|
Kawasaki Syndrome
Kawasaki disease is a syndrome of unknown cause that results in a fever and mainly affects children under 5 years of age. It is a form of vasculitis, where blood vessels become inflamed throughout the body. The fever typically lasts for more than five days and is not affected by usual medications. Other common symptoms include large lymph nodes in the neck, a rash in the genital area, lips, palms, or soles of the feet, and red eyes. Within three weeks of the onset, the skin from the hands and feet may peel, after which recovery typically occurs. In some children, coronary artery aneurysms form in the heart. While the specific cause is unknown, it is thought to result from an excessive immune system response to an infection in children who are genetically predisposed. It does not spread between people. Diagnosis is usually based on a person's signs and symptoms. Other tests such as an ultrasound of the heart and blood tests may support the diagnosis. Diagnosis must take int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
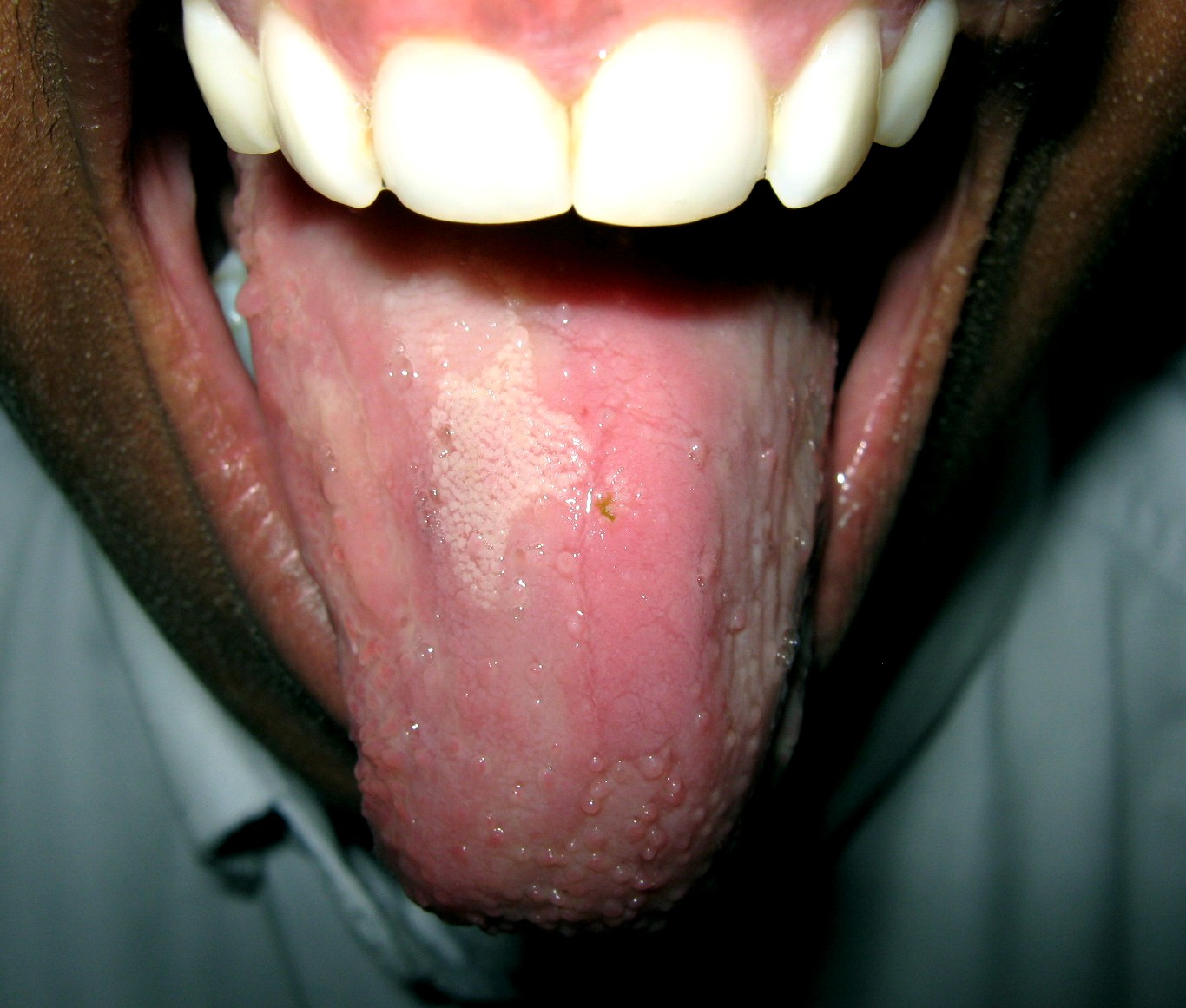
Strawberry Tongue
Glossitis can mean soreness of the tongue, or more usually inflammation with depapillation of the dorsal surface of the tongue (loss of the lingual papillae), leaving a smooth and erythematous (reddened) surface, (sometimes specifically termed atrophic glossitis). In a wider sense, glossitis can mean inflammation of the tongue generally. Glossitis is often caused by nutritional deficiency, nutritional deficiencies and may be painless or cause discomfort. Glossitis usually responds well to treatment if the cause is identified and corrected. Tongue soreness caused by glossitis is differentiated from burning mouth syndrome, where there is no identifiable change in the appearance of the tongue, and there are no identifiable causes. Symptoms Depending upon what exact meaning of the word glossitis is implied, signs and symptoms might include: * Smooth, shiny appearance of the tongue, caused by loss of lingual papillae. * Tongue color changes, usually to a darker red color than the nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antipyretics
An antipyretic (, from ''anti-'' 'against' and ' 'feverish') is a substance that reduces fever. Antipyretics cause the hypothalamus to override a prostaglandin-induced increase in temperature. The body then works to lower the temperature, which results in a reduction in fever. Most antipyretic medications have other purposes. The most common antipyretics in the US are usually ibuprofen and aspirin, which are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) used primarily as anti-inflammatories and analgesics (pain relievers), but which also have antipyretic properties; and paracetamol (acetaminophen), an analgesic without anti-inflammatory properties. There is some debate over the appropriate use of such medications, since fever is part of the body's immune response to infection. A study published by the Royal Society claims that fever suppression causes at least 1% more influenza deaths in the United States, or 700 extra deaths per year. Non-pharmacological treatment Bathing or s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronary Arteries
The coronary arteries are the arterial blood vessels of coronary circulation, which transport oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. The heart requires a continuous supply of oxygen to function and survive, much like any other tissue or organ of the body. The coronary arteries wrap around the entire heart. The two main branches are the left coronary artery and right coronary artery. The arteries can additionally be categorized based on the area of the heart for which they provide circulation. These categories are called ''epicardial'' (above the epicardium, or the outermost tissue of the heart) and ''microvascular'' (close to the endocardium, or the innermost tissue of the heart). Reduced function of the coronary arteries can lead to decreased flow of oxygen and nutrients to the heart. Not only does this affect supply to the heart muscle itself, but it also can affect the ability of the heart to pump blood throughout the body. Therefore, any disorder or disease of the coronary ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspirin
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and/or inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat include Kawasaki disease, pericarditis, and rheumatic fever. Aspirin is also used long-term to help prevent further heart attacks, ischaemic strokes, and blood clots in people at high risk. For pain or fever, effects typically begin within 30 minutes. Aspirin works similarly to other NSAIDs but also suppresses the normal functioning of platelets. One common adverse effect is an upset stomach. More significant side effects include stomach ulcers, stomach bleeding, and worsening asthma. Bleeding risk is greater among those who are older, drink alcohol, take other NSAIDs, or are on other blood thinners. Aspirin is not recommended in the last part of pregnancy. It is not generally recommended in children with infections because of the risk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was COVID-19 pandemic in Hubei, identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease quickly spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic. The symptoms of COVID‑19 are variable but often include fever, cough, headache, fatigue, breathing difficulties, Anosmia, loss of smell, and Ageusia, loss of taste. Symptoms may begin one to fourteen days incubation period, after exposure to the virus. At least a third of people who are infected Asymptomatic, do not develop noticeable symptoms. Of those who develop symptoms noticeable enough to be classified as patients, most (81%) develop mild to moderate symptoms (up to mild pneumonia), while 14% develop severe symptoms (dyspnea, Hypoxia (medical), hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging), and 5% develop critical symptoms (respiratory failure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome In Children
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), or paediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome (PIMS / PIMS-TS), or systemic inflammatory syndrome in COVID-19 (SISCoV), is a rare systemic illness involving persistent fever and extreme inflammation following exposure to SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19. MIS-C has also been monitored as a potential, rare pediatric adverse event following COVID-19 vaccination. It can rapidly lead to medical emergencies such as insufficient blood flow around the body (a condition known as shock). Failure of one or more organs can occur. A warning sign is unexplained persistent fever with severe symptoms following exposure to COVID-19. Prompt referral to paediatric specialists is essential, and families need to seek urgent medical assistance. Most affected children will need intensive care. All affected children have persistent fever. Other clinical features vary. The first symptoms often include acute abdominal pain with dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scarlet Fever
Scarlet fever, also known as Scarlatina, is an infectious disease caused by ''Streptococcus pyogenes'' a Group A streptococcus (GAS). The infection is a type of Group A streptococcal infection (Group A strep). It most commonly affects children between five and 15 years of age. The signs and symptoms include a sore throat, fever, headache, swollen lymph nodes, and a characteristic rash. The face is flushed and the rash is red and blanching. It typically feels like sandpaper and the tongue may be red and bumpy. The rash occurs as a result of capillary damage by exotoxins produced by ''S.pyogenes''. On darker pigmented skin the rash may be hard to discern. Scarlet fever affects a small number of people who have strep throat or streptococcal skin infections. The bacteria are usually spread by people coughing or sneezing. It can also be spread when a person touches an object that has the bacteria on it and then touches their mouth or nose. The diagnosis is typically confirmed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Susceptibility
Public health genomics is the use of genomics information to benefit public health. This is visualized as more effective preventive care and disease treatments with better specificity, tailored to the genetic makeup of each patient. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (U.S.), Public Health genomics is an emerging field of study that assesses the impact of genes and their interaction with behavior, diet and the environment on the population's health. This field of public health genomics is less than a decade old. A number of think tanks, universities, and governments (including the U.S., UK, and Australia) have started public health genomics projects. Research on the human genome is generating new knowledge that is changing public health programs and policies. Advances in genomic sciences are increasingly being used to improve health, prevent disease, educate and train the public health workforce, other healthcare providers, and citizens. Public policy Pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents (pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune System
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use molecules and cells to perform their functions. Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against virus infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient plants and animals and remain in their modern descendants. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronary Artery Aneurysm
Coronary artery aneurysm is an abnormal dilatation of part of the coronary artery. This rare disorder occurs in about 0.3–4.9% of patients who undergo coronary angiography. Signs and symptoms Causes Acquired causes include atherosclerosis in adults, Kawasaki disease in children and coronary catheterization. With the invention of drug eluting stents, there has been more cases implying stents lead to coronary aneurysms. The pathophysiology, although not completely understood, might be comparable to that of aneurysms of larger vessels. This includes disruption of the arterial media, weakening of the arterial wall, increased wall strain and slow dilatation of the coronary artery portion. It can also be congenital. The following risk factors are thought to be associated with coronary artery aneurysms: # Individual's genetic make-up, especially in patients with congenital coronary artery aneurysms # Coronary artery disease (atherosclerosis) # Vasculitic and connective tissue disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |