|
Karo Hills
The Karo Hills () are rounded, ice-free foothills in Antarctica extending for along the west side of the terminus of Scott Glacier, from Mount Salisbury north-northwest to the edge of the Ross Ice Shelf. Discovery and naming The Karo Hills were first seen and roughly mapped by the Byrd Antarctic Expedition between 1928 and 1930, and were named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Vice Admiral Henry Arnold Karo, Director of the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey from 1955 to 1965 and Deputy Director of the U.S. Environmental Science Services Administration from 1965 to 1967. Location The Karo Hills run north-northeast from Mount Salisbury in the south, separating the Koerwitz Glacier to the west from the Scott Glacier to the east. Other peaks include Mount Hastings and Mount Rigby. Features Mount Salisbury . An ice-free mountain, high, standing at the west side of the lower Scott Glacier at the south end of the Karo Hills. First seen and roughly mapped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scott Glacier (Transantarctic Mountains)
The Scott Glacier is a major glacier, long, that drains the East Antarctic Ice Sheet through the Queen Maud Mountains to the Ross Ice Shelf. The Scott Glacier is one of a series of major glaciers flowing across the Transantarctic Mountains, with the Amundsen Glacier to the west and the Leverett and Reedy glaciers to the east. Geography The Scott Glacier originates on the Antarctic Plateau in the vicinity of D'Angelo Bluff and Mount Howe, and descends between the Nilsen Plateau and the mountains of the Watson Escarpment to enter Ross Ice Shelf just west of the Tapley Mountains. The Tapley Mountains, Watson Escarpment, Mount Blackburn, and the La Gorce Mountains bound the Scott Glacier on its eastern margin, while the Karo Hills, Hays Mountains, Faulkner Escarpment, and Rawson Mountains define the western edge of the Scott's drainage. History Scott Glacier was discovered in December 1929 by the Byrd Antarctic Expedition geological party under Laurence Gould. The Scot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
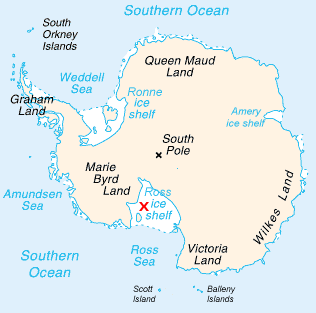
Ross Ice Shelf
The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (, an area of roughly and about across: about the size of France). It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than long, and between high above the water surface. Ninety percent of the floating ice, however, is below the water surface. Most of Ross Ice Shelf is in the Ross Dependency claimed by New Zealand. It floats in, and covers, a large southern portion of the Ross Sea and the entire Roosevelt Island located in the east of the Ross Sea. The ice shelf is named after Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered it on 28 January 1841. It was originally called "The Barrier", with various adjectives including "Great Ice Barrier", as it prevented sailing further south. Ross mapped the ice front eastward to 160° W. In 1947, the U.S. Board on Geographic Names applied the name "Ross Shelf Ice" to this feature and published it in the original U.S. Antarctic Gazetteer. In Januar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byrd Antarctic Expedition
Richard Evelyn Byrd Jr. (October 25, 1888 – March 11, 1957) was an American naval officer and explorer. He was a recipient of the Medal of Honor, the highest honor for valor given by the United States, and was a pioneering American aviator, polar explorer, and organizer of polar logistics. Aircraft flights in which he served as a navigator and expedition leader crossed the Atlantic Ocean, a segment of the Arctic Ocean, and a segment of the Antarctic Plateau. Byrd said that his expeditions had been the first to reach both the North Pole and the South Pole by air. His belief to have reached the North Pole is disputed. He is also known for discovering Mount Sidley, the largest dormant volcano in Antarctica. Family Ancestry Byrd was born in Winchester, Virginia, the son of Esther Bolling (Flood) and Richard Evelyn Byrd Sr. He was a descendant of one of the First Families of Virginia. His ancestors include planter John Rolfe and his wife Pocahontas, William Byrd II of Westover Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vice Admiral (United States)
Vice admiral (abbreviated as VADM) is a three-star commissioned officer rank in the United States Navy, the United States Coast Guard, the United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Commissioned Officer Corps, with the pay grade of O-9. Vice admiral ranks above rear admiral and below admiral. Vice admiral is equivalent to the rank of lieutenant general in the other uniformed services. Statutory limits United States Code explicitly limits the total number of vice admirals that may be on active duty at any given time. U.S. Navy The total number of active-duty flag officers is capped at 162 for the U.S. Navy. For the Navy, no more than 16.7% of the service's active-duty flag officers may have more than two stars. Pub.L. 110-181: National Defense Authorization Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Arnold Karo
Henry Arnold Karo (December 24, 1903 – May 23, 1986) was a vice admiral in the former United States Coast and Geodetic Survey Corps, which is today known as the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Commissioned Officer Corps. Vice Admiral Karo spent most of his working career in the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey, which provided coastal maps and charts for the United States. He rose through the organization's bureaucracy to become the director of the Survey. "Vice Adm. H. Karo, 82, Dies; Headed U.S. Geodetic Survey," ''New York Times.'' May 30, 1986. Karo had been involved in the Survey since 1923, but the advent of |
United States Coast And Geodetic Survey
The United States Coast and Geodetic Survey (abbreviated USC&GS), known from 1807 to 1836 as the Survey of the Coast and from 1836 until 1878 as the United States Coast Survey, was the first scientific agency of the United States Government. It existed from 1807 to 1970, and throughout its history was responsible for mapping and charting the coast of the United States, and later the coasts of U.S. territories. In 1871, it gained the additional responsibility of surveying the interior of the United States and geodesy became a more important part of its work, leading to it being renamed the U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey in 1878. Long the U.S. Government's only scientific agency, the Survey accumulated other scientific and technical responsibilities as well, including astronomy, cartography, meteorology, geology, geophysics, hydrography, navigation, oceanography, exploration, pilotage, tides, and topography. It also was responsible for the standardization of weights and measures th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Science Services Administration
The Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA) was a United States Federal executive agency created in 1965 as part of a reorganization of the United States Department of Commerce. Its mission was to unify and oversee the meteorological, climatological, hydrographic, and geodetic operations of the United States. It operated until 1970, when it was replaced by the new National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The first U.S. Government organization with the word "environment" in its title, ESSA was the first such organization chartered to study the global natural environment as whole, bringing together the study of the oceans with that of both the lower atmosphere and the ionosphere. This allowed the U.S. Government for the first time to take a comprehensive approach to studying the oceans and the atmosphere, also bringing together various technologies – ships, aircraft, satellites, radar, and communications systems – that could operate together in gat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koerwitz Glacier
Koerwitz Glacier () is a low gradient glacier flowing northeast from Mount Griffith in the Hays Mountains of Antarctica to the Karo Hills. It was first seen and roughly mapped by the Byrd Antarctic Expedition, 1928–30. The glacier was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Peter H. Koerwitz, a biolab manager at McMurdo Station McMurdo Station is a United States Antarctic research station on the south tip of Ross Island, which is in the New Zealand-claimed Ross Dependency on the shore of McMurdo Sound in Antarctica. It is operated by the United States through the Unit ... in 1965. References Glaciers of Amundsen Coast {{RossDependency-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hills Of Antarctica
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. It often has a distinct summit. Terminology The distinction between a hill and a mountain is unclear and largely subjective, but a hill is universally considered to be not as tall, or as steep as a mountain. Geographers historically regarded mountains as hills greater than above sea level, which formed the basis of the plot of the 1995 film ''The Englishman who Went up a Hill but Came down a Mountain''. In contrast, hillwalkers have tended to regard mountains as peaks above sea level. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' also suggests a limit of and Whittow states "Some authorities regard eminences above as mountains, those below being referred to as hills." Today, a mountain is usually defined in the UK and Ireland as any summit at least high, while the official UK government's definition of a mountain is a summit of or higher. Some definitions include a topographical prominence requirement, typically or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |