|
Keleivis
''Keleivis iš Karaliaučiaus broliams Lietuvininkams žinias parnešas'' (original spelling: ''Keleiwis isz Karaliaucziaus Broliams Lietuwininkams Žines parnesząs'', ) was a Lithuanian-language weekly periodical published in Königsberg, East Prussia, from 1849 to 1880. It was one of the first Lithuanian periodicals. Edited and published by the linguist and Lutheran pastor Friedrich Kurschat, ''Keleivis'' was politically conservative and propagated religious values. History During the German revolutions of 1848–1849, liberals started publishing Lithuanian texts targeting Prussian Lithuanians. These included the short-lived periodicals ''Lietuviškas prielaiškas'' by teacher Mauras Pucas and '' Lietuvininkų prietelis'' by priest Rudolf Andreas Zippel. The Prussian Conservative Party approached Friedrich Kurschat, a native Lithuanian speaker and politically loyal to the German Empire, who published two pro-monarchy proclamations in 1848 and established weekly ''Keleivis' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Lithuanian-language Periodicals (up To 1904)
This list of Lithuanian-language periodicals includes periodical publications (newspapers, magazines) that were published up to 1904 when the Lithuanian press ban The Lithuanian press ban ( lt, spaudos draudimas) was a ban on all Lithuanian language publications printed in the Latin alphabet in force from 1865 to 1904 within the Russian Empire, which controlled Lithuania proper at the time. Lithuanian-lan ... was lifted in Lithuania Proper (then part of the Russian Empire). The periodicals were printed mostly in Lithuania Minor (then part of East Prussia, German Empire) and by the Lithuanian Americans in the United States. Some publications published in Prussia were intended for Prussian Lithuanians, the local Lithuanian-speaking minority. Others were intended for Lithuanians in Russia and were smuggled by Lithuanian book smugglers across the Prussia–Russia border. Publications The list is sorted in chronological order. The periodicals that lasted for five years or longer ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Kurschat
Friedrich Kurschat ( lt, Frydrichas Kuršaitis; 1806–1884) was a Prussian Lithuanian linguist and professor at the University of Königsberg. He studied the Lithuanian language and published its grammar in 1876 in which he was the first to describe Lithuanian accentuation in detail. Kurschat was born into a family of a poor school teacher and received no formal education until age 28. In 1836, he enrolled into the University of Königsberg where he became an assistant to linguist Ludwig Rhesa. After Rhesa's death in 1840, Kurschat became the leader of the Lithuanian language seminar at the university and held that position for more than forty years. He graduated in 1844 and was ordained as a Lutheran priest. Kurschat published several linguistic studies of the Lithuanian language. His most important work was the grammar of the Lithuanian language published in 1876. He also published two-volume German–Lithuanian dictionary and one-volume Lithuanian–German dictionary. Kursch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lietuvininkų Prietelis
''Lietuvininkų prietelis'' (original spelling: ''Lietuwininku Prietelis''; ) was a short-lived Lithuanian-language political newspaper published in Memel (now Klaipėda) by Lutheran priest Rudolf Andreas Zippel (Rudolfas Endrius Cipelis) in 1849. It was published for less than a year, but it is considered the first "true" Lithuanian periodical (earlier '' Nusidavimai Dievo karalystėje'' contained mostly translated religious texts). It was also the first Lithuanian periodical published in the territory of present-day Lithuania. History During the German revolutions of 1848–1849, many activists tried to publish political proclamations and periodicals for Lithuanian-speaking Prussian Lithuanians. The first issue of ''Lietuvininkų prietelis'' was published on 5 April 1849 by publisher . It was edited by Rudolf Andreas Zippel (Rudolfas Endrius Cipelis), deacon of the Lithuanian parish in Memel. It was published weekly on Thursdays until 28 December 1849. In total, 38 issues we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanization
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In linguistics, Germanisation of non-German languages also occurs when they adopt many German words. Under the policies of states such as the Teutonic Order, Austria, the German Empire and Nazi Germany, non-Germans were often prohibited from using their native language, and had their traditions and culture suppressed in the goal of gradually eliminating foreign cultures, a form of ethnic cleansing. In addition, colonists and settlers were used to upset the population balance. During the Nazi era, Germanisation turned into a policy of genocide against some non-German ethnic groups. Forms Historically there are different forms and degrees of the expansion of the German language and of elements of German culture. There are examples of complete a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publications Established In 1849
To publish is to make content available to the general public.Berne Convention, article 3(3) URL last accessed 2010-05-10.Universal Copyright Convention, Geneva text (1952), article VI . URL last accessed 2010-05-10. While specific use of the term may vary among countries, it is usually applied to text, images, or other content, including paper ( |
1849 Establishments In Germany
Events January–March * January 1 – France begins issue of the Ceres series, the nation's first postage stamps. * January 5 – Hungarian Revolution of 1848: The Austrian army, led by Alfred I, Prince of Windisch-Grätz, enters in the Hungarian capitals, Buda and Pest. The Hungarian government and parliament flee to Debrecen. * January 8 – Hungarian Revolution of 1848: Romanian armed groups massacre 600 unarmed Hungarian civilians, at Nagyenyed.Hungarian HistoryJanuary 8, 1849 And the Genocide of the Hungarians of Nagyenyed/ref> * January 13 ** Second Anglo-Sikh War – Battle of Tooele: British forces retreat from the Sikhs. ** The Colony of Vancouver Island is established. * January 21 ** General elections are held in the Papal States. ** Hungarian Revolution of 1848: Battle of Nagyszeben – The Hungarian army in Transylvania, led by Josef Bem, is defeated by the Austrians, led by Anton Puchner. * January 23 – Elizabeth Blackwell is awarded her M.D. by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
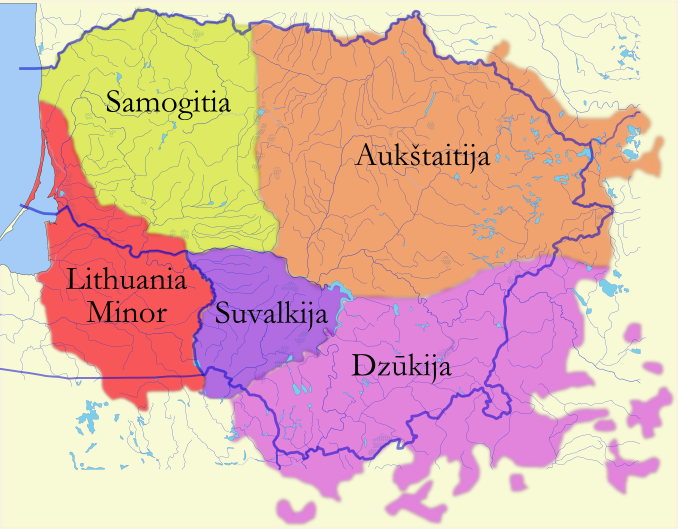
Lithuania Minor
Lithuania Minor ( lt, Mažoji Lietuva; german: Kleinlitauen; pl, Litwa Mniejsza; russian: Ма́лая Литва́), or Prussian Lithuania ( lt, Prūsų Lietuva; german: Preußisch-Litauen, pl, Litwa Pruska), is a historical ethnographic region of Prussia, where Prussian Lithuanians (or Lietuvininkai) lived, now located in Lithuania and the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia. Lithuania Minor encompassed the northeastern part of the region and got its name from the territory's substantial Lithuanian-speaking population. Prior to the invasion of the Teutonic Knights in the 13th century, the main part of the territory later known as Lithuania Minor was inhabited by the tribes of Skalvians and Nadruvians. The land depopulated during the incessant war between Lithuania and the Teutonic Order. The war ended with the Treaty of Melno and the land was repopulated by Lithuanian newcomers, returning refugees, and the remaining indigenous Baltic peoples; the term Lithuania Minor appeared for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian-language Newspapers
Lithuanian ( ) is an Eastern Baltic language belonging to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is the official language of Lithuania and one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.8 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 200,000 speakers elsewhere. Lithuanian is closely related to the neighbouring Latvian language. It is written in a Latin script. It is said to be the most conservative of the existing Indo-European languages, retaining features of the Proto-Indo-European language that had disappeared through development from other descendant languages. History Among Indo-European languages, Lithuanian is conservative in some aspects of its grammar and phonology, retaining archaic features otherwise found only in ancient languages such as Sanskrit (particularly its early form, Vedic Sanskrit) or Ancient Greek. For this reason, it is an important source for the reconstruction of the Proto-Indo-Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian Conservative Election Societies
The Lithuanian Conservative Election Societies ( lt, Lietuviškos konservatyvų skyrimo draugystės) were several loosely connected political societies of Prussian Lithuanians active from 1890 to the German Revolution of 1918–19. They sought to elect Prussian Lithuanians to the German Reichstag and Prussian Landtag and to defend the use of the Lithuanian language. The societies managed to get two representatives to the Reichstag (Jonas Smalakys in 1898–1901 and, after Smalakys' death, in 1901–1903) and two to the Landtag ( in 1903–1918 and in 1913–1918). It is sometimes described as the first Lithuanian political party (the Social Democratic Party of Lithuania was established in 1895). History The first society, the Committee of the Lithuanian Conservative Society ( lt, Lietuviškos konservatyvų draugystės komitetas), was established in 1890 in Tilsit (now Sovetsk) by Martynas Jankus, Jonas Smalakys, Dovas Zaunius, and others. In 1892, the committee broke up to sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sovetsk, Kaliningrad Oblast
Sovetsk (russian: Сове́тск; german: Tilsit; Old Prussian: ''Tilzi''; lt, Tilžė; pl, Tylża) is a town in Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia, located on the south bank of the Neman River which forms the border with Lithuania. Geography Sovetsk lies in the historic region of Lithuania Minor at the confluence of the Tilse and Neman rivers. Panemunė in Lithuania was formerly a suburb of the town; after Germany's defeat in World War I, the trans-Neman suburb was detached from Tilsit (with the rest of the Klaipėda Region) in 1920. Climate Sovetsk has a borderline oceanic climate (''Cfb'' in the Köppen climate classification) using the boundary, or a humid continental climate (''Dfb'') using the boundary. History Tilsit, which received civic rights from Albert, Duke of Prussia in 1552,''Słownik geograficzny Królestwa Polskiego i innych krajów słowiańskich, Tom XII'', p. 703 developed around a castle of the Teutonic Knights, known as the Schalauer Haus, founded in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |