|
Ketil Trout (Iceland)
Ketil Thorkelsson (Old Norse: ), better known by his nickname Ketil Trout or Ketil Salmon (O.N.: ; Modern Icelandic: ) was a Norwegian military commander (''hersir'') of the late ninth century who settled in Iceland around 900 CE. He appears in ''Egils saga'', the ''Landnámabók'', and other Icelandic sources. Biography Ketil was the son of Hrafnhild (daughter of Ketil Trout of Hrafnista) and Thorkel, jarl of Namdalen. Ketil was a man of great wealth and a close friend and kinsman of Thorolf Kveldulfsson and his brother Skallagrim., ''Egil's Saga'', Chapter XXIII, pp. 62–63 With his wife Ingunn, Ketil had several children, including Storolf, Herjolf, Helgi, Vestar, and Hrafn Hængsson, the last of whom was one of the first lawspeakers. A place pivotal in the life of Ketil was an estate named Torgar,. The estate had passed from Ketil's uncle by marriage, Brynjolf,) to his son Bard "the White" Brynjolfsson (Ketil's first cousin). Bard, in turn, bequeathed the estate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their Viking expansion, overseas settlements and chronologically coincides with the Viking Age, the Christianization of Scandinavia and the consolidation of Scandinavian kingdoms from about the 7th to the 15th centuries. The Proto-Norse language developed into Old Norse by the 8th century, and Old Norse began to develop into the modern North Germanic languages in the mid-to-late 14th century, ending the language phase known as Old Norse. These dates, however, are not absolute, since written Old Norse is found well into the 15th century. Old Norse was divided into three dialects: Old West Norse, ''Old West Norse'' or ''Old West Nordic'' (often referred to as ''Old Norse''), Old East Norse, ''Old East Norse'' or ''Old East Nordic'', and ''Ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Cousin Once Removed
Most generally, in the lineal kinship system used in the English-speaking world, a cousin is a type of familial relationship in which two relatives are two or more familial generations away from their most recent common ancestor. Commonly, "cousin" refers to a first cousin – a relative of the same generation whose most recent common ancestor with the subject is a grandparent. Degrees and removals are separate measures used to more precisely describe the relationship between cousins. ''Degree'' measures the separation, in generations, from the most recent common ancestor(s) to a parent of one of the cousins (whichever is closest), while ''removal'' measures the difference in generations between the cousins themselves, relative to their most recent common ancestor(s). To illustrate usage, a second cousin is a cousin with a ''degree'' of two; there are three (not two) generations from the common ancestor(s). When the degree is not specified, first cousin is assumed. A cousin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th-century Icelandic People
The 9th century was a period from 801 ( DCCCI) through 900 ( CM) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Carolingian Renaissance and the Viking raids occurred within this period. In the Middle East, the House of Wisdom was founded in Abbasid Baghdad, attracting many scholars to the city. The field of algebra was founded by the Muslim polymath al-Khwarizmi. The most famous Islamic Scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal was tortured and imprisoned by Abbasid official Ahmad ibn Abi Du'ad during the reign of Abbasid caliph al-Mu'tasim and caliph al-Wathiq. In Southeast Asia, the height of the Mataram Kingdom happened in this century, while Burma would see the establishment of the major kingdom of Pagan. Tang China started the century with the effective rule under Emperor Xianzong and ended the century with the Huang Chao rebellions. While the Maya experienced widespread political collapse in the central Maya region, resulting in internecine warfare, the abandonment of cities, and a northward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viking Warriors
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden), who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9–22. They also voyaged as far as the Mediterranean, North Africa, Volga Bulgaria, the Middle East, and North America. In some of the countries they raided and settled in, this period is popularly known as the Viking Age, and the term "Viking" also commonly includes the inhabitants of the Scandinavian homelands as a collective whole. The Vikings had a profound impact on the early medieval history of Scandinavia, the British Isles, France, Estonia, and Kievan Rus'. Expert sailors and navigators aboard their characteristic longships, Vikings established Norse settlements and governments in the British Isles, the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Greenland, Normandy, and the Baltic coast, as well as alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hof, Iceland
Hof, () in Öræfi, is a cluster of farms in the municipality of Sveitarfélagið Hornafjörður in southeast Iceland, close to Vatnajökull glacier, and twenty two kilometres south of Skaftafell in Vatnajökull National Park. It is on the Route 1 southwest of Höfn, in the narrow strip between the sea coast and the glacier. It is 9.14 km WSW of the centre of Öræfajökull volcano. A notable building in Hof is a turf church, which was built in 1883 and is the youngest turf church in Iceland. Since 1951, it belongs to the National Museum of Iceland National may refer to: Common uses * Nation or country ** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen Places in the United States * National, Maryland, ce .... References Populated places in Eastern Region (Iceland) {{Iceland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markarfljót
Markarfljót () is a river in the south of Iceland. It is approximately 100 kilometers long. The Markarfljót rises in the Rauðafossafjöll massif, east of the volcano Hekla. The main sources for the river are the glaciers Mýrdalsjökull and Eyjafjallajökull. It flows through narrow gorges in the mountainous area between the glaciers Tindfjallajökull and Torfajökull, then spreads in the wide sandur plains at Iceland's south coast, near Þórsmörk. The Markarfljót takes its course first north, then west of Þórsmörk and finally empties into the Atlantic west of Eyjafjallajökull. One of the Markarfljót's tributaries is the river Krossá , flowing through Þórsmörk, which is notorious for sudden changes in its water level. The highest discharge ever measured in the Markarfljót was in 1967, during the Steinholt jökulhlaup A jökulhlaup ( ) (literally "glacial run") is a type of glacial outburst flood. It is an Icelandic term that has been adopted in glac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Þjórsá
Þjórsá () is Iceland's longest river at 230 kilometers (about 143 miles). It is in the south of the island. Þjórsá is a glacier river and has its source on the glacier Hofsjökull. It flows out through narrow gorges in the highlands of Iceland. Further downstream, another river, the Tungnaá, flows into it (see also Háifoss), before it enters the lowlands. There it passes the valley of Þjórsárdalur (Thjorsardalur) where the historical farm of Stöng is located. In the lowlands it flows along the eastern border of the Great Þjórsá Lava. In the middle of the now rather wide river, there is a big island called ''Árnes'', where there used to be a '' Þing''. The administrative unit of Árnessýsla was named after it. The ''hringvegur'' (Road No.1) traverses the river via a bridge between Selfoss and Hella. Some kilometers to the southwest the river flows into the Atlantic Ocean. 'Á' signifies river while 'þjór' means bull and is cognate to Danish - tyr, Swedish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ytri-Rangá
Ytri-Rangá () is a river in Iceland popular for salmon fishing. It is over long, rising north of Hekla, passing to the west of Hella ''Hella'' is an American slang term that originated in the San Francisco Bay Area. It is used as an intensifying adverb such as in "hella bad" or "hella good" and was eventually added to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' in 2002. It is possibl ... before, further south, joining with the river Þverá to become the Hólsá. The designation ''Ytri'', "outer", distinguished it from the ''Eystri'' or East Rangá, an affluent of the Þverá. References Rivers of Iceland {{Iceland-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
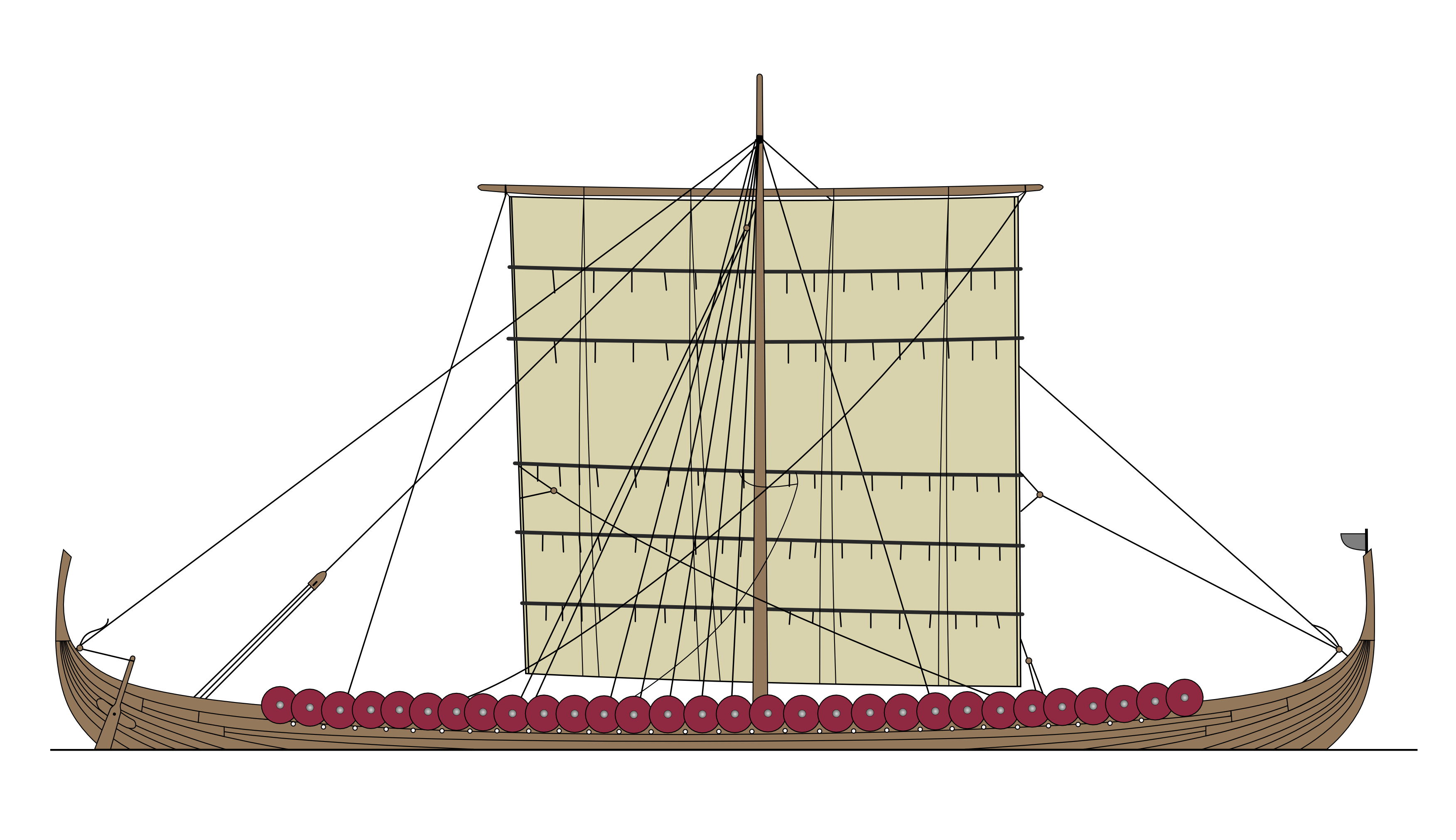
Longship
Longships were a type of specialised Scandinavian warships that have a long history in Scandinavia, with their existence being archaeologically proven and documented from at least the fourth century BC. Originally invented and used by the Norsemen (commonly known as the Vikings) for commerce, exploration, and warfare during the Viking Age, many of the longship's characteristics were adopted by other cultures, like Anglo-Saxons, and continued to influence shipbuilding for centuries. The longship's design evolved over many centuries, and continuing up until the sixth century with clinker-built ships like Nydam. The longship appeared in its complete form between the ninth and 13th centuries. The character and appearance of these ships have been reflected in Scandinavian boatbuilding traditions to the present day. The particular skills and methods employed in making longships are still used worldwide, often with modern adaptations. They were all made out of wood, with cloth sails ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harald I Of Norway
Harald Fairhair no, Harald hårfagreModern Icelandic: ( – ) was a Norwegian king. According to traditions current in Norway and Iceland in the eleventh and twelfth centuries, he reigned from 872 to 930 and was the first King of Norway. Supposedly, two of his sons, Eric Bloodaxe and Haakon the Good, succeeded Harald to become kings after his death. Much of Harald's biography is uncertain. A couple of praise poems by his court poet Þorbjörn Hornklofi survive in fragments, but the extant accounts of his life come from sagas set down in writing around three centuries after his lifetime. His life is described in several of the Kings' sagas, none of them older than the twelfth century. Their accounts of Harald and his life differ on many points, but it is clear that in the twelfth and thirteenth centuries Harald was regarded as having unified Norway into one kingdom. Since the nineteenth century, when Union between Sweden and Norway, Norway was in a personal union with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordland
Nordland (; smj, Nordlánnda, sma, Nordlaante, sme, Nordlánda, en, Northland) is a county in Norway in the Northern Norway region, the least populous of all 11 counties, bordering Troms og Finnmark in the north, Trøndelag in the south, Norrbotten County in Sweden to the east, Västerbotten County to the south-east, and the Atlantic Ocean (Norwegian Sea) to the west. The county was formerly known as ''Nordlandene amt''. The county administration is in the town of Bodø. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen has been administered from Nordland since 1995. In the southern part of the county is Vega, listed on the UNESCO World Heritage Site list. Districts The county is divided into traditional districts. These are Helgeland in the south (south of the Arctic Circle), Salten in the centre, and Ofoten in the north-east. In the north-west lie the archipelagoes of Lofoten and Vesterålen. Geography Nordland is located along the northwestern coast of the Scandinavian pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brønnøy
Brønnøy is a municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is part of the Helgeland region. The administrative centre and commercial centre of the municipality is the town of Brønnøysund. A secondary centre is the village of Hommelstø. Other villages include Tosbotn, Lande, Trælnes, and Indreskomo. The Brønnøysund Register Centre is an important employer in Brønnøy. Also, one of the largest limestone mines in Northern Europe is located in the municipality. Brønnøysund Airport, Brønnøy is located near the town of Brønnøysund. The municipality is the 107th largest by area out of the 356 municipalities in Norway. Brønnøy is the 132nd most populous municipality in Norway with a population of 7,777. The municipality's population density is and its population has increased by 0% over the previous 10-year period. General information The municipality of Brønnøy was established on 1 January 1838 (see formannskapsdistrikt law). On 1 October 1875 the eastern d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |