|
Keele University Science
Keele is a village and civil parish in the Borough of Newcastle-under-Lyme in Staffordshire, England. It is approximately three miles (5 km) west of Newcastle-under-Lyme, and is close to the village of Silverdale. Keele lies on the A53 road from Newcastle-under-Lyme to Market Drayton and Shrewsbury. The village is the location of Keele University (at ) and Keele Services (), a motorway service area on the M6. Keele is located in the Keele ward of the borough of Newcastle-under-Lyme with its name drawing from the old Anglo-Saxon ''Cȳ-hyll'' = "Cow-hill". The 2001 census indicated the parish had a population of 3,664,(increasing to 4,129 at the 2011 census) most of whom students at Keele University as one of the halls of residence, Hawthorns, now sold for land redevelopment, was located in the heart of the village. The Knights Templars & Hospitallers The village is recognised for its association with the university and its position astride the M6. But during the Midd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Census 2011
A Census in the United Kingdom, census of the population of the United Kingdom is taken every ten years. The 2011 census was held in all countries of the UK on 27 March 2011. It was the first UK census which could be completed online via the Internet. The Office for National Statistics (ONS) is responsible for the census in England and Wales, the General Register Office for Scotland (GROS) is responsible for the census in Scotland, and the Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency (NISRA) is responsible for the census in Northern Ireland. The Office for National Statistics is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department formed in 2008 and which reports directly to Parliament. ONS is the UK Government's single largest statistical producer of independent statistics on the UK's economy and society, used to assist the planning and allocation of resources, policy-making and decision-making. ONS designs, manages and runs the census in England an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keele Preceptory
Keele Preceptory was a preceptory (the headquarters of the order within a given geographical area), in Keele, Staffordshire, England. Owned by the Knights Templar until their suppression in the early 14th century, it then passed through a number of owners before falling into the hands of the Knights Hospitaller. History Foundation The estate was granted to the Knights Templar sometime between 1168-69 by King Henry II. The grant was further increased by Henry in 1185 with gifts of land in Onneley, near Madeley, worth some 2 shillings. The estate became a preceptory sometime in the 13th century and by 1308 they were collecting rents from property held in Newcastle-under-Lyme, Onneley, Stanton, and Nantwich. Suppression In 1307, Pope Clement V issued the papal bull '' Pastoralis Praeeminentiae'' calling on all European monarchs to arrest members of the Templar order. In response, the English Crown seized the order's property, including that belonging to Keele Preceptory. The l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duke Michael Mikhailovich Of Russia
Grand Duke Michael Mikhailovich of Russia (Russian: Михаил Михайлович; 16 October 1861 – 26 April 1929) was a son of Grand Duke Michael Nicolaievich of Russia and a grandson of Tsar Nicholas I of Russia. He was raised in the Caucasus, where he lived between 1862 and 1881 with his family, and was educated by private tutors. As Romanov tradition demanded, he followed a military career. He served in the Russo-Turkish War in 1877, became a Colonel and was adjutant at the Imperial court. In 1891 he contracted a morganatic marriage with Countess Sophie von Merenberg, a morganatic daughter of Prince Nicholas William of Nassau and a granddaughter of the Russian poet Alexander Pushkin. For contracting this marriage without permission, Emperor Alexander III of Russia stripped him of his military titles and banished the couple from the Russian Empire. For some years he lived in Wiesbaden, Nassau and in Cannes. He settled permanently in England in 1900, leasing Keele Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle Rising (UK Parliament Constituency)
Castle Rising was a parliamentary borough in Norfolk, which elected two Members of Parliament (MPs) to the House of Commons from 1558 until 1832, when it was abolished by the Great Reform Act. Its famous members of Parliament included the future Prime Minister Robert Walpole and the diarist Samuel Pepys. History The borough extended over four parishes - Castle Rising, Roydon, North Wootton and South Wootton, in rural Norfolk to the north-east of King's Lynn. Castle Rising had once been a market town and seaport, but long before the Reform Act had declined to little more than a village. In 1831, the population of the borough was 888, and contained 169 houses. Castle Rising was a burgage borough, meaning that the right to vote was vested in the owners of particular properties ("burgage tenements"), and that consequently the absolute right to nominate both the MPs could be bought and sold. Although it was possible for the landowner to create multiple voters by giving a reliab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keele Hall
Keele Hall is a 19th-century mansion house at Keele, Staffordshire, England, now standing on the campus of Keele University and serving as the university conference centre. It is a Grade II* listed building. History Early history The manor of Keele was purchased by the Sneyd family in 1544, a Staffordshire gentry family who held the mayoralty of the borough of Newcastle-under-Lyme several times as well as lands in nearby Audley and Bradwell. In about 1580 Ralph Sneyd built a large gabled Tudor style house there. The family prospered as coal (in nearby Silverdale, Staffordshire) and iron owners and also brick and tile manufacturers. During the English Civil War, Keele Hall was briefly instrumental is providing an asylum for King Charles II after the Battle of Worcester in 1651. As royalist supporters, following the final Parliamentarian victory, the Sneyd family were heavily fined. New hall The hall was inherited by Ralph Sneyd in 1829, following the death of his father. By th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Sneyd
Lieutenant-Colonel Walter Sneyd (11 February 1752 – 23 June 1829), of Keele Hall was an English politician who served in the Parliament of Great Britain and as High Sheriff of Staffordshire. Early life Sneyd was born on 11 February 1752 in an old Staffordshire parliamentary family. He was a son of the former Barbara Bagot and Ralph Sneyd of Keele Hall, Staffordshire. His younger brother, the Rev. Ralph Sneyd married Penelope Moore (a daughter of the Hon. Sir John Moore and granddaughter of Henry, Earl of Drogheda) His paternal grandfather was Ralph Sneyd, MP for Staffordshire. His maternal grandfather was Sir Walter Bagot, 5th Baronet and Lady Barbara Legge (daughter of William Legge, 1st Earl of Dartmouth). He was educated at Brasenose College, Oxford, 1769. Career He was admitted to Middle Temple in 1771 and held a commission in the Staffordshire Militia, eventually rising to the rank of Lieutenant-Colonel and being appointed Lt-Col Commandant of the Northern Regiment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fleet Street
Fleet Street is a major street mostly in the City of London. It runs west to east from Temple Bar at the boundary with the City of Westminster to Ludgate Circus at the site of the London Wall and the River Fleet from which the street was named. The street has been an important through route since Roman times. During the Middle Ages, businesses were established and senior clergy lived there; several churches remain from this time including Temple Church and St Bride's. The street became known for printing and publishing at the start of the 16th century, and it became the dominant trade so that by the 20th century most British national newspapers operated from here. Much of that industry moved out in the 1980s after News International set up cheaper manufacturing premises in Wapping, but some former newspaper buildings are listed and have been preserved. The term ''Fleet Street'' remains a metonym for the British national press, and pubs on the street once frequented by jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
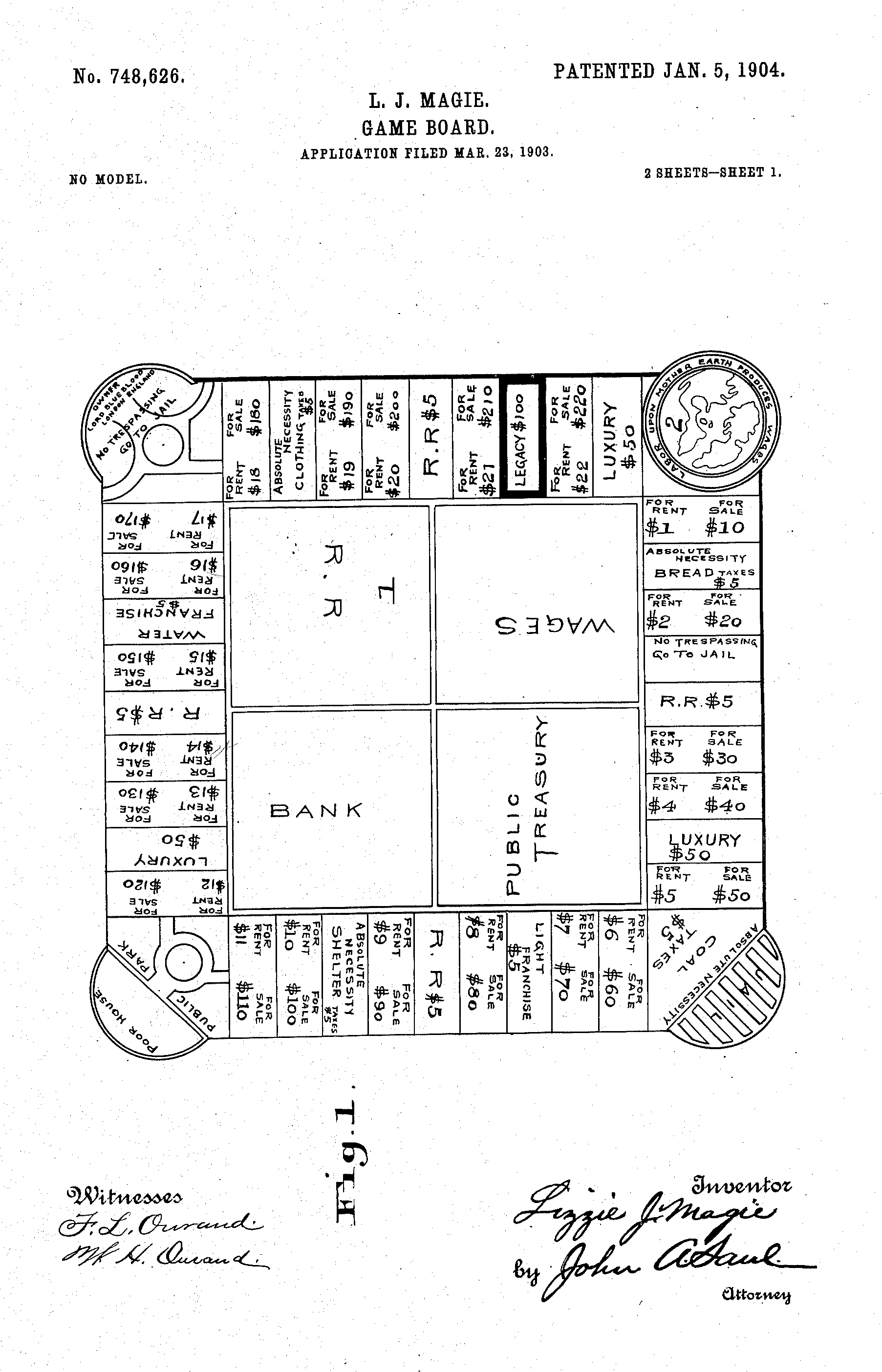
Monopoly (game)
''Monopoly'' is a multi-player economics-themed board game. In the game, players roll two dice to move around the game board, buying and trading properties and developing them with houses and hotels. Players collect rent from their opponents, aiming to drive them into bankruptcy. Money can also be gained or lost through ''Chance'' and ''Community Chest'' cards and tax squares. Players receive a stipend every time they pass "Go" and can end up in jail, from which they cannot move until they have met one of three conditions. House rules, hundreds of different editions, many spin-offs, and related media exist. ''Monopoly'' has become a part of international popular culture, having been licensed locally in more than 103 countries and printed in more than 37 languages. , it was estimated that the game had sold 275 million copies worldwide. ''Monopoly'' is derived from ''The Landlord's Game'', created by Lizzie Magie in the United States in 1903 as a way to demonstrate that an economy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Patton
George Smith Patton Jr. (November 11, 1885 – December 21, 1945) was a general in the United States Army who commanded the Seventh United States Army in the Mediterranean Theater of World War II, and the Third United States Army in France and Germany after the Allied invasion of Normandy in June 1944. Born in 1885, Patton attended the Virginia Military Institute and the United States Military Academy at West Point. He studied fencing and designed the M1913 Cavalry Saber, more commonly known as the "Patton Saber". He competed in modern pentathlon in the 1912 Summer Olympics in Stockholm, Sweden. Patton entered combat during the Pancho Villa Expedition of 1916, the United States' first military action using motor vehicles. He fought in World War I as part of the new United States Tank Corps of the American Expeditionary Forces: he commanded the U.S. tank school in France, then led tanks into combat and was wounded near the end of the war. In the interwar period, Patton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nissen Hut
A Nissen hut is a prefabricated steel structure for military use, especially as barracks, made from a half-cylindrical skin of corrugated iron. Designed during the First World War by the American-born, Canadian-British engineer and inventor Major Peter Norman Nissen, it was used also extensively during the Second World War, being adapted as the similar Quonset hut in the United States. Description A Nissen hut is made from a sheet of metal bent into half a cylinder and planted in the ground with its axis horizontal. The cross-section is not precisely semi-circular, because the bottom of the hut curves out slightly. The exterior is formed from curved corrugated steel sheets 10 feet 6 inches by 2 feet 2 inches (3.2 × 0.7 m), laid with a two-corrugation lap at the side and a 6-inch (15 cm) overlap at the ends. Three sheets cover the arc of the hut. They are attached to five 3 × 2 inch (7.5 × 5 cm) wooden purlins and 3 × 2 inch wooden spiking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkhas, and 28,330 volunteer reserve personnel. The modern British Army traces back to 1707, with antecedents in the English Army and Scots Army that were created during the Restoration in 1660. The term ''British Army'' was adopted in 1707 after the Acts of Union between England and Scotland. Members of the British Army swear allegiance to the monarch as their commander-in-chief, but the Bill of Rights of 1689 and Claim of Right Act 1689 require parliamentary consent for the Crown to maintain a peacetime standing army. Therefore, Parliament approves the army by passing an Armed Forces Act at least once every five years. The army is administered by the Ministry of Defence and commanded by the Chief of the General Staff. The Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |