|
Karađorđevo Estate
The Karađorđevo ( sr-Cyrl, Карађорђево) estate lies 10 km north-west of Bačka Palanka, Serbia. The estate covers an area of and features a manor house, hunting ground, stud farm, agricultural facilities, and forest and wetland habitats. The property is state-owned, and managed by an establishment of the Army of Serbia. Since its establishment as a state property of the Austro-Hungarian Empire in 1885, it has served as a representative hunting ground and resort for statesmen, high-ranking military officials and businessmen. A part of the property is protected as a special nature reserve, occupying the area of . The landscape features centuries-old oak and acacia woods, marshes, variety of flora and fauna species and a long distance from the nearest settlements. It is open to hunters and tourists throughout the year. The property is also famous for its elite stud farm, with a museum of horse racing. The farm was originally created in 1904, using horses from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
League Of Communists Of Yugoslavia
The League of Communists of Yugoslavia, mk, Сојуз на комунистите на Југославија, Sojuz na komunistite na Jugoslavija known until 1952 as the Communist Party of Yugoslavia, sl, Komunistična partija Jugoslavije mk, Комунистичка партија на Југославија, Komunistička partija na Jugoslavija was the founding and ruling party of SFR Yugoslavia. It was formed in 1919 as the main communist opposition party in the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes and after its initial successes in the elections, it was proscribed by the royal government and was at times harshly and violently suppressed. It remained an illegal underground group until World War II when, after the invasion of Yugoslavia in 1941, the military arm of the party, the Yugoslav Partisans, became embroiled in a bloody civil war and defeated the Axis powers and their local auxiliaries. After the liberation from foreign occupation in 1945, the party consolidated it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
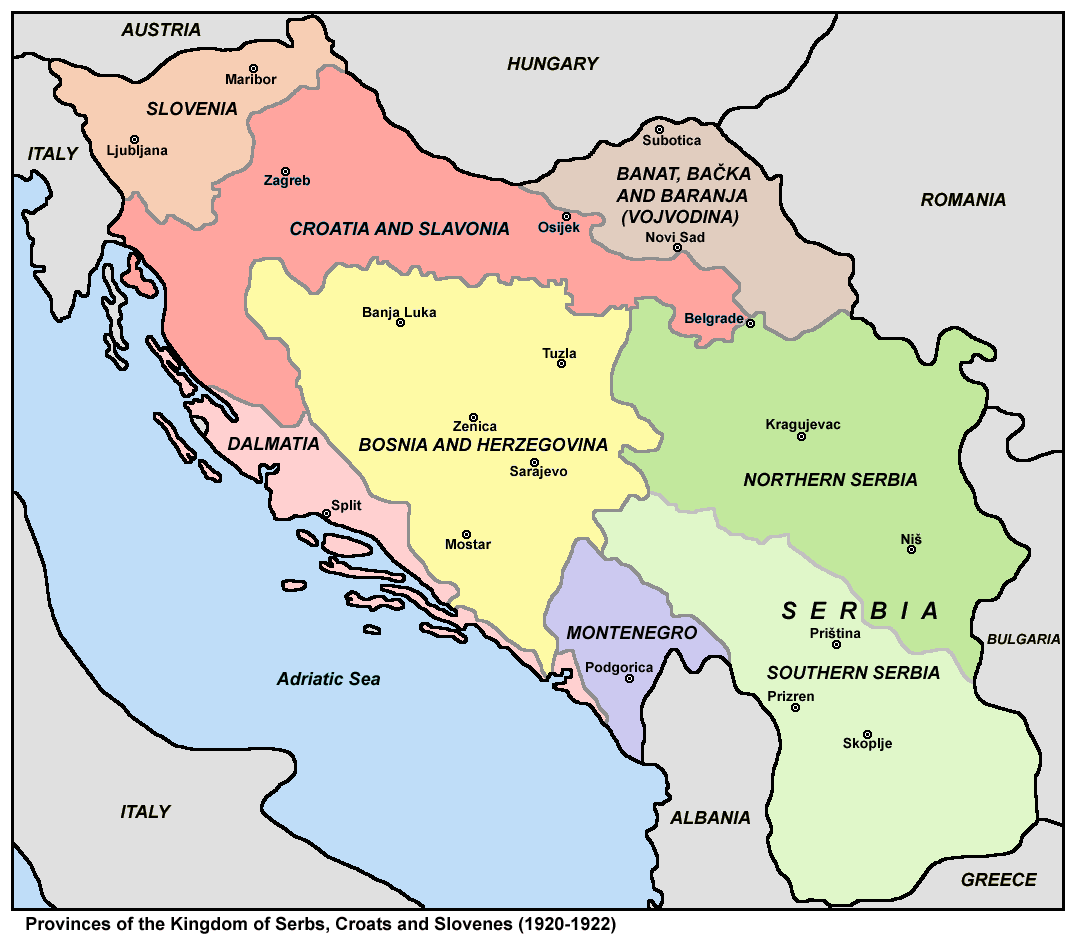
Partition Of Bosnia And Herzegovina
The partition of Bosnia and Herzegovina was discussed and attempted during the 20th century. The issue came to prominence during the Bosnian War, which also involved Bosnia and Herzegovina's largest neighbors, Croatia and Serbia. As of , the country remains one state while internal political divisions of Bosnia and Herzegovina based on the 1995 Dayton Agreement remain in place. Background Bosnia and Herzegovina has been a single entity occupying roughly the same territory since the rise of the medieval Kingdom of Bosnia and the subsequent Ottoman conquest of Bosnia between the 1380s and 1590s. The borders of today's Bosnia and Herzegovina were largely set as the borders of the Ottoman-era Eyalet of Bosnia, fixed in the south and west by the 1699 Treaty of Karlowitz, in the north by the 1739 Treaty of Belgrade, and in the east by the 1878 Treaty of Berlin. Although formally under Ottoman sovereignty, Austria-Hungary occupied the territory and created the Condominium of Bosnia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yugoslav Wars
The Yugoslav Wars were a series of separate but related#Naimark, Naimark (2003), p. xvii. ethnic conflicts, wars of independence, and Insurgency, insurgencies that took place in the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, SFR Yugoslavia from 1991 to 2001. The conflicts both led up to and resulted from the breakup of Yugoslavia, which began in mid-1991, into six independent countries matching the six entities known as republics which previously composed Yugoslavia: Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Serbia, and North Macedonia (previously named ''Macedonia''). Yugoslavia's constituent republics declared independence due to unresolved tensions between ethnic minorities in the new countries, which fuelled the wars. While most of the conflicts ended through peace accords that involved full international recognition of new states, they resulted in a massive number of deaths as well as severe economic damage to the region. During the initial stages of the breaku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franjo Tuđman
Franjo Tuđman (; 14 May 1922 – 10 December 1999), also written as Franjo Tudjman, was a Croatian politician and historian. Following the country's independence from Yugoslavia, he became the first president of Croatia and served as president from 1990 until his death in 1999. He was the ninth and last President of the Presidency of SR Croatia from May to July 1990. Tuđman was born in Veliko Trgovišće. In his youth, he fought during World War II as a member of the Yugoslav Partisans. After the war, he took a post in the Ministry of Defence, later attaining the rank of major general of the Yugoslav Army in 1960. After his military career, he dedicated himself to the study of geopolitics. In 1963, he became a professor at the Zagreb Faculty of Political Sciences. He received a doctorate in history in 1965 and worked as a historian until coming into conflict with the regime. Tuđman participated in the Croatian Spring movement that called for reforms in the count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slobodan Milošević
Slobodan Milošević (, ; 20 August 1941 – 11 March 2006) was a Yugoslav and Serbian politician who was the president of Serbia within Yugoslavia from 1989 to 1997 (originally the Socialist Republic of Serbia, a constituent republic of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, from 1989 to 1992) and president of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia from 1997 to 2000. Formerly a high-ranking member of the League of Communists of Serbia (SKS) during the 1980s, he led the Socialist Party of Serbia from its foundation in 1990 until 2003. Born in Požarevac, he studied law at the University of Belgrade Faculty of Law and joined the League of Socialist Youth of Yugoslavia as a student. During the 1960s he served as an advisor to mayor of Belgrade Branko Pešić, and was later appointed chairman of Tehnogas and Beobanka, roles which he served until the 1980s. Milošević rose to power in 1987 by promoting populist and nationalist views, arguing for the reduction of power of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
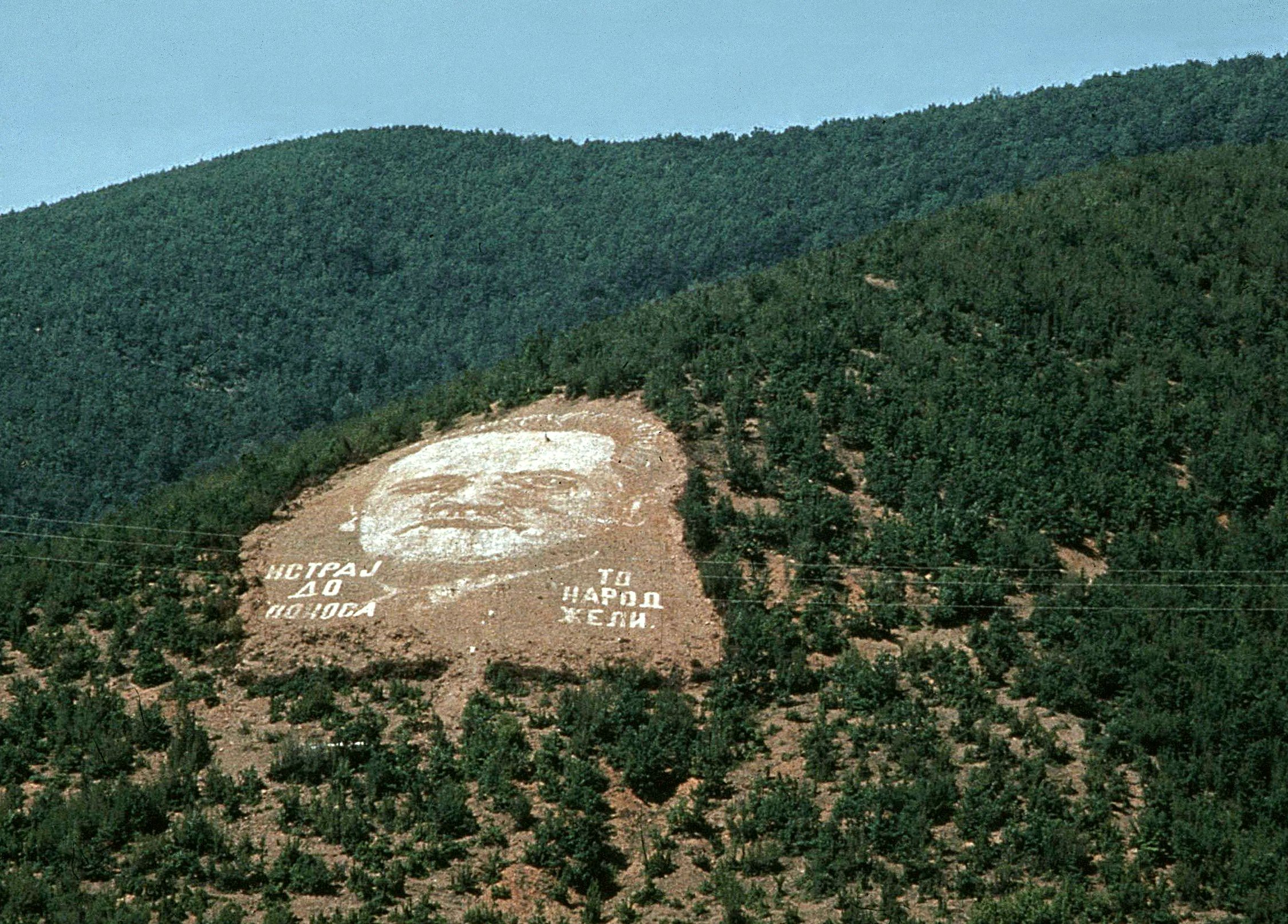
Milošević–Tuđman Karađorđevo Meeting
On 25 March 1991, the presidents of the Yugoslav federal states SR Croatia and SR Serbia, Franjo Tuđman and Slobodan Milošević, met at the Karađorđevo hunting ground in northwest Serbia. The publicized topic of their discussion was the ongoing Yugoslav crisis. Three days later all the presidents of the six Yugoslav republics met in Split. Although news of the meeting taking place was widely publicized in the Yugoslav media at the time, the meeting was overshadowed by the crisis in progress, that would lead to the breakup of Yugoslavia. In the following years, however, the meeting became substantially more controversial, as numerous Yugoslav politicians claimed that Tuđman and Milošević had discussed and agreed to the partitioning of Bosnia and Herzegovina along ethnic lines, such that territories with either a Croat or Serb majority would be annexed to the soon to be independent Croatia or Serbia respectively, with a rump Bosniak buffer state remaining in between. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatian Spring
The Croatian Spring ( hr, Hrvatsko proljeće), or Maspok, was a political conflict that took place from 1967 to 1971 in the Socialist Republic of Croatia, at the time part of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. As one of six republics comprising Yugoslavia at the time, Croatia was ruled by the League of Communists of Croatia (SKH), nominally independent from the League of Communists of Yugoslavia (SKJ), led by President Josip Broz Tito. The 1960s in Yugoslavia were marked by a series of reforms aimed at improving the economic situation in the country and increasingly politicised efforts by the leadership of the republics to protect the economic interests of their respective republics. As part of this, political conflict occurred in Croatia when reformers within the SKH, generally aligned with the Croatian cultural society , came into conflict with conservatives. In the late 1960s, a variety of grievances were aired through , which were adopted in the early 1970s by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
League Of Communists Of Croatia
League of Communists of Croatia ( sh, Savez komunista Hrvatske or SKH) was the Croatian branch of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia (SKJ). It came into power in 1945. Until 1952, it was known as Communist Party of Croatia (''Komunistička partija Hrvatske,'' KPH). In the early 1990s, it underwent several renames and lost power. History Kingdom of Yugoslavia The party was formally founded in 1937 with Pavle Gregorić as its first general secretary. The reasons for KPJ to have its specifically Croatian branch were partly ideological, partly practical. Croatia, just as Slovenia, which would have its Communist Party at the same time, was the most industrialised part of the country, with the biggest percentage of working class in the population, and, therefore, more likely to adopt communism than rural Serbia. The other, more practical, reason was in the increased marginalisation of Communists in Croatian political life due to public more preoccupied with ethnic issues a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josip Broz Tito
Josip Broz ( sh-Cyrl, Јосип Броз, ; 7 May 1892 – 4 May 1980), commonly known as Tito (; sh-Cyrl, Тито, links=no, ), was a Yugoslav communist revolutionary and statesman, serving in various positions from 1943 until his death in 1980. During World War II, he was the leader of the Yugoslav Partisans, often regarded as the most effective resistance movement in German-occupied Europe. He also served as the president of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia from 14 January 1953 until his death on 4 May 1980. He was born to a Croat father and Slovene mother in the village of Kumrovec, Austria-Hungary (now in Croatia). Drafted into military service, he distinguished himself, becoming the youngest sergeant major in the Austro-Hungarian Army of that time. After being seriously wounded and captured by the Russians during World War I, he was sent to a work camp in the Ural Mountains. He participated in some events of the Russian Revolution in 1917 and the subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bačka Palanka
Bačka Palanka ( sr-cyrl, Бачка Паланка, ; hu, Palánka) is a town and municipality located in the South Bačka District of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. It is situated on the left bank of the Danube. In 2011 the town had a total population of 28,239, while Bačka Palanka municipality had 55,528 inhabitants. Name In Serbian, the town is known as Бачка Паланка or ''Bačka Palanka'', in Slovak as ''Báčska Palanka'', in Croatian as ''Bačka Palanka'', in Hungarian as ''Bácspalánka'', in German as ''Plankenburg'' and in Turkish as ''Küçük Hisar''. Its name means "a town in Bačka" in Serbian. The word " palanka" itself originates from Turkish language. This word was also adopted by Serbs and it is used in the Serbian language with the same meaning. Older Serbian names for this town were Palanka (Паланка), Stara Palanka (Стара Паланка), Nova Palanka (Нова Паланка) and Nemačka Palanka (Немачк� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mezőhegyes
Mezőhegyes is a town in Békés county, in the Southern Great Plain region of south-east Hungary. It is home to the Hungarian State Stud ( hu, italic=no, Mezőhegyesi Állami Ménes), founded in 1784 and famous for its Nonius, Furioso-North Star and Gidran breeds of horse. Geography It covers an area of 155.5 km² and has a population of 6355 people (2007). History The Austrian Imperial and Hungarian Royal Apostolic Stud was founded in late 1784 in Mezőhegyes by Emperor Joseph II. As a result, the name of Mezőhegyes became interwoven with the concept of horses. It was here that the Nonius, later on the Gidan, the Furioso and the North Star types of horses and the Mezőhegyes English full bood were bred. The Mezőhegyes English full blood was one of the best horse breeds in Europe. The roofed riding hall designed by János Hild, which is still in use today, is the oldest roofed riding hall in the country. Riding lessons for both experienced riders and beginners are off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

