|
Karol Pollak
Karol Franciszek Pollak (November 15, 1859 – December 17, 1928) was a Polish electrotechnician, inventor and businessman. Early life He was born in Sanok, Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria, part of the Austrian Empire . His father was Karol Pollak (1818–80) who was a printer, bookseller and publisher. Karol (not to be mistaken with his father) worked in his youth as an electrician and showed great technical skills in it. In 1883 he was employed in the laboratory of British company "The Patent Utilisation Co". He designed and recorded his first patents in that period. In 1885 he attended electrotechnics studies at the Royal Polytechnic University in Charlottenburg. Activity In Berlin, Pollak ran electrotechnical factory "G. Wehr Telegraphen-Bau-Anstalt". Later he returned to Britain to commercialize his patents, which were released under anglicised version of his name, "Charles Pollak". In 1886, he became the director of a Paris company of electric tramways of his desig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanok
Sanok (in full the Royal Free City of Sanok — pl, Królewskie Wolne Miasto Sanok, rue, Санок, ''Sanok'', ua, Cянік, ''Sianik'', la, Sanocum, yi, סאניק, ''Sonik'') is a town in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship of south-eastern Poland with 38,397 inhabitants, as of June 2016. Located on the San River and around 52 km south of Przemyśl, Sanok lies directly by the Carpathian Mountains. Once settled by Poles, Jews and Lemkos, the town's history goes back almost 1000 years when it was part of a medieval trade route. The Museum of Folk Architecture as well as the refurbished Sanok Castle and Old Town are popular points of interest. The region also features a 70 km trail for hikers and cyclists. Geography The city of Sanok is the capital of Sanok County in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship in Poland. Previously, it was in the Krosno Voivodeship (1975–1998) and in the Ruthenian Voivodeship (1340–1772), which was part of the Red Ruthenia region, and in wid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw Polytechnic
The Warsaw University of Technology ( pl, Politechnika Warszawska, lit=Varsovian Polytechnic) is one of the leading institutes of technology in Poland and one of the largest in Central Europe. It employs 2,453 teaching faculty, with 357 professors (including 145 titular professors). The student body numbers 36,156 (as of 2011), mostly full-time. There are 19 faculties (divisions) covering almost all fields of science and technology. They are in Warsaw, except for one in Płock. The Warsaw University of Technology has about 5,000 graduates per year. According to the 2008 ''Rzeczpospolita'' newspaper survey, engineers govern Polish companies. Warsaw Tech alums make up the highest percentage of Polish managers and executives. Every ninth president among the top 500 corporations in Poland is a graduate of the Warsaw University of Technology. Professor Kurnik, the rector, explained that the school provides a solid basis for the performance of managers by equipping its students with an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1859 Births
Events January–March * January 21 – José Mariano Salas (1797–1867) becomes Conservative interim President of Mexico. * January 24 ( O. S.) – Wallachia and Moldavia are united under Alexandru Ioan Cuza (Romania since 1866, final unification takes place on December 1, 1918; Transylvania and other regions are still missing at that time). * January 28 – The city of Olympia is incorporated in the Washington Territory of the United States of America. * February 2 – Miguel Miramón (1832–1867) becomes Conservative interim President of Mexico. * February 4 – German scholar Constantin von Tischendorf rediscovers the ''Codex Sinaiticus'', a 4th-century uncial manuscript of the Greek Bible, in Saint Catherine's Monastery on the foot of Mount Sinai, in the Khedivate of Egypt. * February 14 – Oregon is admitted as the 33rd U.S. state. * February 12 – The Mekteb-i Mülkiye School is founded in the Ottoman Empire. * February 17 – French naval forces under Char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrolytic Capacitor
An electrolytic capacitor is a polarized capacitor whose anode or positive plate is made of a metal that forms an insulating oxide layer through anodization. This oxide layer acts as the dielectric of the capacitor. A solid, liquid, or gel electrolyte covers the surface of this oxide layer, serving as the cathode or negative plate of the capacitor. Due to their very thin dielectric oxide layer and enlarged anode surface, electrolytic capacitors have a much higher capacitance-voltage (CV) product per unit volume than ceramic capacitors or film capacitors, and so can have large capacitance values. There are three families of electrolytic capacitor: aluminum electrolytic capacitors, tantalum electrolytic capacitors, and niobium electrolytic capacitors. The large capacitance of electrolytic capacitors makes them particularly suitable for passing or bypassing low-frequency signals, and for storing large amounts of energy. They are widely used for decoupling or noise filtering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo Graetz
Leo Graetz (26 September 1856 – 12 November 1941) was a German physicist. He was born in Breslau, Germany, and was the son of historian Heinrich Graetz. Graetz was one of the first to investigate the propagation of electromagnetic energy. The Graetz number (''Gz''), a dimensionless number describing heat flow, is named after him. Also sometimes known by his name is the diode bridge rectifier circuit that was invented by Polish electrotechnician Karol Pollak in 1896 and that was independently invented and published by Leo Graetz in 1897. In 1880 he confirmed the Stefan–Boltzmann law. Graetz died in Munich Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and Ha ... at age 85. Publications * ''Die Elektrizität und ihre Anwendungen'' (''Electricity and Its Applications''), Stutt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
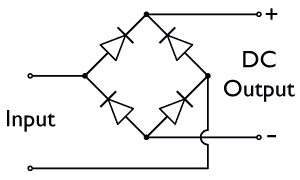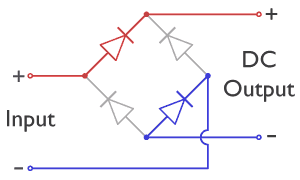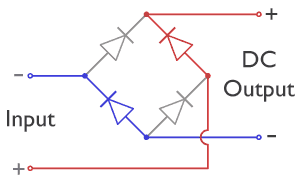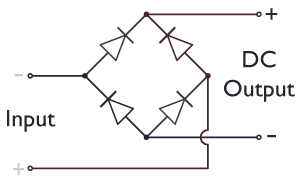
Diode Bridge
A diode bridge is a bridge rectifier circuit of four diodes that is used in the process of converting alternating current (AC) from the input terminals to direct current (DC, i.e. fixed polarity) on the output terminals. Its function is to convert the negative-going AC pulses into positive going pulses, after which a low-pass filter can be used to smooth the result into DC. When used in its most common application, for conversion of an alternating-current (AC) input into a direct-current (DC) output, it is known as a bridge rectifier. A bridge rectifier provides full-wave rectification from a two-wire AC input, resulting in lower cost and weight as compared to a rectifier with a three-wire input from a transformer with a center-tapped secondary winding. The essential feature of a diode bridge is that the polarity of the output is the same regardless of the polarity at the input. The diode bridge circuit was invented by Polish electrotechnician Karol Pollak and patented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The reverse operation (converting DC to AC) is performed by an Power inverter, inverter. The process is known as ''rectification'', since it "straightens" the direction of current. Physically, rectifiers take a number of forms, including Vacuum tube#Diodes, vacuum tube diodes, wet chemical cells, mercury-arc valves, stacks of copper and selenium rectifier, selenium oxide plates, Diode#Semiconductor diodes, semiconductor diodes, silicon-controlled rectifiers and other silicon-based semiconductor switches. Historically, even synchronous electromechanical switches and motor-generator sets have been used. Early radio receivers, called crystal radios, used a "Cat's-whisker detector, cat's whisker" of fine wire pressing on a crystal of galena (lead sulfide) to serve as a point-contact rectifier or "crystal detec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollak Bridge
Pollak is an Austrian surname, and is a variant of ''Polak'' usually of Jewish Ashkenazic origin, it originates as an ethnic surname for Jews between Austria, Poland and Germany. Notable people with the surname include: Athletes * Burglinde Pollak (1951–), German athlete * Egon Pollak (1898–1994), Austrian football player * James Howard Pollak Jr. (1963–), American cyclist * Jaroslav Pollák (1947–), Slovak football player * Josef Pollák, Czech orienteering competitor * Mike Pollak (1985–), American football player * Zoltán Pollák (1984–), Hungarian football player Other people * Cheryl Pollak (1967–), American actress * Felix Pollak (1909–1987), American poet * Henry O. Pollak (1927–), Austrian-American mathematician * Jacob Pollak (c. 1460–1541), Polish rabbi, founder of the ''Pilpul'' method of halakic study * Joachim Pollak (1798–1879), Austrian rabbi * Joel Pollak (1977–), American politician and author * Jonathan Pollak (1982–), Israeli anar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead Acid Battery
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is toxic, even in small amounts, especially to children. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited to organolead compounds. Like the lighter members of the group, le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galvanic Cell
A galvanic cell or voltaic cell, named after the scientists Luigi Galvani and Alessandro Volta, respectively, is an electrochemical cell in which an electric current is generated from spontaneous Oxidation-Reduction reactions. A common apparatus generally consists of two different metals, each immersed in separate beakers containing their respective metal ions in solution that are connected by a salt bridge or separated by a porous membrane. Volta was the inventor of the voltaic pile, the first Battery (electricity), electrical battery. In common usage, the word "battery" has come to include a single galvanic cell, but a battery properly consists of multiple cells. History In 1780, Luigi Galvani discovered that when two different metals (e.g., copper and zinc) are in contact and then both are touched at the same time to two different parts of a muscle of a frog leg, to close the circuit, the frog's leg contracts. He called this "bioelectricity, animal electricity". The frog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Energy
Chemical energy is the energy of chemical substances that is released when they undergo a chemical reaction and transform into other substances. Some examples of storage media of chemical energy include batteries, Schmidt-Rohr, K. (2018). "How Batteries Store and Release Energy: Explaining Basic Electrochemistry", ''J. Chem. Educ.'' 95: 1801-1810. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.8b00479 food, and gasoline (as well as oxygen gas, which is of high chemical energy due to its relatively weak double bond and indispensable for chemical-energy release in gasoline combustion). Schmidt-Rohr, K. (2015). "Why Combustions Are Always Exothermic, Yielding About 418 kJ per Mole of O2", ''J. Chem. Educ.'' 92: 2094-2099. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.5b00333 Breaking and re-making of chemical bonds involves energy, which may be either absorbed by or evolved from a chemical system. If reactants with relatively weak electron-pair bonds convert to more strongly bonded products, energ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microphone
A microphone, colloquially called a mic or mike (), is a transducer that converts sound into an electrical signal. Microphones are used in many applications such as telephones, hearing aids, public address systems for concert halls and public events, motion picture production, live and recorded audio engineering, sound recording, two-way radios, megaphones, and radio and television broadcasting. They are also used in computers for recording voice, speech recognition, VoIP, and for other purposes such as ultrasonic sensors or knock sensors. Several types of microphone are used today, which employ different methods to convert the air pressure variations of a sound wave to an electrical signal. The most common are the dynamic microphone, which uses a coil of wire suspended in a magnetic field; the condenser microphone, which uses the vibrating diaphragm as a capacitor plate; and the contact microphone, which uses a crystal of piezoelectric material. Microphones typically n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |