|
Keynesian Cross
The Keynesian cross diagram is a formulation of the central ideas in Keynes' ''General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money''. It first appeared as a central component of macroeconomic theory as it was taught by Paul Samuelson in his textbook, '' Economics: An Introductory Analysis''. The Keynesian cross plots aggregate income (labelled as Y on the horizontal axis) and planned total spending or aggregate expenditure (labelled as AD on the vertical axis). Overview In the Keynesian cross diagram, the upward sloping blue line represents the aggregate expenditure for goods and services by all households and firms as a function of their income. The 45-degree line represents an aggregate supply curve which embodies the idea that, as long as the economy is operating at less than full employment, anything demanded will be supplied. Aggregate expenditure and aggregate income are measured by dividing the money value of all goods produced in the economy in a given year by a price index. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autarky
Autarky is the characteristic of self-sufficiency, usually applied to societies, communities, states, and their economic systems. Autarky as an ideal or method has been embraced by a wide range of political ideologies and movements, especially left-wing ideologies like African socialism, mutualism, war communism, communalism, swadeshi, syndicalism (especially anarcho-syndicalism), and left-wing populism, generally in an effort to build alternative economic structures or to control resources against structures a particular movement views as hostile. Conservative, centrist and nationalist movements have also adopted autarky in an attempt to preserve part of an existing social order or to develop a particular industry. Proponents of autarky have argued for national self-sufficiency to reduce foreign economic, political and cultural influences, as well as to promote international peace. Economists are generally supportive of free trade. There is a broad consensus among economist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Wolfram Demonstrations Project
The Wolfram Demonstrations Project is an organized, open-source collection of small (or medium-size) interactive programs called Demonstrations, which are meant to visually and interactively represent ideas from a range of fields. It is hosted by Wolfram Research, whose stated goal is to bring computational exploration to a large population. At its launch, it contained 1300 demonstrations but has grown to over 10,000. The site won a Parents' Choice Award in 2008. Technology The Demonstrations run in '' Mathematica'' 6 or above and in '' Wolfram CDF Player'' which is a free modified version of Wolfram's ''Mathematica'' and available for Windows, Linux and macOS and can operate as a web browser plugin. They typically consist of a very direct user interface to a graphic or visualization, which dynamically recomputes in response to user actions such as moving a slider, clicking a button, or dragging a piece of graphics. Each Demonstration also has a brief description of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IS–LM Model
IS–LM model, or Hicks–Hansen model, is a two-dimensional macroeconomic tool that shows the relationship between interest rates and assets market (also known as real output in goods and services market plus money market). The intersection of the "investment–saving" (IS) and "liquidity preference–money supply" (LM) curves models "general equilibrium" where supposed simultaneous equilibria occur in both the goods and the asset markets. Yet two equivalent interpretations are possible: first, the IS–LM model explains changes in national income when the price level is fixed in the short-run; second, the IS–LM model shows why an aggregate demand curve can shift. Hence, this tool is sometimes used not only to analyse economic fluctuations but also to suggest potential levels for appropriate stabilisation policies. The model was developed by John Hicks in 1937 and was later extended by Alvin Hansen, as a mathematical representation of Keynesian macroeconomic theory. Between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AD–AS Model
The AD–AS or aggregate demand–aggregate supply model is a macroeconomic model that explains price level and output (economics), output through the relationship of aggregate demand (AD) and aggregate supply (AS). It is based on the theory of John Maynard Keynes presented in his work ''The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money''. It is one of the primary simplified representations in the modern field of macroeconomics, and is used by a broad array of economists, from Libertarianism, libertarian, monetarist supporters of laissez-faire, such as Milton Friedman, to Post-Keynesian economics, post-Keynesian supporters of economic interventionism, such as Joan Robinson. Modeling The AD/AS model is used to illustrate the Keynesian economics, Keynesian model of the business cycle. Movements of the two curves can be used to predict the effects that various exogenous variable, exogenous events will have on two variables: real GDP and the price level. Furthermore, the model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiscal Multiplier
In economics, the fiscal multiplier (not to be confused with the money multiplier) is the ratio of change in national income arising from a change in government spending. More generally, the exogenous spending multiplier is the ratio of change in national income arising from any autonomous change in spending (including private investment spending, consumer spending, government spending, or spending by foreigners on the country's exports). When this multiplier exceeds one, the enhanced effect on national income may be called the multiplier effect. The mechanism that can give rise to a multiplier effect is that an initial incremental amount of spending can lead to increased income and hence increased consumption spending, increasing income further and hence further increasing consumption, etc., resulting in an overall increase in national income greater than the initial incremental amount of spending. In other words, an initial change in aggregate demand may cause a change in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagion began around September and led to the Wall Street stock market crash of October 24 (Black Thursday). It was the longest, deepest, and most widespread depression of the 20th century. Between 1929 and 1932, worldwide gross domestic product (GDP) fell by an estimated 15%. By comparison, worldwide GDP fell by less than 1% from 2008 to 2009 during the Great Recession. Some economies started to recover by the mid-1930s. However, in many countries, the negative effects of the Great Depression lasted until the beginning of World War II. Devastating effects were seen in both rich and poor countries with falling personal income, prices, tax revenues, and profits. International trade fell by more than 50%, unemployment in the U.S. rose to 23% and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
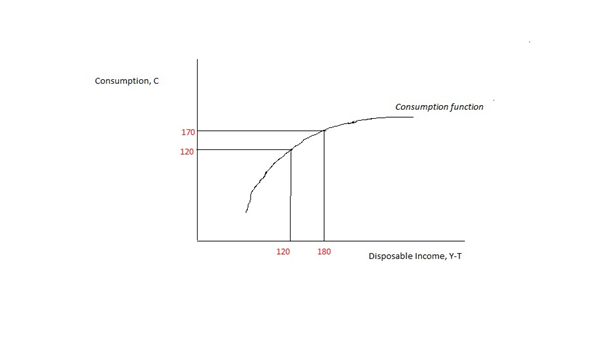
Marginal Propensity To Consume
In economics, the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is a metric that quantifies induced consumption, the concept that the increase in personal consumer spending (consumption) occurs with an increase in disposable income (income after taxes and transfers). The proportion of disposable income which individuals spend on consumption is known as propensity to consume. MPC is the proportion of additional income that an individual consumes. For example, if a household earns one extra dollar of disposable income, and the marginal propensity to consume is 0.65, then of that dollar, the household will spend 65 cents and save 35 cents. Obviously, the household cannot spend ''more'' than the extra dollar (without borrowing or using savings). If the extra money accessed by the individual gives more economic confidence, then the MPC of the individual may well exceed 1, as they may borrow or utilise savings. The MPC is higher in the case of poorer people than in rich. According to John Mayna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affine Function
In Euclidean geometry, an affine transformation or affinity (from the Latin, ''affinis'', "connected with") is a geometric transformation that preserves lines and parallelism, but not necessarily Euclidean distances and angles. More generally, an affine transformation is an automorphism of an affine space (Euclidean spaces are specific affine spaces), that is, a function which maps an affine space onto itself while preserving both the dimension of any affine subspaces (meaning that it sends points to points, lines to lines, planes to planes, and so on) and the ratios of the lengths of parallel line segments. Consequently, sets of parallel affine subspaces remain parallel after an affine transformation. An affine transformation does not necessarily preserve angles between lines or distances between points, though it does preserve ratios of distances between points lying on a straight line. If is the point set of an affine space, then every affine transformation on can be repre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Spirits (Keynes)
Animal spirits is a term used by John Maynard Keynes in his 1936 book '' The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money'' to describe the instincts, proclivities and emotions that ostensibly influence and guide human behavior, and which can be measured in terms of, for example, consumer confidence. Use by Keynes The original passage by Keynes reads: Earlier uses Philosophy and social science The notion of animal spirits has been described by René Descartes, Isaac Newton, and other scientists as how the notion of the vitality of the body is used. In one of his letters about light, Newton wrote that animated spirits very easily live in "the brain, nerves, and muscles, may become a convenient vessel to hold so subtil a spirit." These spirits, as described by Newton, are animated spirits of an ethereal nature, relating to life in the body. Later it became a concept that acquired a psychological content but was always thought of in connection with the life processes of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okun's Law
In economics, Okun's law is an empirically observed relationship between unemployment and losses in a country's production. It is named after Arthur Melvin Okun, who first proposed the relationship in 1962. The "gap version" states that for every 1% increase in the unemployment rate, a country's GDP will be roughly an additional 2% lower than its potential GDP. The "difference version" describes the relationship between quarterly changes in unemployment and quarterly changes in real GDP. The stability and usefulness of the law has been disputed. Imperfect relationship Okun's law may more accurately be called "Okun's rule of thumb" because it is an approximation based on empirical observation rather than a result derived from theory. Okun's law is approximate because factors other than employment, such as productivity, affect output. In Okun's original statement of his law, a 2% increase in output corresponds to a 1% decline in the rate of cyclical unemployment; a 0.5% increase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The General Theory Of Employment, Interest And Money
''The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money'' is a book by English economist John Maynard Keynes published in February 1936. It caused a profound shift in economic thought, giving macroeconomics a central place in economic theory and contributing much of its terminology – the " Keynesian Revolution". It had equally powerful consequences in economic policy, being interpreted as providing theoretical support for government spending in general, and for budgetary deficits, monetary intervention and counter-cyclical policies in particular. It is pervaded with an air of mistrust for the rationality of free-market decision making. Keynes denied that an economy would automatically adapt to provide full employment even in equilibrium, and believed that the volatile and ungovernable psychology of markets would lead to periodic booms and crises. The ''General Theory'' is a sustained attack on the classical economics orthodoxy of its time. It introduced the concepts of the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |