|
Kentucky Cave Wars
Mammoth Cave National Park is an American national park in west-central Kentucky, encompassing portions of Mammoth Cave, the longest cave system known in the world. Since the 1972 unification of Mammoth Cave with the even-longer system under Flint Ridge to the north, the official name of the system has been the Mammoth–Flint Ridge Cave System. The park was established as a national park on July 1, 1941, a World Heritage Site on October 27, 1981, an international Biosphere Reserve on September 26, 1990 and an International Dark Sky Park on October 28, 2021. The park's are located primarily in Edmonson County, with small areas extending eastward into Hart and Barren counties. The Green River runs through the park, with a tributary called the Nolin River feeding into the Green just inside the park. Mammoth Cave is the world's longest known cave system with more than of surveyed passageways, which is nearly twice as long as the second-longest cave system, Mexico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmonson County, Kentucky
Edmonson County is a county located in the south central portion of the U.S. state of Kentucky. As of the 2020 census, the population was 12,126. Its county seat is Brownsville. The county was formed in 1825 and named for Captain John "Jack" Edmonson (1764–1813), who was killed at the Battle of Frenchtown during the War of 1812. This is a dry county where the sale of alcohol is prohibited. Edmonson County is included in the Bowling Green, Kentucky Metropolitan Statistical Area. History Edmonson County was established on January 12, 1825, from land given by Grayson, Hart and Warren counties. A courthouse built in 1873 replaced a former structure rendered unfit when its floor collapsed. Geography According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which is land and (1.7%) is water. Adjacent counties * Grayson County (north) * Hart County (east) * Barren County (southeast) * Warren County (southwest) * Butler County (west) National protected ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippian Age
The Mississippian ( , also known as Lower Carboniferous or Early Carboniferous) is a subperiod in the geologic timescale or a subsystem of the geologic record. It is the earlier of two subperiods of the Carboniferous period lasting from roughly 358.9 to 323.2 million years ago. As with most other geochronologic units, the rock beds that define the Mississippian are well identified, but the exact start and end dates are uncertain by a few million years. The Mississippian is so named because rocks with this age are exposed in the Mississippi Valley. The Mississippian was a period of marine transgression in the Northern Hemisphere: the sea level was so high that only the Fennoscandian Shield and the Laurentian Shield were dry land. The cratons were surrounded by extensive delta systems and lagoons, and carbonate sedimentation on the surrounding continental platforms, covered by shallow seas. In North America, where the interval consists primarily of marine limestones, it is treate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cedar Sink
Cedar Sink is a vertical-walled large depression, or sinkhole, in the ground, that is located in Edmonson County, Kentucky Edmonson County is a county located in the south central portion of the U.S. state of Kentucky. As of the 2020 census, the population was 12,126. Its county seat is Brownsville. The county was formed in 1825 and named for Captain John "Jack" E ... and contained within and managed by Mammoth Cave National Park. The sinkhole measures from the top sandstone plateau to the bottom of the sink and was caused by collapse of the surface soil. The landscape is karst topography, which means the region is influenced by the dissolution of soluble rocks. Sinkholes, caves, and Sinkhole, dolines typically characterize these underground drainage systems. Cedar Sink has a bottom area of about and has more fertile soil compared to the ridgetops. Geomorphology Rock age The rocks of Cedar Sink and the surrounding area are from the Mississippian (geology), Mississippian (al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinkhole
A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are locally also known as ''vrtače'' and shakeholes, and to openings where surface water enters into underground passages known as ''ponor'', swallow hole or swallet. A ''cenote'' is a type of sinkhole that exposes groundwater underneath. A ''sink'' or ''stream sink'' are more general terms for sites that drain surface water, possibly by infiltration into sediment or crumbled rock. Most sinkholes are caused by karst processes – the chemical dissolution of carbonate rocks, collapse or suffosion processes. Sinkholes are usually circular and vary in size from tens to hundreds of meters both in diameter and depth, and vary in form from soil-lined bowls to bedrock-edged chasms. Sinkholes may form gradually or suddenly, and are found worldwide. Formation Natural processes Sinkholes may capture surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
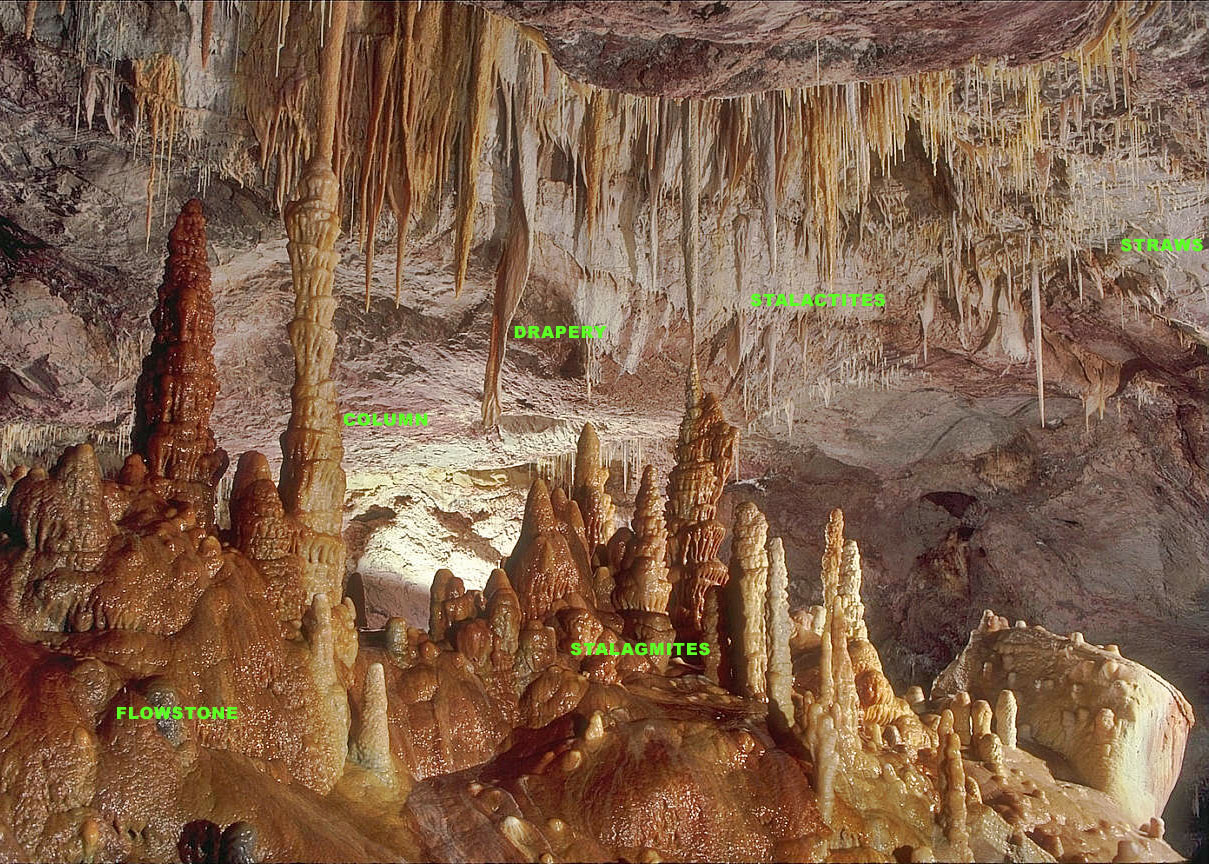
Stalagmite
A stalagmite (, ; from the Greek , from , "dropping, trickling") is a type of rock formation that rises from the floor of a cave due to the accumulation of material deposited on the floor from ceiling drippings. Stalagmites are typically composed of calcium carbonate, but may consist of lava, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rats). The corresponding formation hanging down from the ceiling of a cave is a stalactite. Mnemonics have been developed for which word refers to which type of formation; one is that ''stalactite'' has a C for "ceiling", and ''stalagmite'' has a G for "ground", another is that, as with ants in the pants, the mites go up and the tights (tites) come down. Formation and type Limestone stalagmites The most common stalagmites are speleothems, which usually form in limestone caves. Stalagmite formation occurs only under certain pH conditions within the cavern. They form through deposition of calcium carbonate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stalactite
A stalactite (, ; from the Greek 'stalaktos' ('dripping') via ''stalassein'' ('to drip') is a mineral formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves, hot springs, or man-made structures such as bridges and mines. Any material that is soluble and that can be deposited as a colloid, or is in suspension, or is capable of being melted, may form a stalactite. Stalactites may be composed of lava, minerals, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rats). A stalactite is not necessarily a speleothem, though speleothems are the most common form of stalactite because of the abundance of limestone caves. The corresponding formation on the floor of the cave is known as a stalagmite. Mnemonics have been developed for which word refers to which type of formation; one is that ''stalactite'' has a C for "ceiling", and ''stalagmite'' has a G for "ground". Another example is that ''stalactites'' "hang on ''T''ight" and ''stalagmites'' "''M''ight grow up" � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Girkin Formation
The Girkin Formation is a geologic formation located in the Chester Escarpment of central Kentucky, USA. It comprises a level of Mammoth Cave and lies above the Ste. Genevieve Limestone and St. Louis Limestone and below the Big Clifty Sandstone in that area. The Girkin is a limestone Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ... Mississippian in age. Members of the Girkin are as follows in descending order: * Beech Creek Member * Elwren Member * Reelsville Member * Sample Member * Beaver Bend Member * Bethel Member * Paoli Member References Geologic formations of Kentucky {{US-geologic-formation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratigraphic
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers (strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks. Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithostratigraphy (lithologic stratigraphy), biostratigraphy (biologic stratigraphy), and chronostratigraphy (stratigraphy by age). Historical development Catholic priest Nicholas Steno established the theoretical basis for stratigraphy when he introduced the law of superposition, the principle of original horizontality and the principle of lateral continuity in a 1669 work on the fossilization of organic remains in layers of sediment. The first practical large-scale application of stratigraphy was by William Smith in the 1790s and early 19th century. Known as the "Father of English geology", Smith recognized the significance of strata or rock layering and the importance of fossil markers for correlating strata; he created the first geologic map o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammoth Cave 01 - 1887
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus'', one of the many genera that make up the order of trunked mammals called proboscideans. The various species of mammoth were commonly equipped with long, curved tusks and, in northern species, a covering of long hair. They lived from the Pliocene epoch (from around 5 million years ago) into the Holocene at about 4,000 years ago, and various species existed in Africa, Europe, Asia, and North America. They were members of the family Elephantidae, which also contains the two genera of modern elephants and their ancestors. Mammoths are more closely related to living Asian elephants than African elephants. The oldest representative of ''Mammuthus'', the South African mammoth (''M. subplanifrons''), appeared around 5 million years ago during the early Pliocene in what is now southern and eastern Africa. Descendant species of these mammoths moved north and continued to propagate into numerous subsequent speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caprock
Caprock or cap rock is a more resistant rock type overlying a less resistant rock type,Kearey, Philip (2001). ''Dictionary of Geology'', 2nd ed., Penguin Reference, London, New York, etc., p. 41.. . analogous to an upper crust on a cake that is harder than the underlying layer. Description The Niagara Escarpment, over which Niagara Falls flows, is an example of a scarp or escarpment. At Niagara Falls, the caprock is the riverbed above the falls, and is what prevents the river from eroding the face of the falls very quickly. In the photo, the dark thin layer in the foreground where water is not yet running, is the caprock. The Niagara caprock is made of dolomitic limestone. Other common types of caprock are sandstone and mafic rock. In processes such as scarp retreat, the caprock controls the rate of erosion of the scarp. As the softer rock is cut away, periodically the caprock shears off. Caprock is also found in salt domes and on the top of mesa formations. Petroleum In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karst
Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves. It has also been documented for more weathering-resistant rocks, such as quartzite, given the right conditions. Subterranean drainage may limit surface water, with few to no rivers or lakes. However, in regions where the dissolved bedrock is covered (perhaps by debris) or confined by one or more superimposed non-soluble rock strata, distinctive karst features may occur only at subsurface levels and can be totally missing above ground. The study of ''paleokarst'' (buried karst in the stratigraphic column) is important in petroleum geology because as much as 50% of the world's hydrocarbon reserves are hosted in carbonate rock, and much of this is found in porous karst systems. Etymology The English word ''karst'' was borrowed from German in the late 19th century, which entered German much earlier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Clifty Sandstone
The Big Clifty Sandstone is a geologic formation in Illinois and Kentucky. It is a subunit of the Golconda Formation in Kentucky and is correlative with the Fraileys Shale to which it grades to in southern Illinois. The Big Clifty and Golconda are part of the Chesterian Series of late Mississippian age. The Big Clifty Sandstone was deposited in deltaic to marginal marine environment by the paleo Michigan River which in modern directions flowed south from the Canadian shield, the sediment source, and then westward depositing sediment across Illinois, Kentucky, and Indiana, as the Big Clifty Formation of the Stephensport Group. At Mammoth Cave National Park the Big Clifty overlies the Girkin Formation, the uppermost of three cave forming carbonate formations which the Mammoth-Flint Ridge cave system spans.Palmer, A.N., 1981, Geologic Guide to Mammoth Cave National Park: Teaneck, N.J., Zephyrus Press, 210 p. Below the Girkin Formation are the Ste. Genevieve Limestone, and the St. Lou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



.jpg)