|
Karl Ludwig Von Haller
Karl Ludwig von Haller (1 August 1768 – 20 May 1854) was a Swiss jurist, statesman and political philosopher. He was the author of ''Restauration der Staatswissenschaft'' (Restoration of Political Science, 1816–1834), a book which gave its namesake to the Restoration period after the Congress of Vienna, and which Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel strongly criticized in §258 of '' Elements of the Philosophy of Right''. Von Haller's work, which was burnt during the Wartburg Festival, was a highly systematic defense both of the principles of dynastic legitimacy and monarchy founded on territorial lordship, as well as of pre-modern republics like those of the Swiss city-states, and the most consistent rejection of modern political ideas of the social contract, public law, and state sovereignty. Life Early life Von Haller was a son of Bern statesman and historian Gottlieb Emanuel von Haller, and grandson of poet and polymath Albrecht von Haller. His lineage descended from Johan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Philosophy
Western philosophy encompasses the philosophical thought and work of the Western world. Historically, the term refers to the philosophical thinking of Western culture, beginning with the ancient Greek philosophy of the pre-Socratics. The word ''philosophy'' itself originated from the Ancient Greek (φιλοσοφία), literally, "the love of wisdom" grc, φιλεῖν , "to love" and σοφία '' sophía'', "wisdom"). History Ancient The scope of ancient Western philosophy included the problems of philosophy as they are understood today; but it also included many other disciplines, such as pure mathematics and natural sciences such as physics, astronomy, and biology (Aristotle, for example, wrote on all of these topics). Pre-Socratics The pre-Socratic philosophers were interested in cosmology; the nature and origin of the universe, while rejecting mythical answers to such questions. They were specifically interested in the (the cause or first principle) of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurist
A jurist is a person with expert knowledge of law; someone who analyses and comments on law. This person is usually a specialist legal scholar, mostly (but not always) with a formal qualification in law and often a legal practitioner. In the United Kingdom the term "jurist" is mostly used for legal academics, while in the United States the term may also be applied to a judge. With reference to Roman law, a "jurist" (in English) is a jurisconsult (''iurisconsultus''). The English term ''jurist'' is to be distinguished from similar terms in other European languages, where it may be synonymous with legal professional, meaning anyone with a professional law degree that qualifies for admission to the legal profession, including such positions as judge or attorney. In Germany, Scandinavia Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
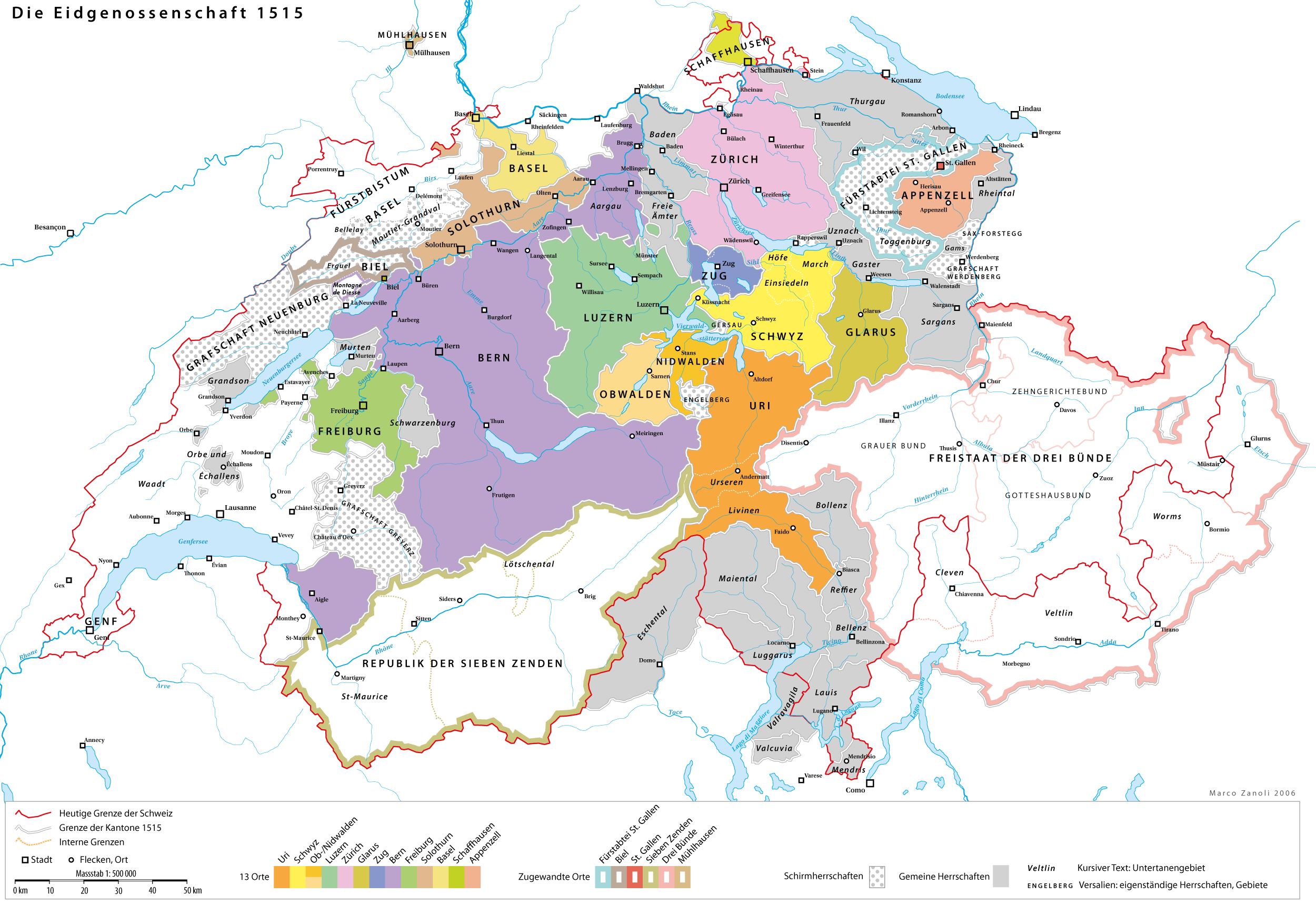
Nyon
Nyon (; outdated German: or ; outdated Italian: , ) is a municipality in Nyon District in the canton of Vaud in Switzerland. It is located some 25 kilometers north east of Geneva's city centre, and since the 1970s it has become part of the Geneva metropolitan area. It lies on the shores of Lake Geneva and is the seat of Nyon District. The town has () a population of and is famous in the sporting world for being the headquarters of the Union of European Football Associations (UEFA) and the European Club Association (ECA). It is connected to the rest of Switzerland by way of the Route Suisse, the A1 Motorway and the railways of the ''Arc Lémanique''. Name Nyon derives from one of the names used by the Romans for the town, '' Noviodunum'' or ''Noiodunum''. Other names for the town, particularly of colonies placed there, are ''Colonia Iulia Equestris'' or ''Colonia Julia Equestris'', ''Colonia Equestris Noiodunum'', ''Equestris'', ''Civitas Equestrium'', and ''Civitas Eque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helvetic Republic
The Helvetic Republic (, , ) was a sister republic of France that existed between 1798 and 1803, during the French Revolutionary Wars. It was created following the French invasion and the consequent dissolution of the Old Swiss Confederacy, marking the end of the ''ancien régime'' in Switzerland. Throughout its existence, the republic incorporated most of the territory of modern Switzerland, excluding the cantons of Geneva and Neuchâtel and the old Prince-Bishopric of Basel. The Swiss Confederacy, which until then had consisted of self-governing cantons united by a loose military alliance (and ruling over subject territories such as Vaud), was invaded by the French Revolutionary Army and turned into an ally known as the "Helvetic Republic". The interference with localism and traditional liberties was deeply resented, although some modernizing reforms took place. Resistance was strongest in the more traditional Catholic cantons, with armed uprisings breaking out in spring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philipp Albert Stapfer
Philipp Albert Stapfer (23 September 1766, in Bern – 27 March 1840, in Paris) was a Swiss politician and philosopher. He was the plenipotentiary envoi of the Helvetic Republic to the French consulate in Paris from 1801 till 1803. ( Act of Mediation ) He married and settled in France, at the Chateau de Talcy (Loir-et-Cher) and in Paris where he became the friend of Maine de Biran -in 1805 at informal gatherings of Cabanis circle at Auteuil. He was also vice-president of the Paris Protestant society. He is the recipient of Maine de Biran's essay: : ''"Réponses aux arguments contre l'aperception immédiate d'une liaison causale entre le vouloir primitif et la motion et contre la dérivation d'un principe universel et nécessaire de causalités de cette source."'' (1818); an important résumé known as: ''"Réponses à Stapfer"'' Pestalozzi Philipp Albert Stapfer also shared with Maine de Biran a pronounced interest in the educational experiments of Johann Heinrich Pestalozzi. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnasium (school)
''Gymnasium'' (and variations of the word) is a term in various European languages for a secondary school that prepares students for higher education at a university. It is comparable to the US English term '' preparatory high school''. Before the 20th century, the gymnasium system was a widespread feature of educational systems throughout many European countries. The word (), from Greek () 'naked' or 'nude', was first used in Ancient Greece, in the sense of a place for both physical and intellectual education of young men. The latter meaning of a place of intellectual education persisted in many European languages (including Albanian, Bulgarian, Estonian, Greek, German, Hungarian, the Scandinavian languages, Dutch, Polish, Czech, Serbo-Croatian, Macedonian, Slovak, Slovenian and Russian), whereas in other languages, like English (''gymnasium'', ''gym'') and Spanish (''gimnasio''), the former meaning of a place for physical education was retained. School ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second War Of Kappel
The Second War of Kappel (german: Zweiter Kappelerkrieg) was an armed conflict in 1531 between the Catholic and the Protestant cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy during the Reformation in Switzerland. Cause The tensions between the two parties had not been resolved by the peace concluded after the First War of Kappel two years earlier, and provocations from both sides continued, fuelled in particular by the Augsburg Confession of 1530. Additionally, the Roman Catholic party accused Zürich of territorial ambitions. As the Catholic cantons refused to help the Three Leagues (''Drei Bünde'') in the Grisons during the Musso war against the Duchy of Milan, Zürich promptly considered this a breach of contracts between the confederacy and the Three Leagues and declared an embargo against the five alpine Catholic cantons, in which Bern also participated. While the ''Tagsatzung'' had successfully mediated in 1529, on this occasion the attempt failed, not least because Huldrych ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huldrych Zwingli
Huldrych or Ulrich Zwingli (1 January 1484 – 11 October 1531) was a leader of the Reformation in Switzerland, born during a time of emerging Swiss patriotism and increasing criticism of the Swiss mercenary system. He attended the University of Vienna and the University of Basel, a scholarly center of Renaissance humanism. He continued his studies while he served as a pastor in Glarus and later in Einsiedeln, where he was influenced by the writings of Erasmus. In 1519, Zwingli became the Leutpriester (people's priest) of the Grossmünster in Zürich where he began to preach ideas on reform of the Catholic Church. In his first public controversy in 1522, he attacked the custom of fasting during Lent. In his publications, he noted corruption in the ecclesiastical hierarchy, promoted clerical marriage, and attacked the use of images in places of worship. Among his most notable contributions to the Reformation was his expository preaching, starting in 1519, throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albrecht Von Haller
Albrecht von Haller (also known as Albertus de Haller; 16 October 170812 December 1777) was a Swiss anatomist, physiologist, naturalist, encyclopedist, bibliographer and poet. A pupil of Herman Boerhaave, he is often referred to as "the father of modern physiology." Early life Haller was born into an old Swiss family at Bern. Prevented by long-continued ill-health from taking part in boyish sports, he had more opportunity for the development of his precocious mind. At the age of four, it is said, he used to read and expound the Bible to his father's servants; before he was ten he had sketched a Biblical Aramaic grammar, prepared a Greek and a Hebrew vocabulary, compiled a collection of two thousand biographies of famous men and women on the model of the great works of Bayle and Moréri, and written in Latin verse a satire on his tutor, who had warned him against a too great excursiveness. When still hardly fifteen he was already the author of numerous metrical trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gottlieb Emanuel Von Haller
Gottlieb Emanuel von Haller (1735–1786) was a Bernese historian, numismatist, botanist, politician, diplomat and librarian. Biography He was the eldest son of polymath Albrecht von Haller. Born in Berne, he studied law and history in Göttingen, where his father was professor for medicine and botany. He returned to Berne in 1753. He entered public service in Berne, in 1763 as vice-librarian, 1765 as secretary of the war council, and from 1775 as member of the city council. He was a fellow of the Academy of Sciences Leopoldina from 1778. He was sent to represent Berne in the transmontane bailiwicks in 1779/80 and from 1785 until his death he served as reeve of Nyon. He married Anna Margarethe Schultheß (1734–1810) in 1761, with whom he had six sons and four daughters. One of his sons was political philosopher Karl Ludwig von Haller. Works As a student, he wrote pamphlets against the Linnean system of taxonomy. During his career he authored numerous works on biblioth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |