|
Kentrophoridae
''Kentrophoros'' is a genus of ciliates in the class Karyorelictea. Ciliates in this genus lack a distinct oral apparatus and depend primarily on symbiotic bacteria for their nutrition. Systematics ''Kentrophoros'' is the sole genus in the family Kentrophoridae Jankowski 1980. The type species of the genus is ''K. fasciolatus'' Sauerbrey 1928, first described from the Bay of Kiel. Synonyms are ''Centrophorus'' Kahl 1931 (an illegitimate synonym because the name was already used for a genus of sharks) and ''Centrophorella'' Kahl 1935. Fifteen species of ''Kentrophoros'' have been formally described, although several of these names may be synonyms for the same species. Description The ciliates are long and ribbon-shaped, like other karyorelictean ciliates that live in the marine interstitial habitat. In some species, the cell body is folded or involuted into a tube or more elaborate shapes. The ventral side is ciliated, while the dorsal side is mostly unciliated except for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karyorelictea
Karyorelictea is a class of ciliates in the subphylum Postciliodesmatophora. Most species are members of the microbenthos community, that is, microscopic organisms found in the marine interstitial habitat, though one genus, ''Loxodes'', is found in freshwater. The majority of karyorelict taxa have not been cultivated in the laboratory, although clonal lines of ''Loxodes'' have been developed. Systematics According to Lynn (2008), the Karyorelictea class is divided into three orders: * Loxodida, containing the families Cryptopharyngidae and Loxodidae; * Protoheterotrichida, containing the families Aveliidae and Geleiidae; * Protostomatida, containing the families Kentrophoridae and Trachelocercidae. These three orders were defined morphologically, and have been confirmed with molecular phylogenetics. An additional family, Wilbertomorphidae, is of uncertain affiliation and has not been assigned to an order. Nuclear dimorphism All ciliates, including karyorelicteans, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kentrophoridae
''Kentrophoros'' is a genus of ciliates in the class Karyorelictea. Ciliates in this genus lack a distinct oral apparatus and depend primarily on symbiotic bacteria for their nutrition. Systematics ''Kentrophoros'' is the sole genus in the family Kentrophoridae Jankowski 1980. The type species of the genus is ''K. fasciolatus'' Sauerbrey 1928, first described from the Bay of Kiel. Synonyms are ''Centrophorus'' Kahl 1931 (an illegitimate synonym because the name was already used for a genus of sharks) and ''Centrophorella'' Kahl 1935. Fifteen species of ''Kentrophoros'' have been formally described, although several of these names may be synonyms for the same species. Description The ciliates are long and ribbon-shaped, like other karyorelictean ciliates that live in the marine interstitial habitat. In some species, the cell body is folded or involuted into a tube or more elaborate shapes. The ventral side is ciliated, while the dorsal side is mostly unciliated except for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
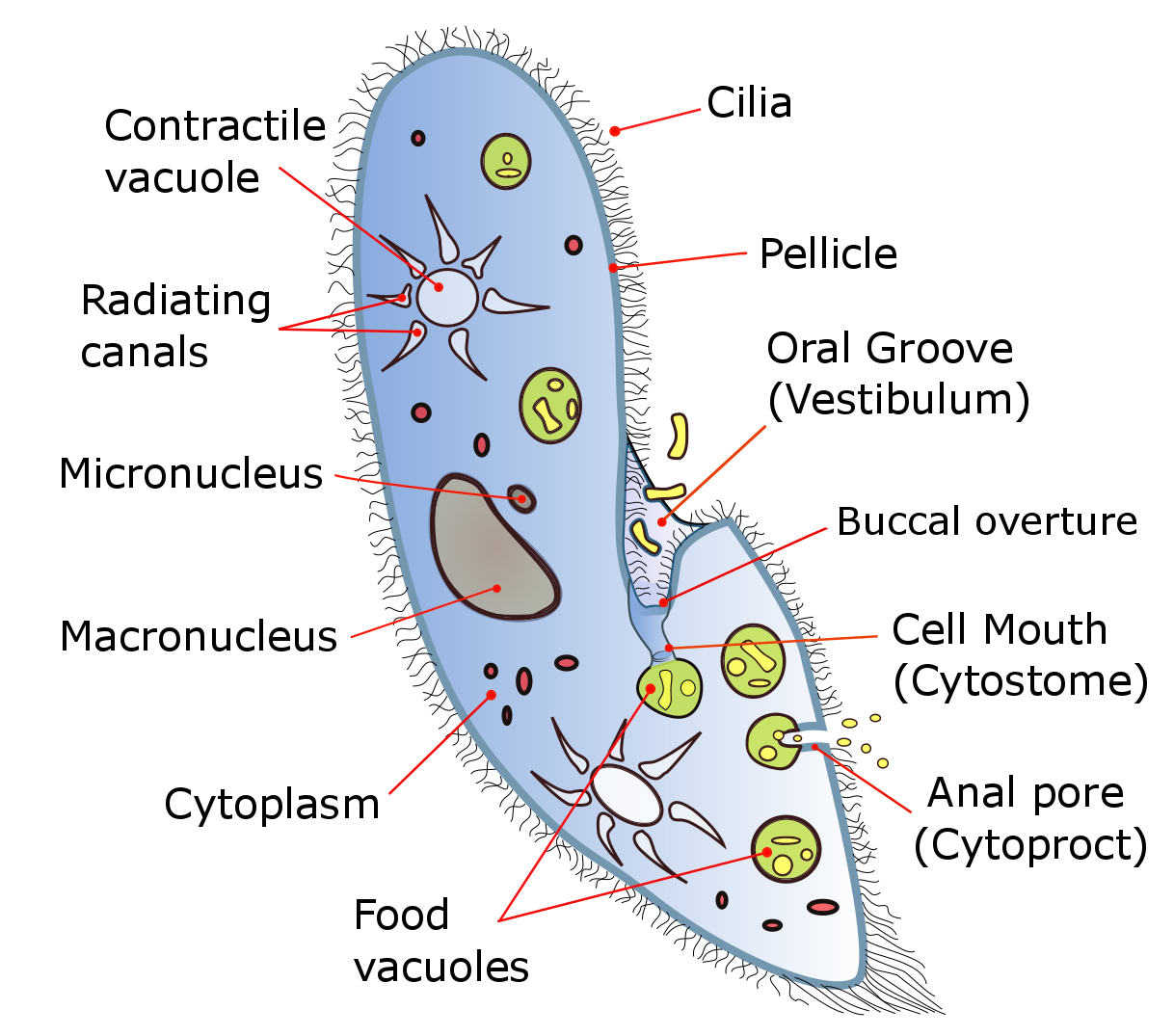
Ciliates
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different wikt:undulating, undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group (although the peculiar Suctoria only have them for part of their biological life cycle, life cycle) and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation. Ciliates are an important group of protists, common almost anywhere there is water—in lakes, ponds, oceans, rivers, and soils. About 4,500 unique free-living species have been described, and the potential number of extant species is estimated at 27,000–40,000. Included in this number are many Ectosymbiosis, ectosymbiotic and endosymbiotic species, as well as some Obligate parasite, obligate and Facultative parasite, opportunistic parasites. Ciliate species r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
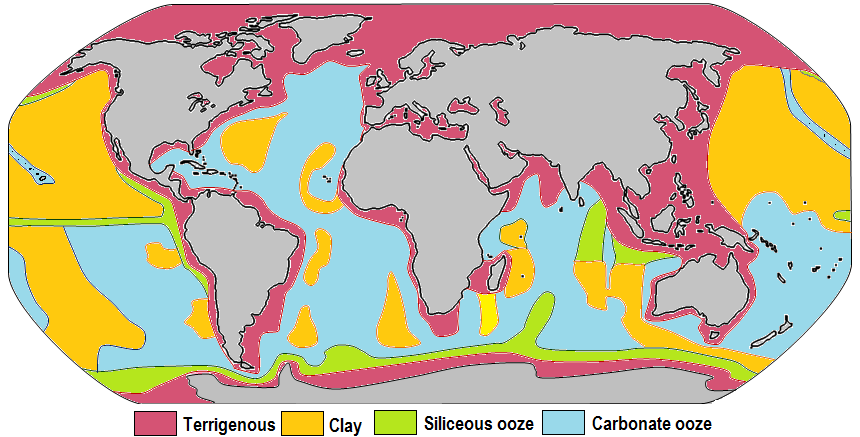
Marine Sediments
Marine sediment, or ocean sediment, or seafloor sediment, are deposits of insoluble particles that have accumulated on the seafloor. These particles have their origins in soil and rocks and have been transported from the land to the sea, mainly by rivers but also by dust carried by wind and by the flow of glaciers into the sea. Additional deposits come from marine organisms and chemical precipitation in seawater, as well as from underwater volcanoes and meteorite debris. Except within a few kilometres of a mid-ocean ridge, where the volcanic rock is still relatively young, most parts of the seafloor are covered in sediment. This material comes from several different sources and is highly variable in composition. Seafloor sediment can range in thickness from a few millimetres to several tens of kilometres. Near the surface seafloor sediment remains unconsolidated, but at depths of hundreds to thousands of metres the sediment becomes lithified (turned to rock). Rates of sediment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olavius Algarvensis
''Olavius algarvensis'' is a species of gutless oligochaete worm in the family Tubificidae which depends on symbiotic bacteria for its nutrition. Habitats and research ''Olavius algarvensis'' lives in coastal sediments in the Mediterranean. It was first described from the Algarve Coast of Portugal, but has also been found elsewhere, e.g. off the Italian island Elba, where it co-occurs with another species, '' O. ilvae.'' It was the first species of ''Olavius'' described from the East Atlantic coast; previously the genus was only known from the Caribbean. Description ''Olavius algarvensis'' is 12–25 mm long, about 0.25 mm wide, and has between 100 and 150 segments. Like all other species in the genus ''Olavius'', this species has no digestive tract. Instead, the body cavity contains the ventral nerve cord (inside a muscular sheath) and two blood vessels which are surrounded by a "fluffy" layer of chloragocytic cells. They are distinguished from other species of ''Ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
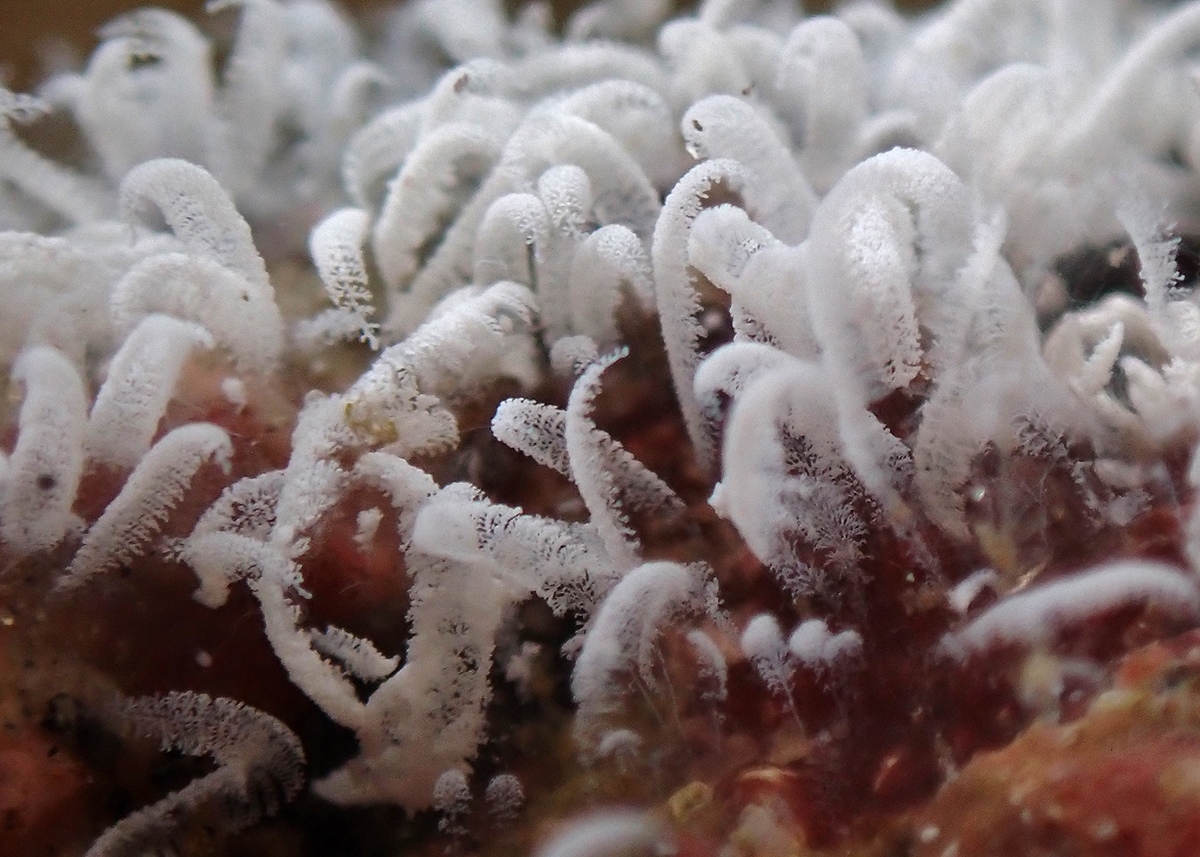
Zoothamnium Niveum
''Zoothamnium niveum'' is a species of ciliate protozoan which forms feather-shaped colonies in marine coastal environments. The ciliates form a symbiosis with sulfur-oxidizing chemosynthetic bacteria of the species "''Candidatus'' Thiobios zoothamnicoli", which live on the surface of the colonies and give them their unusual white color. Characteristics The conspicuously white and feather-shaped colonies are composed of individual bell-shaped cells known as zooids. The stalks of individual cells grow from a single central stalk. Colonies can reach a length of up to 15 mm, formed from hundreds of single zooids, each with a length of only 120 µm. An entire colony can contract into a ball-shaped bunch through the contraction of myonemes in their stalks. The white color is produced by chemolithoautotrophic sulfur-oxidizing bacteria, which cover the entire surface of the ''Z. niveum'' colony. In most other species of ''Zoothamnium'', bacteria are only known to cover the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candidatus
In prokaryote nomenclature, ''Candidatus'' (Latin for candidate of Roman office) is used to name prokaryotic phyla that are well characterized but yet-uncultured. Contemporary sequencing approaches, such as 16S sequencing or metagenomics, provide much information about the analyzed organisms and thus allow to identify and characterize individual species. However, the majority of prokaryotic species remain uncultivable and hence inaccessible for further characterization in ''in vitro'' study. The recent discoveries of a multitude of candidate taxa has led to candidate phyla radiation expanding the tree of life through the new insights in bacterial diversity. Nomenclature History The initial International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes as well as early revisions did not account for the possibility of identifying prokaryotes which were not yet cultivable. Therefore, the term ''Candidatus'' was proposed in the context of a conference of the International Committee on Systemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gammaproteobacteria
Gammaproteobacteria is a class of bacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota (synonym Proteobacteria). It contains about 250 genera, which makes it the most genera-rich taxon of the Prokaryotes. Several medically, ecologically, and scientifically important groups of bacteria belong to this class. It is composed by all Gram-negative microbes and is the most phylogenetically and physiologically diverse class of Proteobacteria. These microorganisms can live in several terrestrial and marine environments, in which they play various important roles, including ''extreme environments'' such as hydrothermal vents. They generally have different shapes - rods, curved rods, cocci, spirilla, and filaments and include free living bacteria, biofilm formers, commensals and symbionts, some also have the distinctive trait of being bioluminescent. Metabolisms found in the different genera are very different; there are both aerobic and anaerobic (obligate or facultative) species, chemolithoautotrophic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitchen Garden
The traditional kitchen garden, vegetable garden, also known as a potager (from the French ) or in Scotland a kailyaird, is a space separate from the rest of the residential garden – the ornamental plants and lawn areas. It is used for growing edible plants and often some medicinal plants, especially historically. The plants are grown for domestic use; though some seasonal surpluses are given away or sold, a commercial operation growing a variety of vegetables is more commonly termed a market garden (or a farm). The kitchen garden is different not only in its history, but also its functional design. It differs from an allotment in that a kitchen garden is on private land attached or very close to the dwelling. It is regarded as essential that the kitchen garden could be quickly accessed by the cook. Historically, most small country gardens were probably mainly or entirely used as kitchen gardens, but in large country houses the kitchen garden was a segregated area, nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotroph
A Chemotroph is an organism that obtains energy by the oxidation of electron donors in their environments. These molecules can be organic ( chemoorganotrophs) or inorganic (chemolithotrophs). The chemotroph designation is in contrast to phototrophs, which use photons. Chemotrophs can be either autotrophic or heterotrophic. Chemotrophs can be found in areas where electron donors are present in high concentration, for instance around hydrothermal vents. Chemoautotroph Chemoautotrophs, in addition to deriving energy from chemical reactions, synthesize all necessary organic compounds from carbon dioxide. Chemoautotrophs can use inorganic energy sources such as hydrogen sulfide, elemental sulfur, ferrous iron, molecular hydrogen, and ammonia or organic sources to produce energy. Most chemoautotrophs are extremophiles, bacteria or archaea that live in hostile environments (such as deep sea vents) and are the primary producers in such ecosystems. Chemoautotrophs generally fall into s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxic
{{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micronucleus
Micronucleus is the name given to the small nucleus that forms whenever a chromosome or a fragment of a chromosome is not incorporated into one of the daughter nuclei during cell division. It usually is a sign of genotoxic events and chromosomal instability. Micronuclei are commonly seen in cancerous cells and may indicate genomic damage events that can increase the risk of developmental or degenerative diseases. Micronuclei form during anaphase from lagging acentric chromosome or chromatid fragments caused by incorrectly repaired or unrepaired DNA breaks or by nondisjunction of chromosomes. This incorrect segregation of chromosomes may result from hypomethylation of repeat sequences present in pericentromeric DNA, irregularities in kinetochore proteins or their assembly, dysfunctional spindle apparatus, or flawed anaphase checkpoint genes. Micronuclei can contribute to genome instability by promoting a catastrophic mutational event called chromothripsis. Many micronucleus assays ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |