|
Kasuri (other)
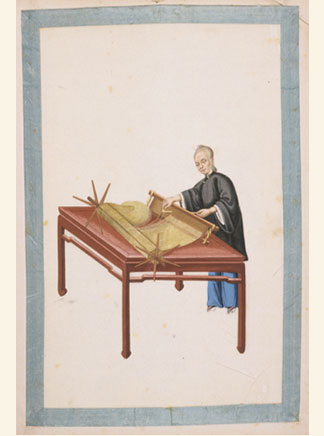
is the Japanese term for fabric that has been woven with fibers dyed specifically to create patterns and images in the fabric, typically referring to fabrics produced within Japan using this technique. It is a form of ikat dyeing, traditionally resulting in patterns characterized by their blurred or brushed appearance. The warp and weft threads are resist-dyed in specific patterns prior to dyeing, with sections of the warp and weft yarns tightly wrapped with thread to protect them from the dye. When woven together, the undyed areas interlace to form patterns, with many variations – including highly pictographic and multi-colored results – possible to achieve. patterns may be applied to either the warp or the weft, or to both in order to create a resulting woven pattern, with the cloth classified using different names depending on the method used. Though commonly confused, the terms and are not interchangeable. While refers to a dyeing technique, , literally translating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San'in Region
The is an area in the southwest of Honshū, the main island of Japan. It consists of the northern part of the Chūgoku region, facing the Sea of Japan. Etymology The name San'in in the Japanese language is formed from two kanji characters. The first, , "mountain", and the second, represents the "yin" of yin and yang. The name means the northern, shady side of the mountains in contrast to the ''yang'' "southern, sunny" San'yō region to the south. History Early history The San'in region has numerous Paleolithic and Jōmon period (14,000 – 300 BC) remains, but its Yayoi period (300 BC – 250 AD) remains are the largest in Japan. The Mukibanda Yayoi remains in the low foothills of Mount Daisen in the cities of Daisen and Yonago, Tottori Prefecture are the largest in Japan. The site is still only partially excavated, but indicates that the San'in was a regional center of power in the period. The mythology of the Shinto religion is largely based in the Izumo area o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ōshima-tsumugi
Ōshima-tsumugi is a traditional craft textile produced in the Amami Islands (mainly Amami Ōshima) in southern Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan. It is a hand woven plain-weave silk cloth dyed in mud. The textile is most commonly used for making kimonos. Oshima-tsumugi kimonos are often simply called Ōshima. Outline Ōshima-tsumugi is considered one of the three finest textiles in the world, along with French Gobelin weaving, and Persian carpets in Iran. Ōshima-tsumugi has a long history of about 1,300 years. Ōshima-tsumugi is known for being supple, lightweight, and wrinkle-resistant. Oshima tsumugi kimono are also traditionally dyed using mud and a dye produced from the bark of the Techigi Tree (Rhaphiolepis umbellata) Indigo and other natural dyes as well as synthetic dyes are also used. Due to its hardwearing nature, it is often said that up to three generations can wear the same kimono. Ōshima-tsumugi kimono are hugely valued for their detailed kasuri patterns and deep b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bokashi (other) , an image effect related to ''Bokashi''.
{{Disambiguation ...
Bokashi (ぼかし) is Japanese for "shading off" or "gradation." It may refer to: * Bokashi (printing), a printing technique * Bokashi gasuri, a dyeing technique for textiles * Fogging (censorship), blurring an image as a form of censorship * Bokashi (horticulture), an organic waste fermentation-process like silage * Bokeh In photography, bokeh ( or ; ) is the aesthetic quality of the blur produced in out-of-focus parts of an image. Bokeh has also been defined as "the way the lens renders out-of-focus points of light". Differences in lens aberrations and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miyakojima, Okinawa
is a Cities of Japan, city in Okinawa Prefecture, Japan, located on the Miyako Islands. As of 2012, it had a population of 54,908. The current mayor is Kazuyuki Zakimi, who took office on January 25, 2021. History The modern city of Miyakojima was established on October 1, 2005, from the merger of the old city of Hirara, Okinawa, Hirara, the towns of Gusukube, Okinawa, Gusukube, Irabu, Okinawa, Irabu and Shimoji, Okinawa, Shimoji, and the village of Ueno, Okinawa, Ueno (all from Miyako District, Okinawa, Miyako District). As a result of the merger, Miyako District only has one remaining village. Geography Since the city was created by merging several towns that were located on different islands, the city of Miyakojima consists of multiple islands. The islands administered by the city include: * Miyako-jima * Ikema Island, Ikema-jima * Ogami Island, Ōgami-jima * Irabu Island, Irabu-jima * Shimojishima * Kurimajima, Kurima-jima Several of the islands are connected by bridge. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramie
Ramie (pronounced: , ; from Malay ) is a flowering plant in the nettle family Urticaceae, native to eastern Asia. It is a herbaceous perennial growing to tall;Ramie: Old Fiber - New Image at the (September 17, 2002). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amami Ōshima
, also known as Amami, is the largest island in the Amami archipelago between Kyūshū and Okinawa. It is one of the Satsunan Islands. The island, 712.35 km2 in area, has a population of approximately 73,000 people. Administratively it is divided into the city of Amami, the towns of Tatsugō, Setouchi, and the villages of Uken and Yamato in Kagoshima Prefecture. Much of the island is within the borders of the Amami Guntō National Park. In 2021, it was listed as part of the serial UNESCO World Heritage Site of Amami-Ōshima Island, Tokunoshima Island, northern part of Okinawa Island, and Iriomote Island. History It is uncertain when Amami Ōshima was first settled. Stone tools indicate settlement in the Japanese Paleolithic period, and other artifacts, including pottery, indicate a constant contact with Jōmon, Yayoi and Kofun period Japan. The island is mentioned in the ancient Japanese chronicle '' Nihon Shoki'' in an entry for the year 657 AD. During the Nara peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Ikat
''Ikat'' (in Indonesian languages means "bind") is a dyeing technique originating from Indonesia used to pattern textiles that employs resist dyeing on the yarns prior to dyeing and weaving the fabric. In ''ikat'', the resist is formed by binding individual yarns or bundles of yarns with a tight wrapping applied in the desired pattern. The yarns are then dyed. The bindings may then be altered to create a new pattern and the yarns dyed again with another colour. This process may be repeated multiple times to produce elaborate, multicolored patterns. When the dyeing is finished all the bindings are removed and the yarns are woven into cloth. In other resist-dyeing techniques such as tie-dye and ''batik'' the resist is applied to the woven cloth, whereas in ikat the resist is applied to the yarns before they are woven into cloth. Because the surface design is created in the yarns rather than on the finished cloth, in ikat both fabric faces are patterned. A characteristic of ''ik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |