|
Karabiga
Karabiga (Karabuga) is a town in Biga District, Çanakkale Province, in the Marmara region of Turkey. It is located at the mouth of the Biga River, on a small east-facing bay, known as Karabiga Bay. Its ancient name was Priapus or Priapos ( grc, Πρίαπος). History Originally a town of ancient Mysia, it was a colony of Miletus or of Cyzicus. It had a good harbour. Strabo mentions that the area produced fine wine and that the god Priapus gave the town its ancient name. Thucydides mentions the town as a naval station. Arrian reports that in 334 BCE Alexander the Great sent Panegorus to take possession of the city and the city surrendered without contest, prior to the Battle of Granicus. Besides the aforementioned authors, the town was noted by numerous ancient writers and geographers including Pomponius Mela, Pliny the Elder, Stephanus of Byzantium, and the Geographer of Ravenna. Under the Eastern Roman Empire, the town was known as Pegae or Pegai (Πηγαί) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biga, Çanakkale
Biga is a town and district of Çanakkale Province in the Marmara region of Turkey. It is located on the Biga River, northeast from Çanakkale city centre. According to the 2000 census, population of the district is 80,982 of which 37,196 live in the town of Biga. The district covers an area of , and the town lies at an elevation of . The center of COMU Faculty of Economics and Administrative Sciences is in Biga. History Within the area of Biga (at Karabiga) is the site of the ancient city of Pegaea ( el, Πηγαία), also known as Pegae or Pegai (Πηγαί, "the Springs") until late Byzantine times (in Crusader sources it is also known as Spiga). Archaeologists have not yet established how far back the site has been occupied. In ancient times, Pegaea, located on the plain of Adrastea on the border between the Troad and Mysia, was sometimes included as part of one and sometimes the other. Since coming under Ottoman rule in 1364 it has been known as Biga. Under the Ottomans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priapus
In Greek mythology, Priapus (; grc, Πρίαπος, ) is a minor rustic fertility god, protector of livestock, fruit plants, gardens and male genitalia. Priapus is marked by his oversized, permanent erection, which gave rise to the medical term priapism. He became a popular figure in Roman erotic art and Latin literature, and is the subject of the often humorously obscene collection of verse called the ''Priapeia''. Mythology Relationship with other deities Priapus was described in varying sources as the son of Aphrodite by Dionysus; as the son of Dionysus and Chione; as perhaps the father or son of Hermes; or as the son of Zeus or Pan. According to legend, Hera cursed him with inconvenient impotence (he could not sustain an erection when the time came for sexual intercourse), ugliness and foul-mindedness while he was still in Aphrodite's womb, in revenge for the hero Paris having the temerity to judge Aphrodite more beautiful than Hera. In another account, Hera's anger and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miletus
Miletus (; gr, Μῑ́λητος, Mī́lētos; Hittite transcription ''Millawanda'' or ''Milawata'' (exonyms); la, Mīlētus; tr, Milet) was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in ancient Ionia. Its ruins are located near the modern village of Balat in Aydın Province, Turkey. Before the Persian rule that started in the 6th century BC, Miletus was considered among the greatest and wealthiest of Greek cities. Evidence of first settlement at the site has been made inaccessible by the rise of sea level and deposition of sediments from the Maeander. The first available evidence is of the Neolithic. In the early and middle Bronze Age the settlement came under Minoan influence. Legend has it that an influx of Cretans occurred displacing the indigenous Leleges, and the site was renamed Miletus after a place in Crete. Recorded history at Miletus begins with the records of the Hittite Empire, and the Mycenaean records of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biga Çayı
The Biga River ( tr, Biga Çayı) is a small river in Çanakkale Province in northwestern Turkey. The river begins at the base of Mount Ida and trends generally northeasterly to the Sea of Marmara. It is about east of the Dardanelles. It flows past the towns of Çan and Biga and enters the Sea of Marmara at Karabiga. It is also known as the Çan (''Çan Çayı'') NW quadrant, CIA Map Number 802565, July 2002, U.S. Central Intelligence Agency and the Kocabaş (''Kocabaş Çayı''). The Biga was the classical Granicus ( grc, Γρανικὸς ποταμός, ''Granikòs Potamós''). The banks near the modern-day town of Biga were the site of the |
Anzavur Ahmed Pasha
Anzavur Ahmed Anchok Pasha (; ; 1885 – 15 April 1921) was an Ottoman soldier, gendarme officer, pasha, and militia leader of Circassian origin. He was declared a Pasha by the late Ottoman government. Biography Anzavur served as a major during World War I. After the Ottomans lost in World War I, he believed that the only way to salvation was to cooperate with the invading British forces as he was loyal to the caliph, and he believed Atatürk's Turkish national movement was not only blasphemous, but also would only hurt the future of the land as it would eventually fail and would do nothing but anger the British-Greek forces. Thus, he became a guerrilla leader in Anatolia and started what is known as Revolt of Ahmet Anzavur. He was then declared a Pasha by the Istanbul government, had massive power, lots of support from the British, and he gathered a lot of men, whom he convinced by using religion, under his command. He secured a deal with local Greeks and captured the entire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
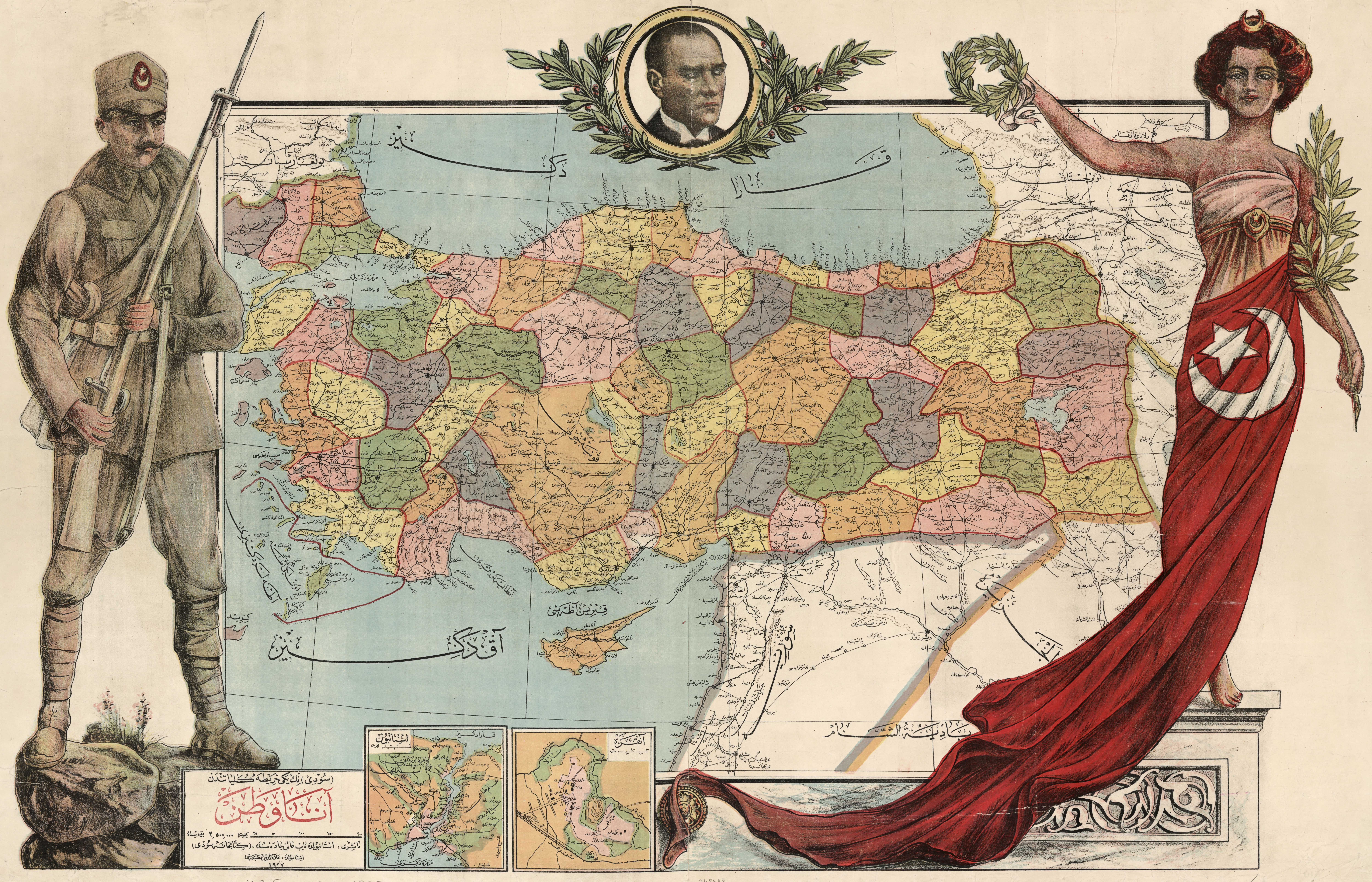
Provinces Of Turkey
Turkey is divided into 81 provinces ( tr, il). Each province is divided into a number of districts (). Each provincial government is seated in the central district (). For non- metropolitan municipality designated provinces, the central district bears the name of the province (e.g. the city/district of Rize is the central district of Rize Province Rize Province ( tr, Rize ili) is a province of northeast Turkey, on the eastern Black Sea coast between Trabzon and Artvin. The province of Erzurum is to the south. It was formerly known as Lazistan, the designation of the term of Lazistan was o ...). Each province is administered by an appointed governor () from the Ministry of the Interior (Turkey), Ministry of the Interior. List of provinces Below is a list of the 81 provinces of Turkey, sorted according to their license plate codes. Initially, the order of the codes matched the alphabetical order of the province names. After Zonguldak (code 67), the ordering is not alphab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander The Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II of Macedon, Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20, and spent most of his ruling years conducting a lengthy military campaign throughout Western Asia and ancient Egypt, Egypt. By the age of thirty, he had created one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in history, stretching from Greece to northwestern Historical India, India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's greatest and most successful military commanders. Until the age of 16, Alexander was tutored by Aristotle. In 335 BC, shortly after his assumption of kingship over Macedon, he Alexander's Balkan campaign, campaigned in the Balkans and reasserted control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allies Of World War I
The Allies of World War I, Entente Powers, or Allied Powers were a coalition of countries led by France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States against the Central Powers of Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, Bulgaria, and their colonies during the First World War (1914–1918). By the end of the first decade of the 20th century, the major European powers were divided between the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance. The Triple Entente was made up of France, Britain, and Russia. The Triple Alliance was originally composed of Germany, Austria–Hungary, and Italy, but Italy remained neutral in 1914. As the war progressed, each coalition added new members. Japan joined the Entente in 1914 and after proclaiming its neutrality at the beginning of the war, Italy also joined the Entente in 1915. The term "Allies" became more widely used than "Entente", although France, Britain, Russia, and Italy were also referred to as the Quadruple Entente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ravenna Cosmography
The ''Ravenna Cosmography'' ( la, Ravennatis Anonymi Cosmographia, "The Cosmography of the Unknown Ravennese") is a list of place-names covering the world from India to Ireland, compiled by an anonymous cleric in Ravenna around 700 AD. Textual evidence indicates that the author frequently used maps as his source. The text There are three known copies of the Cosmography in existence. The Vatican Library holds a 14th-century copy, there is a 13th-century copy in Paris at the Bibliothèque Nationale, and the library at Basle University has another 14th-century copy. The Vatican copy was used as the source for the first publication of the manuscript in 1688 by Porcheron. The German scholar Joseph Schnetz published the text in 1940, basing it on the Vatican and Paris editions, which he believed to be more reliable than the Basle edition. Parts of the text, notably that covering Britain, have been published by others, including Richmond and Crawford in 1949, but their document sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographer Of Ravenna
The ''Ravenna Cosmography'' ( la, Ravennatis Anonymi Cosmographia, "The Cosmography of the Unknown Ravennese") is a list of place-names covering the world from India to Ireland, compiled by an anonymous cleric in Ravenna around 700 AD. Textual evidence indicates that the author frequently used maps as his source. The text There are three known copies of the Cosmography in existence. The Vatican Library holds a 14th-century copy, there is a 13th-century copy in Paris at the Bibliothèque Nationale, and the library at Basle University has another 14th-century copy. The Vatican copy was used as the source for the first publication of the manuscript in 1688 by Porcheron. The German scholar Joseph Schnetz published the text in 1940, basing it on the Vatican and Paris editions, which he believed to be more reliable than the Basle edition. Parts of the text, notably that covering Britain, have been published by others, including Richmond and Crawford in 1949, but their document sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |