|
Keminub
Keminub was an ancient Egyptian woman with the title ''king's wife''. She is only known from her burial next to the pyramid of Amenemhet II at Dahshur. For that reason, it has been suggested she was his wife. Keminub was buried together with a treasurer named Amenhotep, who is dated to the 13th Dynasty. The style of her coffin and burial is close to burials of the 13th dynasty. She may therefore have been a queen of this dynasty instead. The name of her husband is so far unknown.K. S. B. Ryholt, Adam Bülow-Jacobsen, The political situation in Egypt during the second intermediate period, c. 1800-1550 B.C., Museum Tusculanum Press, 1997 On the fragments of her coffin appears one of the earliest attestations of chapter 151 of the ''Book of the Dead The ''Book of the Dead'' ( egy, 𓂋𓏤𓈒𓈒𓈒𓏌𓏤𓉐𓂋𓏏𓂻𓅓𓉔𓂋𓅱𓇳𓏤, ''rw n(y)w prt m hrw(w)'') is an ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenemhet II
Nubkaure Amenemhat II, also known as Amenemhet II, was the third pharaoh of the 12th Dynasty of ancient Egypt. Although he ruled for at least 35 years, his reign is rather obscure, as well as his family relationships. Family Archaeological findings have provided the name of Amenemhat's mother, the "king's mother" Neferu III, but not the name of his father. Nevertheless, it is commonly assumed that he was a son of his predecessor Senusret I. An early attestation of Amenemhat may have come from the tomb of the namesake nomarch Amenemhat, buried at Beni Hasan. This nomarch, who lived under Senusret I, escorted the "King's son Ameny" in an expedition to Nubia, and it is believed that this prince Ameny was no other than Amenemhat II in his youth. The identity of Amenemhat's queen consort is unknown. Many royal women were buried within his pyramid complex, but their relationships with the king are unclear: a queen Keminub must be dated to the later 13th Dynasty, and three "king's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenhotep (treasurer)
Amenhotep was an ancient Egyptian treasurer and ''royal sealer'' of the Thirteenth Dynasty (around 1750 BC). The treasurer was one of the most important officials at the royal court. He is mainly known from his burial found next to the White Pyramid of king Amenemhat II at Dahshur. His burial chamber was placed next to the burial chamber of queen Keminub and still contained the fragments of his inscribed wooden coffin, decorated with religious texts, so far not yet securely identified. He is also known from several scarab seals. The style of the seals but also of the burial equipment suggest that he dates from the Thirteenth Dynasty and not under Amenemhat III :''See Amenemhat, for other individuals with this name.'' Amenemhat III ( Ancient Egyptian: ''Ỉmn-m-hꜣt'' meaning 'Amun is at the forefront'), also known as Amenemhet III, was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the sixth king of the Twelfth Dy ... as hitherto believed.K.S.B. Ryholt, ''The Political Situation in Egy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Pyramid
The White Pyramid ( ar, الهرم الأبيض, al-Haram al'Abyad) of Amenemhat II is located in the pyramid field at Dahshur, Egypt, and is now nothing more than a pile of rubble, having been heavily quarried for stone. The remaining limestone rubble has given rise to its modern name. The pyramid is surrounded by a large rectangular enclosure wall. A number of intact tombs were found inside this enclosure wall belonging to the relatives of Amenemhat II including the tombs of prince Amenemhatankh and princesses Ita, Khnumet, Itaweret and Sithathormeret. A wide variety of funerary furniture was recovered from these tombs including wooden coffins, alabaster perfume jars, and canopic chests. There was also a large quantity of beautiful jewellery in the tombs of Ita and Khnumet. In 1894 and 1895, Jacques de Morgan dug in the pyramid complex, concentrating on the surrounding royal graves, with other areas not being explored. A full-scale investigation of the whole complex has yet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dahshur
DahshurAlso transliterated ''Dahshour'' (in English often called ''Dashur'' ar, دهشور ' , ''Dahchur'') is a royal necropolis located in the desert on the west bank of the Nile approximately south of Cairo. It is known chiefly for several pyramids, two of which are among the oldest, largest and best preserved in Egypt, built from 2613 to 2589 BC. Pyramids The Dahshur pyramids were an extremely important learning experience for the Egyptians. It provided them with the knowledge and know-how to transition from step-sided pyramids to smooth-sided pyramids. Ultimately their breadth of experience would allow them to build the Great Pyramid of Giza; the last of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World still standing to this date. The first of the Dahshur pyramids was the Bent Pyramid (2613–2589 BC), built under the rule of King Sneferu. The Bent Pyramid was the first attempt at building a smooth sided pyramid, but proved to be an unsuccessful build due to the miscalcula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirteenth Dynasty Of Egypt
In music or music theory, a thirteenth is the Musical note, note thirteen scale degrees from the root (chord), root of a chord (music), chord and also the interval (music), interval between the root and the thirteenth. The interval can be also described as a Interval (music)#Simple and compound, compound major sixth, sixth, spanning an octave plus a sixth. The thirteenth is most commonly major or minor . A thirteenth chord is the stacking of six (major third, major or minor third, minor) thirds, the last being above the 11th of an eleventh chord. Thus a thirteenth chord is a tertian (built from thirds) chord containing the interval of a thirteenth, and is an extended chord if it includes the ninth and/or the eleventh. "The jazzy thirteenth is a very versatile chord and is used in many genres." Since 13th chords tend to become unclear or confused with other chords when Inverted chord, inverted, they are generally found in root position.Benward & Saker (2009). ''Music in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
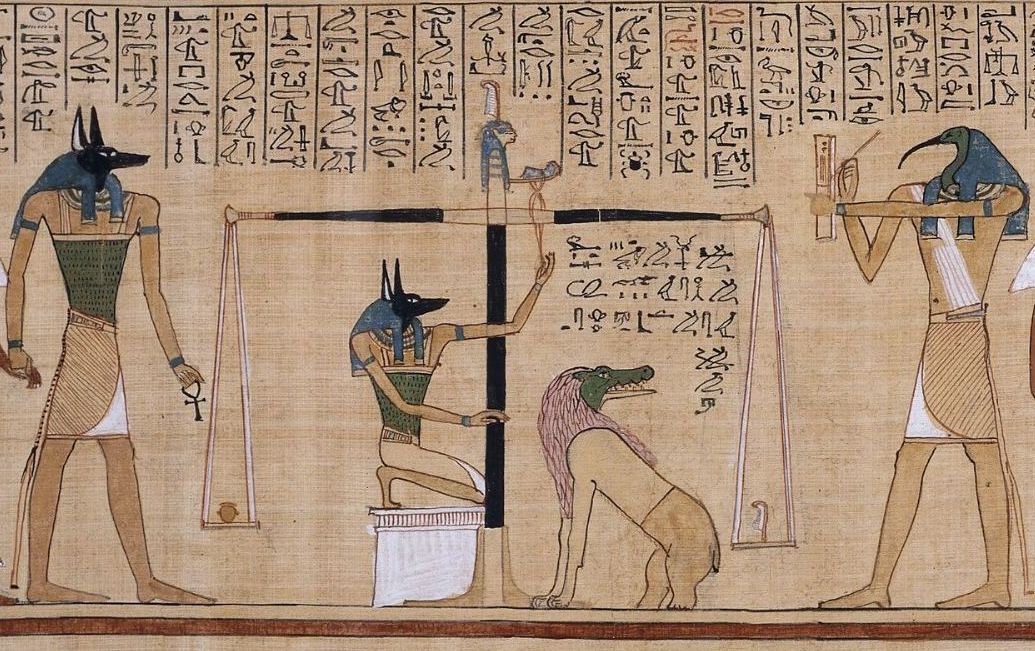
Book Of The Dead
The ''Book of the Dead'' ( egy, 𓂋𓏤𓈒𓈒𓈒𓏌𓏤𓉐𓂋𓏏𓂻𓅓𓉔𓂋𓅱𓇳𓏤, ''rw n(y)w prt m hrw(w)'') is an ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the New Kingdom (around 1550 BCE) to around 50 BCE. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated ''rw nw prt m hrw'', is translated as ''Book of Coming Forth by Day'' or ''Book of Emerging Forth into the Light''. "Book" is the closest term to describe the loose collection of texts consisting of a number of magic spells intended to assist a dead person's journey through the '' Duat'', or underworld, and into the afterlife and written by many priests over a period of about 1,000 years. Karl Richard Lepsius introduced for these texts the German name ''Todtenbuch'' (modern spelling ''Totenbuch''), translated to English as Book of the Dead. The ''Book of the Dead'', which was placed in the coffin or burial chamber of the deceased, was part of a tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century BC Women
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected events. To historians who expand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th-century BC Women
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 ( MDCI), to December 31, 1700 ( MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age, the Dutch Golden Age, the French ''Grand Siècle'' dominated by Louis XIV, the Scientific Revolution, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company, and according to some historians, the General Crisis. From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France of Louis XIV, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded royal court could be more easily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)