|
Kerman Seljuk Sultanate
The Kerman Seljuk Sultanate (Persian: سلجوقیان کرمان Saljūqiyān-i Kerman) was a Persianate Sunni Muslim state, established in the parts of Kerman and Makran which had been conquered from the Buyid dynasty by the Seljuk Empire which was established by the Seljuk dynasty, which was of Oghuz Turkic origin. The Founder of this dynasty, Emadeddin Kara Arslan Ahmad Qavurt who succeeded the ruler of this dynasty after the surrender of the ruler of Buyyids, Abu Kalijar Marzuban. For first time in this period, an independent state was formed in Kerman; eventually, after 150 years, with the invasion of the Ghuzz leader Malik Dinar, the Kerman Seljuk Sultanate fell. The government is the first powerful local government in the Kerman and Makran region, which, in addition to political and security stability, could create economic prosperity in the provinces. It was during this period that the Silk Road burgeoned with the flourishing of the ports of Tiz, Hormuz and Kish, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with '' de jure'' ("by law"), which refers to things that happen according to official law, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. History In jurisprudence, it mainly means "practiced, but not necessarily defined by law" or "practiced or is valid, but not officially established". Basically, this expression is opposed to the concept of "de jure" (which means "as defined by law") when it comes to law, management or technology (such as standards) in the case of creation, development or application of "without" or "against" instructions, but in accordance with "with practice". When legal situations are discussed, "de jure" means "expressed by law", while "de facto" means action or what is practiced. Similar expressions: "essentially", "unofficial", " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oghuz Turks
The Oghuz or Ghuzz Turks (Middle Turkic: ٱغُز, ''Oγuz'', ota, اوغوز, Oġuz) were a western Turkic people that spoke the Oghuz branch of the Turkic language family. In the 8th century, they formed a tribal confederation conventionally named the Oghuz Yabgu State in Central Asia. The name ''Oghuz'' is a Common Turkic word for "tribe". Byzantine sources call the Oghuz the Uzes (Οὐ̑ζοι, ''Ouzoi''). By the 10th century, Islamic sources were calling them Muslim Turkmens, as opposed to Tengrist or Buddhist. By the 12th century, this term had passed into Byzantine usage and the Oghuzes were overwhelmingly Muslim. The term "Oghuz" was gradually supplanted among the Turks themselves by the terms ''Turkmen'' and '' Turcoman'', ( ota, تركمن, Türkmen or ''Türkmân'') from the mid-10th century on, a process which was completed by the beginning of the 13th century. The Oghuz confederation migrated westward from the Jeti-su area after a conflict with the Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khaganate
A khaganate or khanate was a polity ruled by a khan, khagan, khatun, or khanum. That political territory was typically found on the Eurasian Steppe and could be equivalent in status to tribal chiefdom, principality, kingdom or empire. Mongol-ruled khanates Chagatai Khanate (1226–1347) After Genghis Khan established appanages for his family in the Mongol Empire during his rule (1206–1227), his sons, daughters, and grandsons inherited separate sections of the empire. The Mongol Empire and Mongolian khanates that emerged from those appanages are listed below. In 1226, the second son of Genghis Khan, Chagatai Khan established the Chagatai Khanate. At its height in the late 13th century, the khanate extended from the Amu Darya south of the Aral Sea to the Altai Mountains in the border of modern-day Mongolia and China, roughly corresponding to the defunct Qara Khitai Empire. Initially the rulers of the Chagatai Khanate recognized the supremacy of the Great Khan, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yabghu
Yabghu ( otk, 𐰖𐰉𐰍𐰆, yabγu,Entr"𐰖𐰉𐰍𐰆 [yabγuйабғұ"in "Ethno-Cultural Dictionary" ''Türik Bitig'' ), also rendered as Jabgu, Djabgu or Yabgu, was a state office in the early Turkic peoples">Turkic states, roughly equivalent to viceroy. The title carried autonomy in different degrees, and its links with the central authority of Khagan varied from economical and political subordination to superficial political deference. The title had also been borne by Turkic princes in the upper Oxus region in post-Hephthalite times. The position of Yabgu was traditionally given to the second highest member of a ruling clan ( Ashina), with the first member being the Kagan himself. Frequently, Yabgu was a younger brother of the ruling Kagan, or a representative of the next generation, called Shad (blood prince). Mahmud Kashgari defined the title Yabgu as "position two steps below Kagan", listing heir apparent Shad a step above Yabgu.Golden P.B., "Khazar studies", Buda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aral Sea
The Aral Sea ( ; kk, Арал теңізі, Aral teñızı; uz, Орол денгизи, Orol dengizi; kaa, Арал теңизи, Aral teńizi; russian: Аральское море, Aral'skoye more) was an endorheic lake lying between Kazakhstan (Aktobe and Kyzylorda Regions) in the north and Uzbekistan (Karakalpakstan autonomous region) in the south which began shrinking in the 1960s and had largely dried up by the 2010s. The name roughly translates as "Sea of Islands", referring to over 1,100 islands that had dotted its waters. In the Mongolic and Turkic languages, ''aral'' means "island, archipelago". The Aral Sea drainage basin encompasses Uzbekistan and parts of Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, Afghanistan, and Iran. Formerly the fourth largest lake in the world with an area of , the Aral Sea began shrinking in the 1960s after the rivers that fed it were diverted by Soviet irrigation projects. By 2007, it had declined to 10% of its original size, splitt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia, south of the fertile plains of Southern Russia in Eastern Europe, and north of the mountainous Iranian Plateau of Western Asia. It covers a surface area of (excluding the highly saline lagoon of Garabogazköl to its east) and a volume of . It has a salinity of approximately 1.2% (12 g/L), about a third of the salinity of average seawater. It is bounded by Kazakhstan to the northeast, Russia to the northwest, Azerbaijan to the southwest, Iran to the south, and Turkmenistan to the southeast. The sea stretches nearly from north to south, with an average width of . Its gross coverage is and the surface is about below sea level. Its main freshwater Inflow (hydrology), inflow, Europe's longest river, the Volga, enters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kınık (tribe)
Qiniq ( az, Qınıq; tr, Kınık; tk, Gynyk; fa, قنق) also spelled Qïnïq, Qynyk or Qynyq, was an Oghuz Turkic (or Turkmen) tribe. Oghuz tribes Oghuz Turks were a branch of Turkic peoples. In the early Medieval Ages, most of them were nomads and their political structure was tribal. There were 22 or 24 Oghuz tribes. The tribes were listed in a number of medieval books with Islamic sources calling Muslim Oghuzes as Turkmen by the 10th century. They were also mentioned in Oghuz legend. According to the myth, there were 24 tribes in two main groups. Each group was represented by three brothers and each brother was supposed to have four sons. In this classification Qiniq tribe is the descendant of Deniz Khan who in turn was in the group of Üçok. According to Islam Encyclopaedia, Kınık means "Great everywhere". In the 11th-century compendium of Turkic languages Dīwānu l-Luġat al-Turk, produced by Mahmud of Kashgar, the Qiniq tribe is listed first. However, in the lis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad-Shah Ibn Bahram-Shah
Muhammad-Shah II was the last Seljuk amir of Kerman, from 1183 until 1186.Bosworth, p. 174 Biography The son of Bahram-Shah, Muhammad-Shah succeeded his uncle Turan-Shah to the throne of Kerman in 1183. By the time of his ascension Kerman had been overrun by bands of Ghuzz Turks. Their devastation of the province had made the city of Bardasir virtually uninhabitable, so Muhammad-Shah made Bam his capital. By 1186, however, Muhammad-Shah been unable to handle the Ghuzz, and he decided to abandon Bam and departed from Kerman. The Ghuzz chief Malik Dinar quickly seized control of Kerman in his place. Muhammad-Shah at first hoped to receive foreign assistance to reacquire Kerman, and traveled to Fars and Iraq requesting help. He also sought for aid from the Khwarezmshah Ala ad-Din Tekish. Eventually, however, he realized that he could get no assistance in recovering Kerman. He made his way to the Ghurid Empire The Ghurid dynasty (also spelled Ghorids; fa, دودمان غور ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
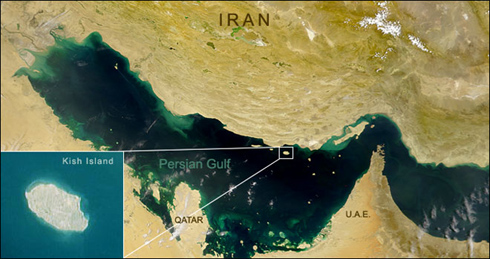
Kish Island
Kish ( fa, کیش ) is a resort island in Bandar Lengeh County, Hormozgān Province, off the southern coast of Iran in the Persian Gulf. Owing to its free trade zone status, the island is touted as a consumer's paradise, with numerous malls, shopping centres, tourist attractions, and resort hotels. It has an estimated population of almost 40,000 residents and about 1 million visitors annually. Kish Island is one of the most-visited vacation destinations in the Middle East, after Dubai and Sharm el-Sheikh. Tourists from many countries for which Iran typically requires a visa, who wish to enter Kish Free Zone, are exempt from having to obtain a visa. For those travelers, travel permits are issued on arrival by Kish officials and are valid for 14 days. History Kish Island has been mentioned in history variously as Kamtina, Arakia ( grc, Αρακία), Arakata, and Ghiss. Kish Island's strategic geographic location served as a way-station and link for the ancient Assyrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ormuz
The Kingdom of Ormus (also known as Hormoz; fa, هرمز; pt, Ormuz) was located in the eastern side of the Persian Gulf and extended as far as Bahrain in the west at its zenith. The Kingdom was established in 11th century initially as a dependency of the Kerman Seljuk Sultanate, and later as an autonomous tributary of the Salghurids and the Ilkhanate of Iran. In its last phase Ormus became a client state of the Portuguese Empire in the East. Most of its territory was eventually annexed by the Safavid Empire in the 17th century. The monarchy received its name from the fortified port city which served as its capital. It was one of the most important ports in the Middle East at the time as it controlled seaway trading routes through the Persian Gulf to China, India, and East Africa. This port was originally located on the southern coast of Iran to the east of the Strait of Hormuz, near the modern city of Minab, and was later relocated to the Island of Jarun which came to be know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the East and West. The name "Silk Road", first coined in the late 19th century, has fallen into disuse among some modern historians in favor of Silk Routes, on the grounds that it more accurately describes the intricate web of land and sea routes connecting East and Southeast Asia, the Indian subcontinent, Central Asia, the Middle East, East Africa and Europe. The Silk Road derives its name from the highly lucrative trade of silk textiles that were produced almost exclusively in China. The network began with the Han dynasty's expansion into Central Asia around 114 BCE, which largely pacified the once untamed region. Imperial envoy Zhang Qian was commissioned to explore the unknown lands beyond the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |