 |
Kaédi FC
Kaédi ( ar, كيهيدي) is the largest city and administrative center of the Gorgol Region of Southern Mauritania, located on the border with Senegal. It is approximately 435 km from Mauritania's capital, Nouakchott. Overview The city sits within the " Chemama" Riverine zone along the north bank of the River Senegal where it connects with the Gorgol River. This region is one of the few areas of settled agriculture in the country. Culturally, the city is among the most diverse in Mauritania, consisting of ethnic "White Moors" (Arabic: البيضان) and "Black Moors" (Arabic: السودان), as well as Pulaar, and Soninke communities. It is known as a market town, a medical centre, and a centre for local farmers. The market reflects the sub-Saharan culture of neighboring Senegal somewhat more than the Moorish-Arabic culture found further north in the country. Most of the architecture consists of brown, flat-roofed buildings, undistinguished except that most are su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Communes Of Mauritania
There are 216 administrative communes of Mauritania recognised by the Government of Mauritania. Urban Agricultural * Adel Bagrou * Aere Mbar * Aghchorguitt * Ain Ehel Taya * Aioun * Ajar * Aleg * Amourj * Aoueinat Zbel * Aoujeft * Arr * Atar * Azgueilem Tiyab * Bababe * Bagrou * Barkeol * Bassiknou * Bethet Meit * Boghé * Bokkol * Bou Lahrath * Bougadoum * Bouheida * Bouhdida * Boulenoir * Bouly * Boumdeid * Bousteila * Boutilimitt * Cheggar * Chinguitti * Dafor * Daghveg * Dar El Barka * Dionaba * Djeol * Djiguenni * El Ghabra * El Ghaire * Fassala * Foum Gleita * Ghabou * Gouraye * Gueller * Guerou * Hamod * Hassichegar * Jidr-El Mouhguen * Kaédi * Kamour * Kankossa * Keur-Macene * Kobeni * Koumbi Saleh * Lahraj * Legrane * Leouossy * Lexeiba * Maghama * Magta-Lahjar * Male * Mbagne * Mbalal * Mbout * Mederdra * Monguel * Moudjeria * Nbeika * Ndiago * Néma * Niabina * Noual * Ouad Naga * Ouadane * Oualata * Oueid Jrid * Ould Yenge * Rdheidhi * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
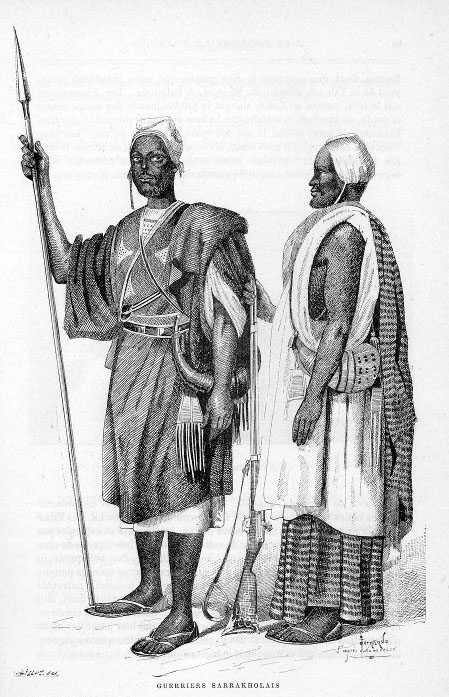 |
Soninke People
The Soninke people are a West African Mande-speaking ethnic group found in Mali, Fouta Djallon, southern Mauritania, eastern Senegal, Guinea and The Gambia. They speak the Soninke language, also called the Serakhulle or Azer language, which is one of the Mande languages. Soninke people were the founders of the ancient empire of Ghana or Wagadou c. 300–1240 CE, Subgroups of Soninke include the Maraka and Wangara. When the Ghana empire was destroyed, the resulting diaspora brought Soninkes to Mali, Mauritania, Senegal, Gambia, Burkina Faso, Côte d'Ivoire, Guinée-Conakry, modern-day Republic of Ghana, and Guinea-Bissau where some of this trading diaspora was called Wangara. Predominantly Muslims, the Soninke were one of the early ethnic groups from West Africa to convert to Islam in about the 10th century. The contemporary population of Soninke people is estimated to be over 2 million. The cultural practices of Soninke people are similar to the Mandé peoples, and thos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Railway Stations In Mauritania
Citizens of Mauritania have various transportation methods. Railways and highways connect major cities in the country. Mauritania is a coastal country so there are many ports along its coast and there are a few big rivers that run through the country. Lastly, there are 26 airports spread out throughout the country. Railways *717 km total of single track ( standard gauge), owned and operated by a government mining company, Société Nationale Industrielle et Minière (National Mining and Industrial Company, SNIM). The railway goes from the mines at Zouerat and El Rhein, passes another mine at Fderik, and ends at the port of Nouadhibou/Cansado. *One of the world's longest trains (up to 2.5 km long) runs here, with more than 200 wagons mainly transporting iron ore, and some carriages for passengers; alternatively, people sit on top of the iron piles. There are no rail links with adjacent countries. In 2008, a railway was proposed that would link Nouakchott with Ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Transport In Mauritania
Citizens of Mauritania have various transportation methods. Railways and highways connect major cities in the country. Mauritania is a coastal country so there are many ports along its coast and there are a few big rivers that run through the country. Lastly, there are 26 airports spread out throughout the country. Railways *717 km total of single track ( standard gauge), owned and operated by a government mining company, Société Nationale Industrielle et Minière (National Mining and Industrial Company, SNIM). The railway goes from the mines at Zouerat and El Rhein, passes another mine at Fderik, and ends at the port of Nouadhibou/Cansado. *One of the world's longest trains (up to 2.5 km long) runs here, with more than 200 wagons mainly transporting iron ore, and some carriages for passengers; alternatively, people sit on top of the iron piles. There are no rail links with adjacent countries. In 2008, a railway was proposed that would link Nouakchott with Ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
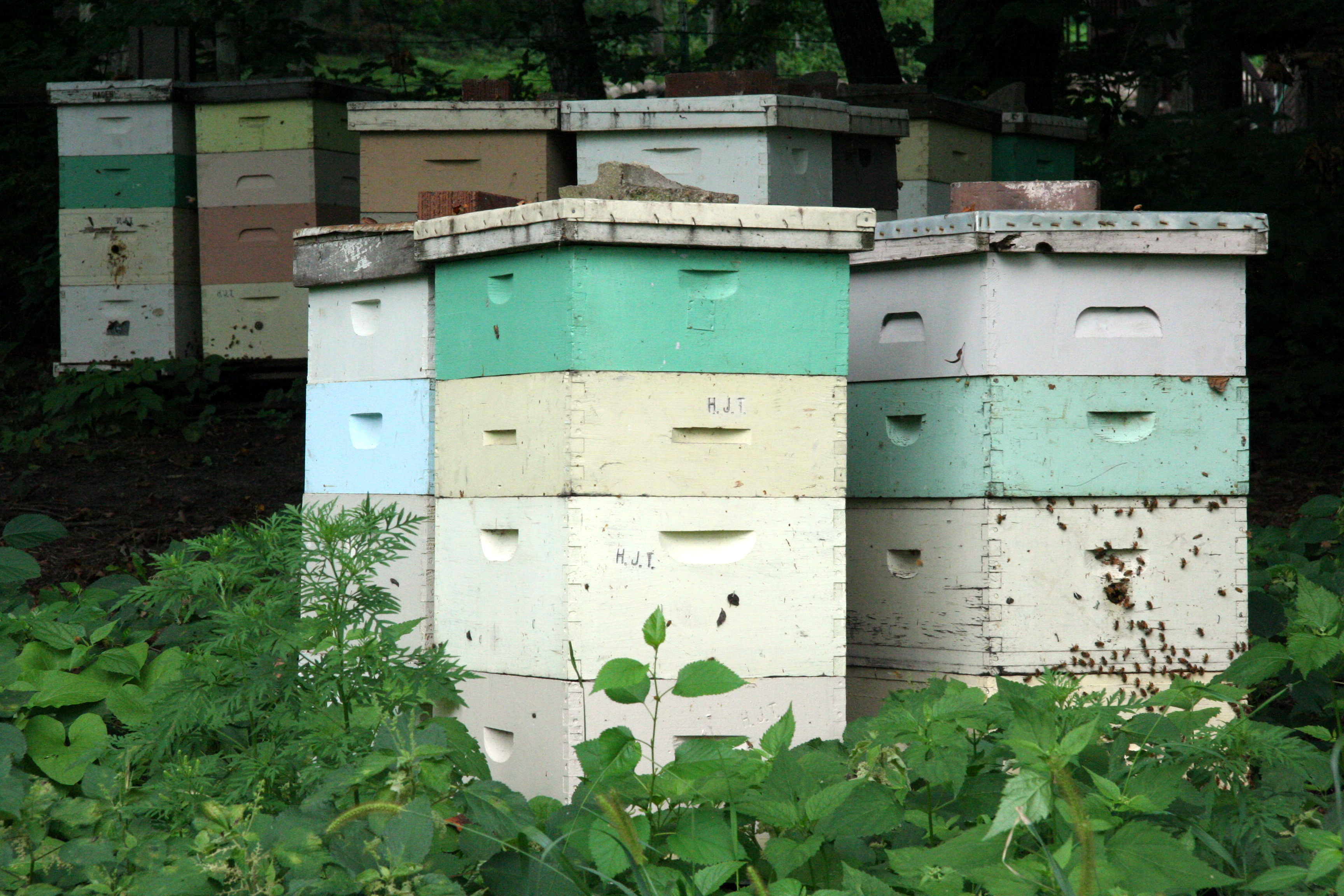 |
Beehive
A beehive is an enclosed structure in which some honey bee species of the subgenus ''Apis'' live and raise their young. Though the word ''beehive'' is commonly used to describe the nest of any bee colony, scientific and professional literature distinguishes ''nest'' from ''hive''. ''Nest'' is used to discuss colonies that house themselves in natural or artificial cavities or are hanging and exposed. ''Hive'' is used to describe an artificial/man-made structure to house a honey bee nest. Several species of ''Apis'' live in colonies, but for honey production the western honey bee (''Apis mellifera'') and the eastern honey bee (''Apis cerana'') are the main species kept in hives. The nest's internal structure is a densely packed group of hexagonal prismatic cells made of beeswax, called a honeycomb. The bees use the cells to store food (honey and pollen) and to house the brood (eggs, larvae, and pupae). Beehives serve several purposes: production of honey, pollination of nea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Kaédi Regional Hospital
The Kaedi Regional Hospital is the largest health facility in the Gorgol Region in southern Mauritania, and one known for its innovative architecture. The new hospital (actually a large extension onto an existing concrete structure) involves the use of handfired locally made brick and a design based on a sequence of simple and complex dome structures. The structure was intended to be both to be naturally cool even while letting in significant light from the outdoors. The hospital was designed by Fabrizio Carola of ADAUA, the Association for the Development of Traditional African Urbanism and Architecture. ADUA also used the design and construction project to develop and disseminate both a new "urban vernacular" architecture for the region and to train workers in new, low-cost and locally appropriate techniques in construction. Workmen were trained on site in the new techniques The hospital won the Aga Khan Award for Architecture The Aga Khan Award for Architecture (AKAA) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Dutch Brick (stabilized Earth Block)
A compressed earth block (CEB), also known as a pressed earth block or a compressed soil block, is a building material made primarily from an appropriate mix of fairly dry inorganic subsoil, non-expansive clay, sand, and aggregate. Forming compressed earth blocks requires dampening, mechanically pressing at high pressure, and then drying the resulting material. If the blocks are stabilized with a chemical binder such as Portland cement they are called ''compressed stabilized earth block'' (CSEB) or ''stabilized earth block'' (SEB). Typically, around of pressure is applied in compression, and the original material volume is reduced by about half. Creating CEBs differs from rammed earth in that the latter uses a larger formwork into which earth is poured and manually tamped down, creating larger forms such as a whole wall or more at one time, rather than building blocks. CEBs differ from mud bricks in that the latter are not compressed, but solidify through chemical changes that tak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
African Architecture
Like other aspects of the culture of Africa, the architecture of Africa is exceptionally diverse. Throughout the history of Africa, Africans have developed their own local architectural traditions. In some cases, broader regional styles can be identified, such as the Sudano-Sahelian architecture of West Africa. A common theme in traditional African architecture is the use of fractal scaling: small parts of the structure tend to look similar to larger parts, such as a circular village made of circular houses. African architecture in some areas has been influenced by external cultures for centuries, according to available evidence. Western architecture has influenced coastal areas since the late 15th century and is now an important source of inspiration for many larger buildings, particularly in major cities. African architecture uses a wide range of materials, including thatch, stick/wood, mud, mudbrick, rammed earth, and stone. These material preferences vary by region: North Af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the African countries and territories that are situated fully in that specified region, the term may also include polities that only have part of their territory located in that region, per the definition of the United Nations (UN). This is considered a non-standardized geographical region with the number of countries included varying from 46 to 48 depending on the organization describing the region (e.g. UN, WHO, World Bank, etc.). The African Union uses a different regional breakdown, recognizing all 55 member states on the continent - grouping them into 5 distinct and standard regions. The term serves as a grouping counterpart to North Africa, which is instead grouped with the definition of MENA (i.e. Middle East–North Africa) as it is part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Farmer
A farmer is a person engaged in agriculture, raising living organisms for food or raw materials. The term usually applies to people who do some combination of raising field crops, orchards, vineyards, poultry, or other livestock. A farmer might own the farm land or might work as a laborer on land owned by others. In most developed economies, a "farmer" is usually a farm owner ( landowner), while employees of the farm are known as ''farm workers'' (or farmhands). However, in other older definitions a farmer was a person who promotes or improves the growth of plants, land or crops or raises animals (as livestock or fish) by labor and attention. Over half a billion farmers are smallholders, most of whom are in developing countries, and who economically support almost two billion people. Globally, women constitute more than 40% of agricultural employees. History Farming dates back as far as the Neolithic, being one of the defining characteristics of that era. By the Bronze Age, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
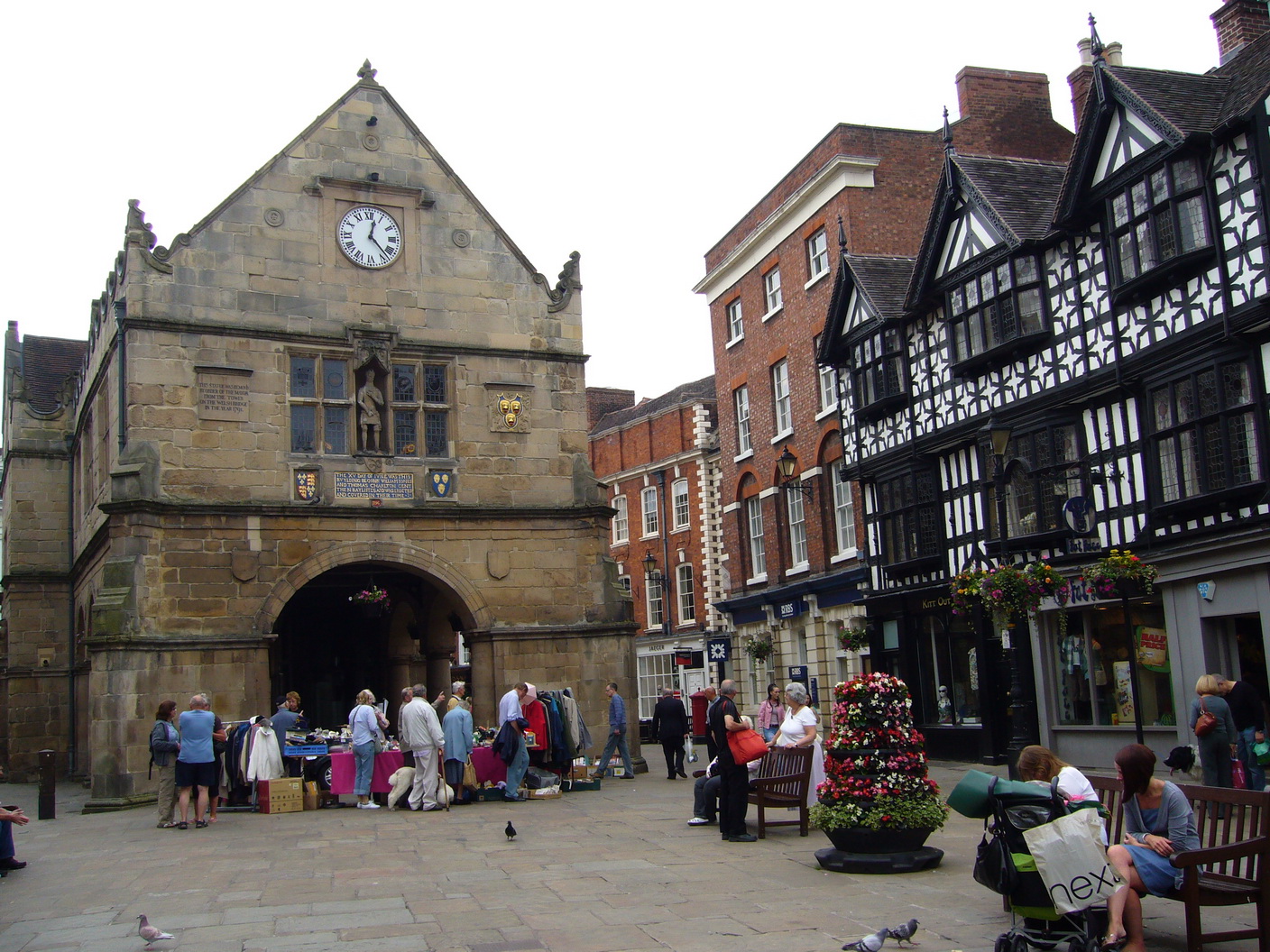 |
Market Town
A market town is a Human settlement, settlement most common in Europe that obtained by custom or royal charter, in the Middle Ages, a market right, which allowed it to host a regular marketplace, market; this distinguished it from a village or city. In Britain, small rural towns with a hinterland of villages are still commonly called market towns, as sometimes reflected in their names (e.g. Downham Market, Market Rasen, or Market Drayton). Modern markets are often in special halls, but this is a recent development, and the rise of permanent retail establishments has reduced the need for periodic markets. Historically the markets were open-air, held in what is usually called (regardless of its actual shape) the market square (or "Market Place" etc), and centred on a market cross (mercat cross in Scotland). They were and are typically open one or two days a week. History The primary purpose of a market town is the provision of goods and services to the surrounding locality. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |