|
Kentigern
Kentigern ( cy, Cyndeyrn Garthwys; la, Kentigernus), known as Mungo, was a missionary in the Brittonic Kingdom of Strathclyde in the late sixth century, and the founder and patron saint of the city of Glasgow. Name In Wales and England, this saint is known by his birth and baptismal name Kentigern ( cy, Cyndeyrn). This name probably comes from the British *''Cuno-tigernos'', which is composed of the elements *''cun'', a hound, and *''tigerno'', a lord, prince, or king. The evidence is based on the Old Welsh record ''Conthigirn(i)''. Other etymologies have been suggested, including British *''Kintu-tigernos'' 'chief prince' based on the English form Kentigern, but the Old Welsh form above and Old English ''Cundiʒeorn'' do not appear to support this. Particularly in Scotland, he is known by the pet name Mungo, possibly derived from the Cumbric equivalent of the cy, fy nghu 'my dear (one)'. The Mungo pet name or hypocorism has a Gaelic parallel in the form Mo Choe or Mo Cha, un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crosthwaite Parish Church
Crosthwaite Parish Church is a church at Great Crosthwaite on the outskirts of Keswick, Cumbria, Keswick in Cumbria, England. It is dedicated to St Kentigern and is the Anglican church of the parish of Crosthwaite. Since 1951 it has been a Grade II* listed building. The church has an evangelical tradition. There has been a church on the site since the 6th century. The present building is largely medieval, with some Victorian era, Victorian internal alterations. Among the vicars of the parish was Hardwicke Rawnsley, co-founder of the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, National Trust. History The first church at Crosthwaite is believed to have been built in 553 Anno Domini, AD under the direction of St Kentigern, who preached the Gospel in the area before moving on to Wales. No records survive of this building, or of its Saxon successor. Both were probably wooden structures.Wilson and Kaye, p. 8 In 1181 Jocelyn of Furness wrote of a new church at Cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jocelyn Of Furness
Jocelyn of Furness (fl. 1175–1214) was an English Cistercian hagiographer, known for his Lives of Saint Waltheof, Saint Patrick, Saint Kentigern and Saint Helena of Constantinople. He is probably responsible for the popular legendary association of Saint Patrick with snakes, which he purportedly cast out of Ireland. Biography He was a monk of Furness Abbey (now in Barrow-in-Furness, Cumbria), and translated or adapted Celtic hagiographical material for Anglo-Norman readers. He wrote for Jocelyn, Bishop of Glasgow, a Life of Kentigern, and for John de Courcy and Thomas (Tommaltach), Archbishop of Armagh a Life of St Patrick. His Life of Waltheof was written to promote the cult of a former abbot of Melrose. The Life of St Helena was probably commissioned by a female community in England. Another work attributed to him was a book of British bishops. It has been claimed that he was also Abbot of Rushen Abbey Rushen Abbey is a former abbey on the Isle of Man, located in Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
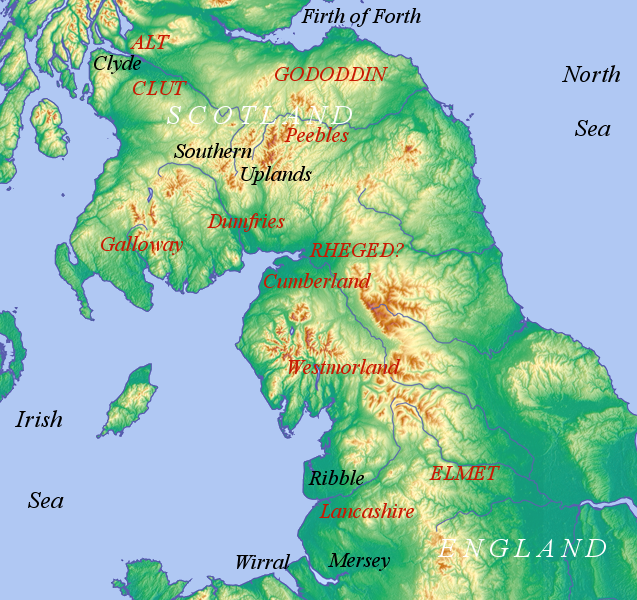
Cumbric Language
Cumbric was a variety of the Common Brittonic language spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North" in what is now the counties of Westmorland, Cumberland and northern Lancashire in Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands. It was closely related to Old Welsh and the other Brittonic languages. Place name evidence suggests Cumbric may also have been spoken as far south as Pendle and the Yorkshire Dales. The prevailing view is that it became extinct in the 12th century, after the incorporation of the semi-independent Kingdom of Strathclyde into the Kingdom of Scotland. Problems with terminology Dauvit Broun sets out the problems with the various terms used to describe the Cumbric language and its speakers.Broun, Dauvit (2004): 'The Welsh identity of the kingdom of Strathclyde, ca 900-ca 1200', ''Innes Review'' 55, pp 111–80. The people seem to have called themselves the same way that the Welsh called themselves (most likely from reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirkmahoe
Kirkmahoe is a civil parish in Dumfries and Galloway. The parish contains the settlements Kirkton, where the parish church is located, Dalswinton and Duncow. It is bounded by the parishes of Dumfries to the south, Holywood and Dunscore to the west, and Kirkmichael and Tinwald to the east. The name Kirkmahoe commemorates St Kentigern, the patron saint of Glasgow. Mo Choe is the Gaelic equivalent of Mungo, the Cumbric hypocoristic A hypocorism ( or ; from Ancient Greek: (), from (), 'to call by pet names', sometimes also ''hypocoristic'') or pet name is a name used to show affection for a person. It may be a diminutive form of a person's name, such as ''Izzy'' for I ... form of Kentigern. *For the linguistic details of these names see and References External links Kirkmahoe ascotlandsplaces.gov.uk Parishes in Dumfries and Galloway {{DumfriesGalloway-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 635,640. Straddling the border between historic Lanarkshire and Renfrewshire, the city now forms the Glasgow City Council area, one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, and is governed by Glasgow City Council. It is situated on the River Clyde in the country's West Central Lowlands. Glasgow has the largest economy in Scotland and the third-highest GDP per capita of any city in the UK. Glasgow's major cultural institutions – the Burrell Collection, Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum, the Royal Conservatoire of Scotland, the Royal Scottish National Orchestra, Scottish Ballet and Scottish Opera – enjoy international reputations. The city was the European Capital of Culture in 1990 and is notable for its architecture, cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culross
Culross (/ˈkurəs/) (Scottish Gaelic: ''Cuileann Ros'', 'holly point or promontory') is a village and former royal burgh, and parish, in Fife, Scotland. According to the 2006 estimate, the village has a population of 395. Originally, Culross served as a port city on the Firth of Forth and is believed to have been founded by Saint Serf during the 6th century. The civil parish had a population of 4,348 in 2011.Census of Scotland 2011, Table KS101SC – Usually Resident Population, publ. by National Records of Scotland. Web site http://www.scotlandscensus.gov.uk/ retrieved March 2016. See "Standard Outputs", Table KS101SC, Area type: Civil Parish 1930 Founding legend A legend states that when the Brittonic princess (and future saint) Teneu, daughter of the king of Lothian, became pregnant before marriage, her family threw her from a cliff. She survived the fall unharmed, and was soon met by an unmanned boat. She knew she had no home to go to, so she got into the boat; it sai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Strathclyde
Strathclyde (lit. "Strath of the River Clyde", and Strað-Clota in Old English), was a Brittonic successor state of the Roman Empire and one of the early medieval kingdoms of the Britons, located in the region the Welsh tribes referred to as Yr Hen Ogledd (“the Old North"), which comprised the Brythonic-speaking parts of what is now southern Scotland and northern England. The kingdom developed during Britain's post-Roman period. It is also known as ''Alt Clut'', a Brittonic term for Dumbarton Castle, the medieval capital of the region. It may have had its origins with the Damnonii people of Ptolemy's ''Geography''. The language of Strathclyde is known as Cumbric, a language that is closely related to Old Welsh, and, among modern languages, is most closely related to Welsh, Cornish, and Breton. Scottish toponymy and archaeology points to some later settlement by Vikings or Norse–Gaels (see Scandinavian Scotland), although to a lesser degree than in neighbouring Galloway. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Mungo's Church, Dearham
St Mungo's Church is in the village of Dearham, Cumbria, England. The church is dedicated to St Mungo, also known as Kentigern, the apostle of Strathclyde. It is an active Anglican parish church in the deanery of Solway, the archdeaconry of West Cumberland, and the diocese of Carlisle. The church is recorded in the National Heritage List for England as a designated Grade I listed building. History St Mungo's dates from the late 12th century, and the chancel was added in the 13th century. The architectural historian Nikolaus Pevsner was of the opinion that the Norman features, including the south door and some windows, date from about 1170–90, and that the tunnel vault in the lowest stage of the tower is also from this period or "a little later". The north aisle was added by C. J. Ferguson in 1882. Architecture Exterior The church is constructed in sandstone with green slate roofs. The foundations incorporate stones from former Roman buildings. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penicuik
Penicuik ( ; sco, Penicuik; gd, Peighinn na Cuthaig) is a town and former burgh in Midlothian, Scotland, lying on the west bank of the River North Esk. It lies on the A701 midway between Edinburgh and Peebles, east of the Pentland Hills. Name The town's name is pronounced 'Pennycook' and is derived from ''Pen Y Cog'', meaning "Hill of the Cuckoo" in the British language (Celtic), Old Brythonic language (also known as Ancient British and the forerunner of modern Welsh language, Welsh). History In 1296, Thomas Rymer's ''Foedera'' mentions a "Walter Edgar a person of Penicok south of Edenburgh", which logically can only be what is now called Penicuik. Penycook appears as the name on John Adair's map of 1682 and the ruined old parish church, in the centre of the graveyard, dates from the late 17th century. Penicuik became home to an early paper mill, Valleyfield Mill, which was established by Agnes Campbell (printer), Agnes Campbell in 1709. The Pomathorn Bridge was a toll b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
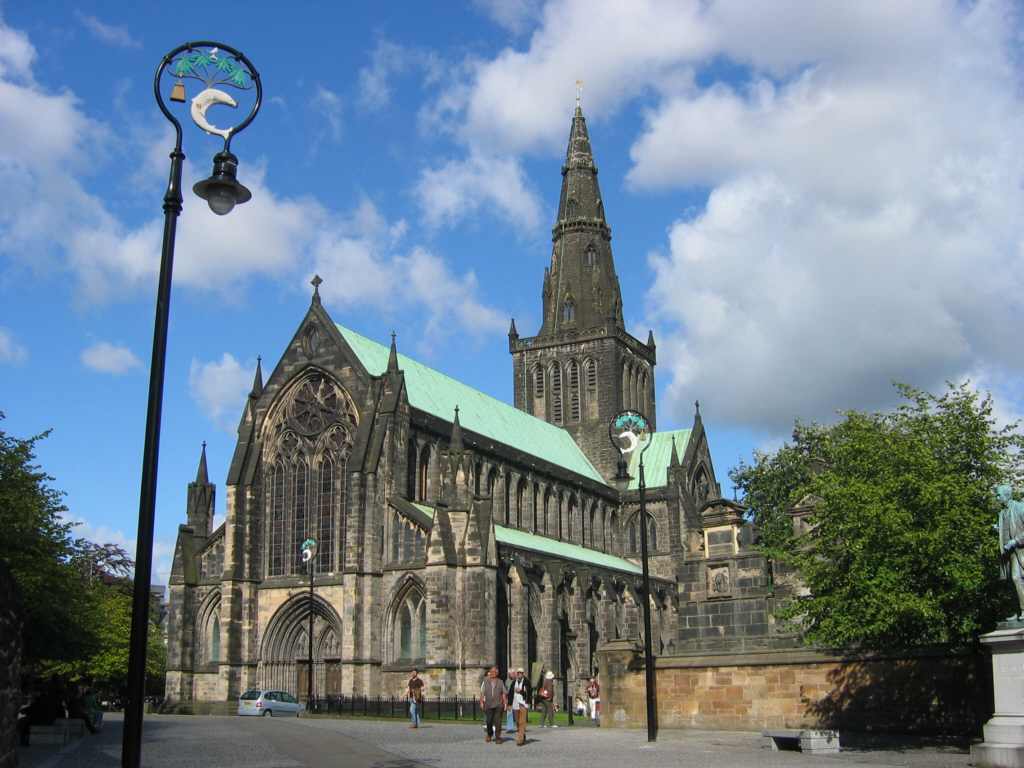
Glasgow Cathedral
Glasgow Cathedral ( gd, Cathair-eaglais Ghlaschu) is a parish church of the Church of Scotland in Glasgow, Scotland. It is the oldest cathedral in mainland Scotland and the oldest building in Glasgow. The cathedral was the seat of the Archbishop of Glasgow, and the mother church of the Archdiocese of Glasgow and the Province of Glasgow, until the Scottish Reformation in the 16th century. Glasgow Cathedral and St Magnus Cathedral in Orkney are the only medieval cathedrals in Scotland to have survived the Reformation virtually intact. The medieval Bishop's Castle stood to the west of the cathedral until the 18th century. The cathedral is dedicated to Saint Mungo, the patron saint of Glasgow, whose tomb lies at the centre of the building's Lower Church. The first stone cathedral was dedicated in 1136, in the presence of David I. Fragments of this building have been found beneath the structure of the present cathedral, which was dedicated in 1197, although much of the present cathedr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickname
A nickname is a substitute for the proper name of a familiar person, place or thing. Commonly used to express affection, a form of endearment, and sometimes amusement, it can also be used to express defamation of character. As a concept, it is distinct from both pseudonym and stage name, and also from a title (for example, City of Fountains), although there may be overlap in these concepts. Etymology The compound word ''ekename'', literally meaning "additional name", was attested as early as 1303. This word was derived from the Old English phrase ''eac'' "also", related to ''eacian'' "to increase". By the 15th century, the misdivision of the syllables of the phrase "an ekename" led to its rephrasing as "a nekename". Though the spelling has changed, the pronunciation and meaning of the word have remained relatively stable ever since. Conventions in various languages English nicknames are generally represented in quotes between the bearer's first and last names (e.g., '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypocorism
A hypocorism ( or ; from Ancient Greek: (), from (), 'to call by pet names', sometimes also ''hypocoristic'') or pet name is a name used to show affection for a person. It may be a diminutive form of a person's name, such as ''Izzy'' for Isabel or ''Bob (given name), Bob'' for Robert, or it may be unrelated. In linguistics, the term can be used more specifically to refer to the morphological process by which the standard form of the word is transformed into a form denoting affection, or to words resulting from this process. In English, a word is often Clipping (morphology), clipped down to a closed monosyllable and then suffixed with ''-y/-ie'' (phonologically /i/). Sometimes the suffix ''-o'' is included as well as other forms or templates. Hypocoristics are often affective in meaning and are particularly common in Australian English, but can be used for various purposes in different semantic fields, including personal names, place names and nouns. Hypocorisms are usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |