modern-day Cairo, Saqqara covers an area of around . Saqqara contains the oldest complete stone building complex known in history, the Pyramid of Djoser, built during the Third Dynasty. Another sixteen Egyptian kings built pyramids at Saqqara, which are now in various states of preservation. High officials added private funeral monuments to this necropolis during the entire Pharaonic period. It remained an important complex for non-royal burials and cult ceremonies for more than 3,000 years, well into Ptolemaic and Roman times. North of the area known as Saqqara lie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
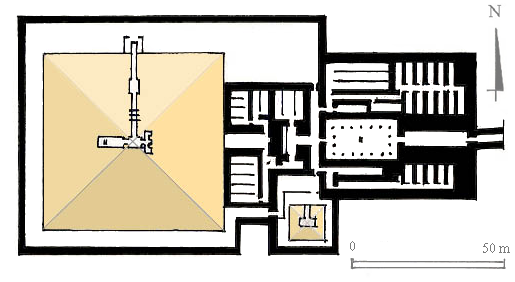
Pyramid Of Unas
The pyramid of Unas (Egyptian: ''Nfr swt Wnjs'' "Beautiful are the places of Unas") is a smooth-sided pyramid built in the 24th century BC for the Egyptian pharaoh Unas, the ninth and final king of the Fifth Dynasty. It is the smallest Old Kingdom pyramid, but significant due to the discovery of Pyramid Texts, spells for the king's afterlife incised into the walls of its subterranean chambers. Inscribed for the first time in Unas's pyramid, the tradition of funerary texts carried on in the pyramids of subsequent rulers, through to the end of the Old Kingdom, and into the Middle Kingdom through the Coffin Texts that form the basis of the ''Book of the Dead''. Unas built his pyramid between the complexes of Sekhemket and Djoser, in North Saqqara. Anchored to the valley temple at a nearby lake, a long causeway was constructed to provide access to the pyramid site. The causeway had elaborately decorated walls covered with a roof which had a slit in one section allowing light to e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)