|
Karenia Brevis
''Karenia brevis'' is a microscopic, single-celled, photosynthetic organism in the genus '' Karenia''. It is a marine dinoflagellate commonly found in the waters of the Gulf of Mexico. It is the organism responsible for the "Florida red tides" that affect the Gulf coasts of Florida and Texas in the U.S., and nearby coasts of Mexico. ''K. brevis'' has been known to travel great lengths around the Florida peninsula and as far north as the Carolinas. Each cell has two flagella that allow it to move through the water in a spinning motion. ''K. brevis'' is unarmored, and does not contain peridinin. Cells are between 20 and 40 μm in diameter. ''K. brevis'' naturally produces a suite of potent neurotoxins collectively called brevetoxins, which cause gastrointestinal and neurological problems in other organisms and are responsible for large die-offs of marine organisms and seabirds. History ''Karenia brevis'' was named for Dr. Karen A. Steidinger in 2001, and was previously known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karenia (dinoflagellate)
''Karenia'' is a genus that consists of unicellular, photosynthetic, planktonic organisms found in marine environments. The genus currently consists of 12 described species. They are best known for their dense toxic algal blooms and red tides that cause considerable ecological and economical damage; some ''Karenia'' species cause severe animal mortality. One species, ''Karenia brevis'', is known to cause respiratory distress and neurotoxic shellfish poisoning (NSP) in humans. Taxonomy The genus ''Karenia'' is named for Dr. Karen Steidinger for her exceptional contributions to dinoflagellate research. She has spent many decades researching ''Karenia brevis''. 12 species have been described in the genus ''Karenia'' thus far: * ''Karenia asterichroma'' * ''Karenia bicuneiformis'' * ''Karenia brevis'' * ''Karenia brevisulcata'' * ''Karenia concordia'' * ''Karenia cristata'' * ''Karenia digitata'' * ''Karenia longicanalis'' * ''Karenia mikimotoi'' * ''Karenia papilionacea'' * ''Kare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnodiniales
The Gymnodiniales are an order of dinoflagellates, of the class Dinophyceae. Members of the order are known as gymnodinioid or gymnodinoid (terms that can also refer to any organism of similar morphology). They are athecate, or lacking an armored exterior, and as a result are relatively difficult to study because specimens are easily damaged. Many species are part of the marine plankton and are of interest primarily due to being found in algal blooms. As a group the gymnodinioids have been described as "likely one of the least known groups of the open ocean phytoplankton." Of the families in the order, the Polykrikaceae and Warnowiaceae are well known for possessing exceptionally complex assemblies of organelles, such as nematocysts, trichocysts, and pistons. The Warnowiaceae uniquely possess an ocelloid, an extremely complex light-sensitive subcellular structure composed of mitochondria and plastid The plastid (Greek: πλαστός; plastós: formed, molded – plural plastids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southwest and south by the Mexico, Mexican States of Mexico, states of Tamaulipas, Veracruz, Tabasco, Campeche, Yucatan, and Quintana Roo; and on the southeast by Cuba. The Southern United States, Southern U.S. states of Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, which border the Gulf on the north, are often referred to as the "Third Coast" of the United States (in addition to its Atlantic and Pacific Ocean, Pacific coasts). The Gulf of Mexico took shape approximately 300 million years ago as a result of plate tectonics.Huerta, A.D., and D.L. Harry (2012) ''Wilson cycles, tectonic inheritance, and rifting of the North American Gulf of Mexico continental margin.'' Geosphere. 8(1):GES00725.1, first p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Tide
A harmful algal bloom (HAB) (or excessive algae growth) is an algal bloom that causes negative impacts to other organisms by production of natural phycotoxin, algae-produced toxins, mechanical damage to other organisms, or by other means. HABs are sometimes defined as only those algal blooms that produce toxins, and sometimes as any algal bloom that can result in severely lower oxygen saturation, oxygen levels in natural waters, killing organisms in marine habitats, marine or fresh waters. Blooms can last from a few days to many months. After the bloom dies, the microorganism, microbes that decompose the dead algae use up more of the oxygen, generating a "dead zone (ecology), dead zone" which can cause fish kill, fish die-offs. When these zones cover a large area for an extended period of time, neither fish nor plants are able to survive. Harmful algal blooms in marine environments are often called "red tides". It is sometimes unclear what causes specific HABs as their occurrence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to the south by the Straits of Florida and Cuba; it is the only state that borders both the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. Spanning , Florida ranks 22nd in area among the 50 states, and with a population of over 21 million, it is the third-most populous. The state capital is Tallahassee, and the most populous city is Jacksonville. The Miami metropolitan area, with a population of almost 6.2 million, is the most populous urban area in Florida and the ninth-most populous in the United States; other urban conurbations with over one million people are Tampa Bay, Orlando, and Jacksonville. Various Native American groups have inhabited Florida for at least 14,000 years. In 1513, Spanish explorer Juan Ponce de León became the first k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by both List of U.S. states and territories by area, area (after Alaska) and List of U.S. states and territories by population, population (after California). Texas shares borders with the states of Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the west, and the Mexico, Mexican States of Mexico, states of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas to the south and southwest; and has a coastline with the Gulf of Mexico to the southeast. Houston is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in Texas and the List of United States cities by population, fourth-largest in the U.S., while San Antonio is the second most pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and to the east by the Gulf of Mexico. Mexico covers ,Mexico ''''. . making it the world's 13th-largest country by are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagella
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'' for example uses its multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium, where it may cause a gastric ulcer to develop. In some bacteria the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means " whip" to describe its lash-like swimming motion. The flagellum in archaea is called the archaellum to note its difference from the bacterial flagellum. Eukaryoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peridinin
Peridinin is a light-harvesting apocarotenoid, a pigment associated with chlorophyll and found in the peridinin-chlorophyll-protein (PCP) light-harvesting complex in dinoflagellates, best studied in ''Amphidinium carterae''. Biological significance Peridinin is an apocarotenoid pigment that some organisms use in photosynthesis. Many photosynthetic dinoflagellates use peridinin, which absorbs blue-green light in the 470-550nm range, outside the range accessible to chlorophyll molecules. The peridinin-chlorophyll-protein complex is a specialized molecular complex consisting of a boat-shaped protein molecule with a large central cavity that contains peridinin, chlorophyll, and lipid molecules, usually in a 4:1 ratio of peridinin to chlorophyll. Spectral characteristics * Absorption maximum: 483 nm * Emission maximum: 676 nm * Extinction coefficient (ε): 1.96 x 106 M−1cm−1 * A483/A280 ≥ 4.6 Applications Peridinin chlorophyll (PerCP) is commonly used in immunoassa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they also are common in freshwater habitats. Their populations vary with sea surface temperature, salinity, and depth. Many dinoflagellates are photosynthetic, but a large fraction of these are in fact mixotrophic, combining photosynthesis with ingestion of prey (phagotrophy and myzocytosis). In terms of number of species, dinoflagellates are one of the largest groups of marine eukaryotes, although substantially smaller than diatoms. Some species are endosymbionts of marine animals and play an important part in the biology of coral reefs. Other dinoflagellates are unpigmented predators on other protozoa, and a few forms are parasitic (for example, ''Oodinium'' and ''Pfiesteria''). Some dinoflagellates pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
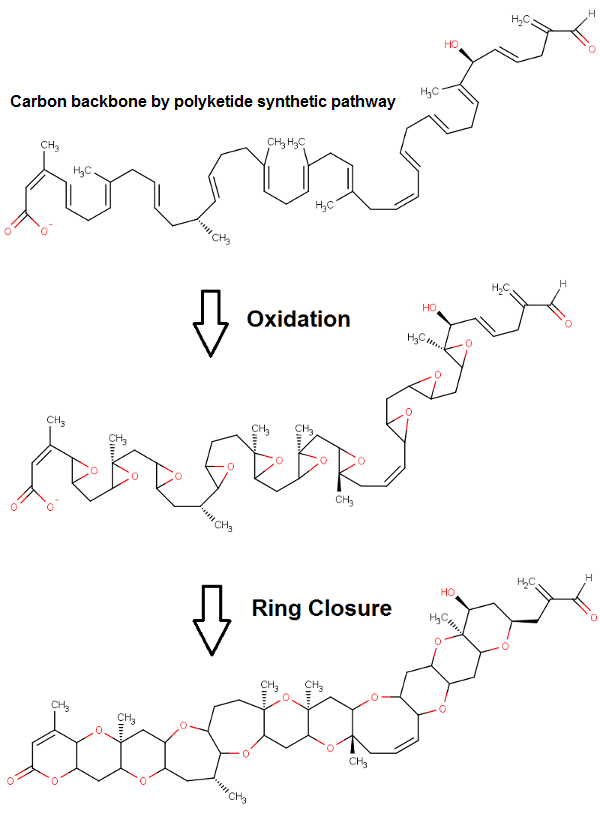
Brevetoxin
Brevetoxin (PbTx), or brevetoxins, are a suite of cyclic polyether compounds produced naturally by a species of dinoflagellate known as '' Karenia brevis''. Brevetoxins are neurotoxins that bind to voltage-gated sodium channels in nerve cells, leading to disruption of normal neurological processes and causing the illness clinically described as neurotoxic shellfish poisoning (NSP). Although brevetoxins are most well-studied in ''K. brevis'', they are also found in other species of '' Karenia'' and at least one large fish kill has been traced to brevetoxins in ''Chattonella''. Other Brevetoxins: *Brevetoxin-5 (PbTx-5): like PbTx-2, but acetylated hydroxyl group in position 38. *Brevetoxin-6 (PbTx-6): like PbTx-2, but double bond 27-28 is epoxidated. Brevetoxin-B was synthesized in 1995 by K. C. Nicolaou and coworkers in 123 steps with 91% average yield (final yield ~9·10−6) and in 2004 in a total of 90 steps with an average 93% yield for each step (0.14% overall). K. C. Nic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnodinium
''Gymnodinium'' is a genus of dinoflagellates, a type of marine and freshwater plankton. It is one of the few naked dinoflagellates, or species lacking armor known as cellulosic plates. Since 2000, the species which had been considered to be part of ''Gymnodinium'' have been divided into several genera, based on the nature of the apical groove and partial LSU rDNA sequence data. Amphidinium was redefined later. Gymnodinium belong to red dinoflagellates that, in concentration, can cause red tides. The red tides produced by some Gymnodinium, such as Gymnodinium catenatum, are toxic and pose risks to marine and human life, including paralytic shellfish poisoning. Species * ''Amphidinium'' * ''Aureolum'' *''Gymnodinium'' sensu stricto * ''Gyrodinium'' *'' Akashiwo'' *'' Karenia'' *''Karlodinium'' *''Katodinium'' *'' Takayama'' Former species ''Torodinium'' (with ''Torodinium robustum'' and the type species In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |