|
Kattsund-Koster Dyke Swarm
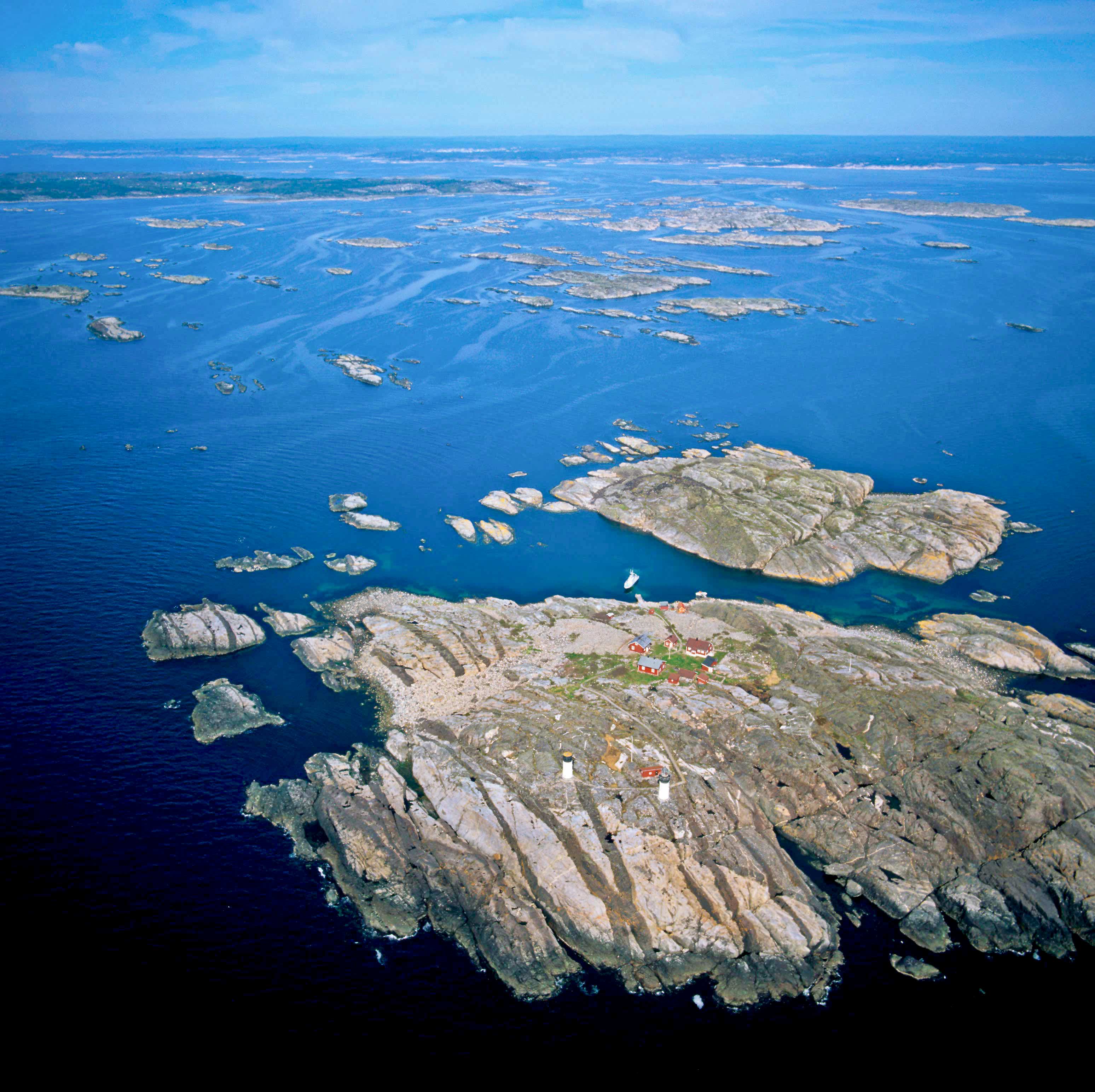
The Kattsund-Koster dyke swarm is a collection of dykes of Mesoproterozoic age in southeastern Norway and the West Coast of Sweden. The most prominent outcrops are in the Koster Islands in Sweden and Kattsund in Norway, hence the name. The dykes are made up of tholeiitic diabase and some dykes of intermediate composition. Some dykes are deformed and metamorphosed into amphibolite. Radiometric dating has shown that the dyke swarm is about 1421 million years old. Geologists have suggested that the dyke swarm is related to extensional tectonics. See also *Bohus granite *Gothian orogeny *Jotnian *Satakunta dike swarms *Sveconorwegian orogeny The Sveconorwegian orogeny was an orogenic system active 1140 to 960 million years ago and currently exposed as the Sveconorwegian orogenic belt in southwestern Sweden and southern Norway. In Norway the orogenic belt is exposed southeast of the f ... References {{Geology of Fennoscandia Dike swarms Mesoproterozoic magmatism Geography of Ă ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensional Tectonics
Extensional tectonics is concerned with the structures formed by, and the tectonic processes associated with, the stretching of a planetary body's crust or lithosphere. Deformation styles The types of structure and the geometries formed depend on the amount of stretching involved. Stretching is generally measured using the parameter ''β'', known as the ''beta factor'', where : \beta = \frac \,, ''t''0 is the initial crustal thickness and ''t''1 is the final crustal thickness. It is also the equivalent of the strain parameter ''stretch''. Low beta factor In areas of relatively low crustal stretching, the dominant structures are high to moderate angle normal faults, with associated half grabens and tilted fault blocks. High beta factor In areas of high crustal stretching, individual extensional faults may become rotated to too low a dip to remain active and a new set of faults may be generated. Large displacements may juxtapose syntectonic sediments against metamorphic roc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of VÀstra Götaland County
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words âGeoâ (The Earth) and âGraphienâ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γΔÏÎłÏαÏία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276â194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexitiesânot merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Ăstfold
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words âGeoâ (The Earth) and âGraphienâ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γΔÏÎłÏαÏία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276â194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexitiesânot merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoproterozoic Magmatism
The Mesoproterozoic Era is a geologic era that occurred from . The Mesoproterozoic was the first era of Earth's history for which a fairly definitive geological record survives. Continents existed during the preceding era (the Paleoproterozoic), but little is known about them. The continental masses of the Mesoproterozoic were more or less the same ones that exist today, although their arrangement on the Earth's surface was different. Major events and characteristics The major events of this era are the breakup of the Columbia supercontinent, the formation of the Rodinia supercontinent, and the evolution of sexual reproduction. This era is marked by the further development of continental plates and plate tectonics. The supercontinent of Columbia broke up between 1500 and 1350 million years ago, and the fragments reassembled into the supercontinent of Rodinia around 1100 to 900 million years ago, on the time boundary between the Mesoproterozoic and the subsequent Neoproterozoic. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dike Swarms
Dyke (UK) or dike (US) may refer to: General uses * Dyke (slang), a slang word meaning "lesbian" * Dike (geology), a subvertical sheet-like intrusion of magma or sediment * Dike (mythology), ''DikÄ'', the Greek goddess of moral justice * Dikes, diagonal pliers, also called side-cutting pliers, a hand tool used by electricians and others * Dyke (automobile company), established 1899 Structures * Dyke (embankment) or dike, a natural or artificial slope or wall to regulate water levels, often called a levee in American English * Ditch, a water-filled drainage trench * A regional term for a dry stone wall People * Dyke (surname) * Dyke baronets, a title in the Baronetage of England * Dykes (surname), a British surname found particularly in northern England Places Settlements * Dike, Iowa, United States * Dykes, Missouri, United States * Dyke, Moray, Scotland * Dike, Texas, United States * Dyke, Virginia, United States * Dyke, Lincolnshire, England * Little Dyke, Nova Scotia, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sveconorwegian Orogeny
The Sveconorwegian orogeny was an orogenic system active 1140 to 960 million years ago and currently exposed as the Sveconorwegian orogenic belt in southwestern Sweden and southern Norway. In Norway the orogenic belt is exposed southeast of the front of the Caledonian nappe system and in nappe windows. The Sveconorwegian orogen is commonly grouped within the Grenvillian Mesoproterozoic orogens. Contrary to many other known orogenic belts the Sveconorwegian orogens eastern border does not have any known suture zone with ophiolites. Tectonic segments The Sveconorwegian orogen orogenic belt is composed of five segments largely made up of gneiss that were disrupted by both extension and compression in the timespan between 1140 and 980 million years ago. From west to east the segments are the terranes of Telemarkia, Bamble, Kongsberg and Idefjorden plus the Eastern Segment. The segments are separated from each other by large-scale shear zones. *Bamble Terrane: The Bamble Terrane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satakunta Dike Swarms
The Satakunta dyke swarms are a series of dyke swarms, a group of magmatic intrusions, of Mesoproterozoic age in the Bothnian Sea and western and central Finland. They are made up of Subjotnian diabase dikes, associated with rapakivi magmatism. They were most likely formed on the Columbia supercontinent. Föglö dyke swarm HÀme dyke swarm The HÀme dyke swarm formed due to the upwelling of mantle, possibly related to the Gothian orogeny. The swarms were triggered by extensional plate tectonics and convection of hot upper mantle. Tholeiitic magmas, formed under the continental lithosphere, were probably encouraged by elevated mantle temperature underneath the Columbia supercontinent. The time of formation was approximately 1640 million years ago. Satakunta-Ulvö dyke swarm The dyke swarm has been considered to be a result of a failed rift in the Bothnian Sea that developed as part of an extensional tectonic setting within the supercontinent of Columbia. At various locatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jotnian
In north European geology, Jotnian sediments are a group of Precambrian rocks more specifically assigned to the Mesoproterozoic Era ( Riphean), albeit some might be younger. Jotnian sediments include the oldest known sediments in the Baltic area that have not been subject to metamorphism. Stratigraphically, Jotnian sediments overlie the rapakivi granites and other igneous and metamorphic rocks and are often intruded by younger diabases. Overview Jotnian sediments include quartz-rich sandstones, siltstones, arkose, shale and conglomerates. The characteristic red colour of Jotnian sediments is due to their deposition in subaerial (e.g. non-marine) conditions. Jotnian sediments are the oldest known sediments in the Baltic area that have not been subject to metamorphism. Their age is poorly constrained, but generally they are younger than the rapakivi granites and older than ''Postjotnian'' diabases that intrude the sediments. This means that Jotnian sediments were deposited ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothian Orogeny
The Gothian orogeny ( sv, Gotiska orogenesen) or Kongsberg orogeny was an orogeny in western Fennoscandia that occurred between 1750 and 1500 million years ago. It precedes the younger Sveconorwegian orogeny that has overprinted much of it. The Gothian orogeny formed along a subduction zone and resulted in the formation of calc-alkaline igneous rocks 1700 to 1550 million years ago, including some of the younger members of the Transscandinavian Igneous Belt. The deformation associated with the orogeny can be seen in metatonalite, paragneiss and biotite orthogneisses in southeast Norway. These rocks were all subject to amphibolite facies metamorphism Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of ch .... Footnotes References * * {{Geology of Europe Orogenies of Europe Paleop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohus Granite
The Bohus granite ( sv, Bohusgranit) is a type of granite that crops out along the Swedish West Coast in BohuslĂ€n. In Norway the same granites are termed Iddefjord granite ( no, Iddefjordsgranitt), Ăstfold granite and Halden granite. A large quarrying industry has developed around the granites, mainly producing blocks. Large scale extraction begun in the 1840s and employment in the quarries peaked in the 1920s with over 7,000 people working in the industry. The rock is valued for its durability. In the first half of the 20th century the transport of quarried Bohus granite was done with the aid of by the Lysekil Line. In Norway Iddefjord granite has been a relatively common rock in architecture, and many of the statues of Frogner Park in Oslo are made of Iddefjord granite. Iddefjord granite is the official county rock of Ăstfold in Norway. Geology Geologically the Bohus is a monzogranite, a subtype of granite. Besides the main minerals plagioclase, K-feldspar and quartz the Bohus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiometric Dating
Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to date materials such as rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurities were selectively incorporated when they were formed. The method compares the abundance of a naturally occurring radioactive isotope within the material to the abundance of its decay products, which form at a known constant rate of decay. The use of radiometric dating was first published in 1907 by Bertram Boltwood and is now the principal source of information about the absolute age of rocks and other geological features, including the age of fossilized life forms or the age of Earth itself, and can also be used to date a wide range of natural and man-made materials. Together with stratigraphic principles, radiometric dating methods are used in geochronology to establish the geologic time scale. Among the best-known techniques are radiocarbon dating, potassiumâargon dating and uraniumâlead dating. By al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |