|
Kezlev
Yevpatoria ( uk, Євпаторія, Yevpatoriia; russian: Евпатория, Yevpatoriya; crh, , , gr, Ευπατορία) is a city of regional significance in Western Crimea, north of Kalamita Bay. Yevpatoria serves as the administrative center of Yevpatoria Municipality, one of the districts (''raions'') into which Crimea is divided. It had a population of History Greek settlement The first recorded settlement in the area, called ''Kerkinitis'' (), was built by Greek colonists around 500 BCE. Along with the rest of the Crimea, Kerkinitis formed part of the dominions of King Mithridates VI Eupator ( BCE), from whose nickname, ''Eupator'' "of noble father" the city's modern name derives. Khanate period From roughly the 7th through the 10th centuries, Yevpatoria was a Khazar settlement; its name in Khazar language was probably ''Güzliev'' (literally "beautiful house"). It was later subject to the Cumans (Kipchaks), the Mongols and the Crimean Khanate. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the longest-lived of the Turkic khanates that succeeded the empire of the Golden Horde. Established by Hacı I Giray in 1441, it was regarded as the direct heir to the Golden Horde and to Desht-i-Kipchak. In 1783, violating the 1774 Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca (which had guaranteed non-interference of both Russia and the Ottoman Empire in the affairs of the Crimean Khanate), the Russian Empire annexed the khanate. Among the European powers, only France came out with an open protest against this act, due to the longstanding Franco-Ottoman alliance. Naming and geography Crimean khans, considering their state as the heir and legal successor of the Golden Horde and Desht-i Kipchak, called themselves khans of "the Great Horde, the Great State an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
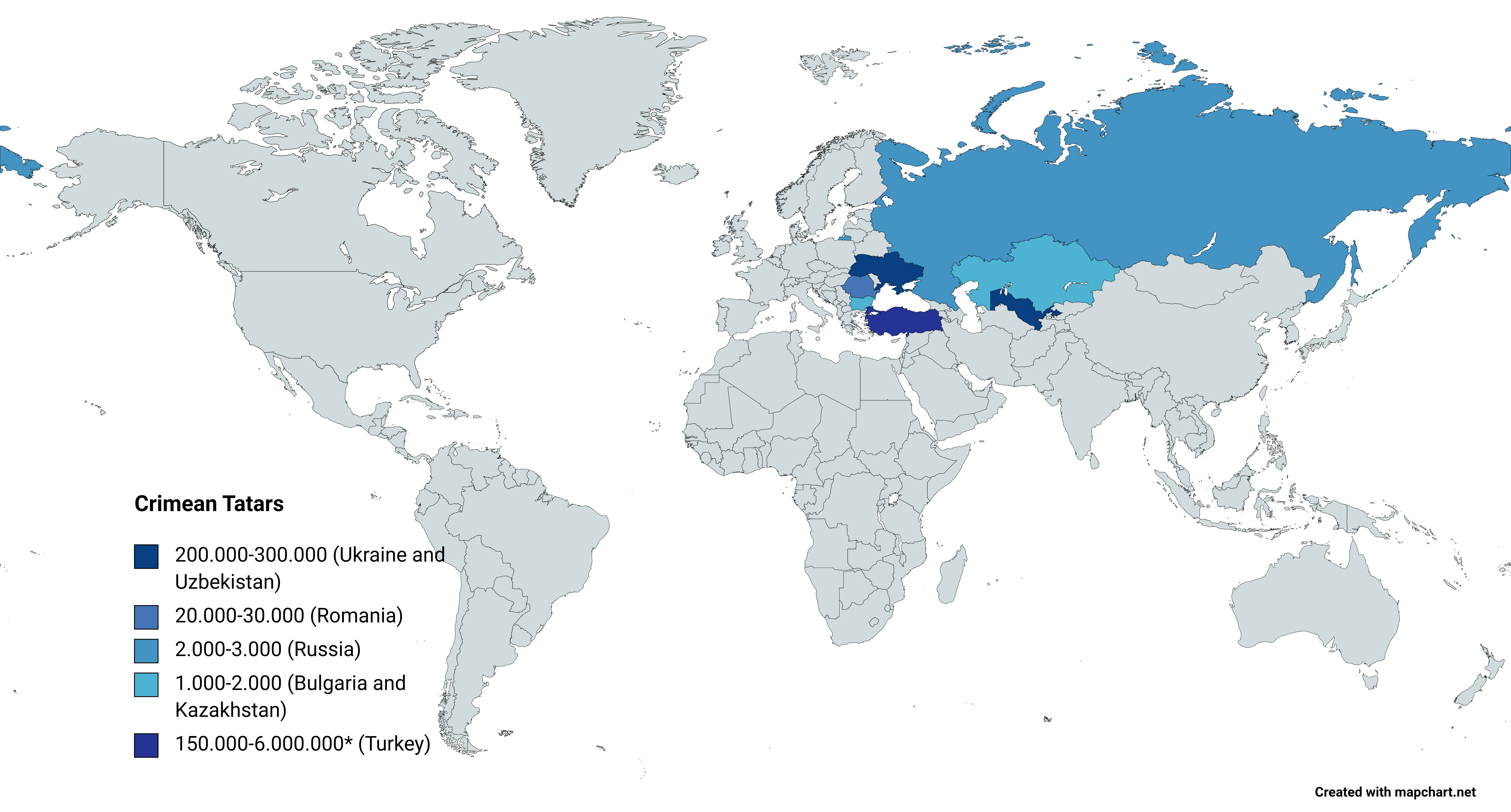
Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg , flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars , image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg , caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace , poptime = , popplace = , region1 = , pop1 = 3,500,000 6,000,000 , ref1 = , region2 = * , pop2 = 248,193 , ref2 = , region3 = , pop3 = 239,000 , ref3 = , region4 = , pop4 = 24,137 , ref4 = , region5 = , pop5 = 2,449 , ref5 = , region7 = , pop7 = 1,803 , ref7 = , region8 = , pop8 = 1,532 , ref8 = , region9 = *() , pop9 = 7,000(500–1,000) , ref9 = , region10 = Total , pop10 = 4.024.114 (or 6.524.1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yevpatoria Municipality
The Yevpatoria City Municipality ( uk, Євпаторійська міськрада, translit. ''Yevpatoriis'ka mis'krada'') is one of the 25 regions of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea, a territory recognized by almost all countries as part of Ukraine but occupied by Russia as the Republic of Crimea. The region is located on the western coast of Crimea on the Black Sea's shore. Its administrative center is the city of Yevpatoria. Population: Name The Yevpatoria City Municipality is also known by its two other native official names; in Russian as ''Evpatoriyskiy gorsovet'' (), and in Crimean Tatar as . Colloquially, the municipality is known as "the territory governed by the Yevpatoria City Council ( uk, Євпаторійська міська рада). History The Yevpatoria City Municipality was formed on February 11, 1963 when the territory of the Yevpatoria Raion was absorbed into the already existing Saky Raion. At that time, the Yevpatoria municipality was established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimean Sonnets
The Crimean Sonnets (''Sonety krymskie'') are a series of 18 Polish sonnets by Adam Mickiewicz, constituting an artistic telling of a journey through the Crimea. They were published in 1826, together with a cycle of love poems called "The Odessan Sonnets" (''Sonety Odeskie''), in a collection called "Sonnets" (''Sonety''). Importance ''The Crimean Sonnets'' is an expression of Mickiewicz's interest in the Orient, shared by many of the students of the University of Vilnius. Involuntarily residing in Russia, Mickiewicz left Odessa and went on a journey, which turned out to be a trek to another world, his first initiation into "the East". The Crimean Sonnets are romantic descriptions of oriental nature and culture of the East which show the despair of the poet—a pilgrim, an exile longing for the homeland, driven from his home by a violent enemy. ''The Crimean Sonnets'' is considered the first sonnet cycle in Polish literature and a significant example of early romanticism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Mickiewicz
Adam Bernard Mickiewicz (; 24 December 179826 November 1855) was a Polish poet, dramatist, essayist, publicist, translator and political activist. He is regarded as national poet in Poland, Lithuania and Belarus. A principal figure in Polish Romanticism, he is one of Poland's " Three Bards" ( pl, Trzej Wieszcze) and is widely regarded as Poland's greatest poet. He is also considered one of the greatest Slavic and European poets and has been dubbed a "Slavic bard". A leading Romantic dramatist, he has been compared in Poland and Europe to Byron and Goethe. He is known chiefly for the poetic drama '' Dziady'' (''Forefathers' Eve'') and the national epic poem '' Pan Tadeusz''. His other influential works include ''Konrad Wallenrod'' and ''Grażyna''. All these served as inspiration for uprisings against the three imperial powers that had partitioned the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth out of existence. Mickiewicz was born in the Russian-partitioned territories of the forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. The rise of the Russian Empire coincided with the decline of neighbouring rival powers: the Swedish Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Qajar Iran, the Ottoman Empire, and Qing dynasty, Qing China. It also held colonies in North America between 1799 and 1867. Covering an area of approximately , it remains the list of largest empires, third-largest empire in history, surpassed only by the British Empire and the Mongol Empire; it ruled over a population of 125.6 million people per the Russian Empire Census, 1897 Russian census, which was the only census carried out during the entire imperial period. Owing to its geographic extent across three continents at its peak, it featured great ethnic, linguistic, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hakham
''Hakham'' (or ''chakam(i), haham(i), hacham(i)''; he, חכם ', "wise") is a term in Judaism, meaning a wise or skillful man; it often refers to someone who is a great Torah scholar. It can also refer to any cultured and learned person: "He who says a wise thing is called a ''hakham'', even if he be not a Jew." Hence in Talmudic-Midrashic literature, wise gentiles are commonly called ' ("wise men of the nations of the world"). In Sephardic usage, ''hakham'' is a synonym for "rabbi". In ancient times ''Hakham'' as an official title is found as early as the first Sanhedrin, after the reconstruction of that body, when the Hadrianic religious persecutions had ceased. In addition to the nasi Simeon ben Gamliel, two other scholars stood at the head of the Sanhedrin, namely Nathan the Babylonian as '' Av Beit Din'' and Rabbi Meir as ''hakham''. Another ''hakham'' mentioned by name was Simon, the son of Judah the Prince, who after the death of his father officiated as ''hakham'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimean Karaites
The Crimean Karaites or Krymkaraylar (Crimean Karaim: Кърымкъарайлар, ''Qrımqaraylar'', singular къарай, ''qaray''; Trakai dialect: ''karajlar'', singular ''karaj''; he, קראי מזרח אירופה; crh, Qaraylar; ), also known as ''Karaims'' and ''Qarays'', are an ethnicity of Turkic-speaking adherents of Karaite Judaism in Central and Eastern Europe, especially in the territory of the old Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and Crimea. "Karaim" is a Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian, Polish and Lithuanian name for the community. Origins Turkic-speaking Karaite Jews (in the Crimean Tatar language, ''Qaraylar'') have lived in Crimea for centuries. Their origin is a matter of great controversy. Most modern scientists regard them as descendants of Karaite Jews who settled in Crimea and adopted a Kypchak language. Others view them as descendants of Khazar or Cuman, Kipchak converts to Karaite Judaism. Today, many Crimean Karaites reject ethnic Semitic or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eupatoria 04-14 Img16 Karaimskaya Street
Eupatoria may refer to: * Eupatoria or Yevpatoria Yevpatoria ( uk, Євпаторія, Yevpatoriia; russian: Евпатория, Yevpatoriya; crh, , , gr, Ευπατορία) is a city of regional significance in Western Crimea, north of Kalamita Bay. Yevpatoria serves as the administrative ..., a city of Crimea ** the Battle of Eupatoria, 1855 * Eupatoria (Pontus), an ancient city of Pontus * '' Agrimonia eupatoria'', common agrimony {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakhchysarai
Bakhchysarai ( crh, Bağçasaray, italic=yes; russian: Бахчисара́й; ua, Бахчисара́й; tr, Bahçesaray) is a town in Crimea, a territory recognized by a majority of countries as part of Ukraine and annexed by Russia as the Republic of Crimea. It is the administrative center of the Bakhchysarai Raion (district), as well as the former capital of the Crimean Khanate. Its main landmark is Hansaray, the only extant palace of the Crimean Khans, currently open to tourists as a museum. Population: Geography Bakhchysarai lies in a narrow valley of the river, about 30 Kilometers south-west of Simferopol. History The earliest known artifacts of human provenance found in the valley date from the Mesolithic period. Settlements have existed in the valley since Late Antiquity. The founding of Bakhchysarai was preceded by the Qırq Yer fortress (modern Çufut Qale), Salaçıq, and Eski Yurt — these have become incorporated into the urban area of modern Bakhchysar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimar Sinan
Mimar Sinan ( ota, معمار سينان, translit=Mi'mâr Sinân, , ) ( 1488–1490 – 17 July 1588) also known as Koca Mi'mâr Sinân Âğâ, ("Sinan Agha the Grand Architect" or "Grand Sinan") was the chief Ottoman architect ( tr, links=no, mimar) and civil engineer for sultans Suleiman the Magnificent, Selim II and Murad III. He was responsible for the construction of more than 300 major structures and other more modest projects, such as schools. His apprentices would later design the Sultan Ahmed Mosque in Istanbul and Stari Most in Mostar. The son of a stonemason, he received a technical education and became a military engineer. He rose rapidly through the ranks to become first an officer and finally a Janissary commander, with the honorific title of Sinan.Goodwin (2001), p. 87 He refined his architectural and engineering skills while on campaign with the Janissaries, becoming expert at constructing fortifications of all kinds, as well as military infrastructure p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |