|
Kara Ahmed Pasha Mosque
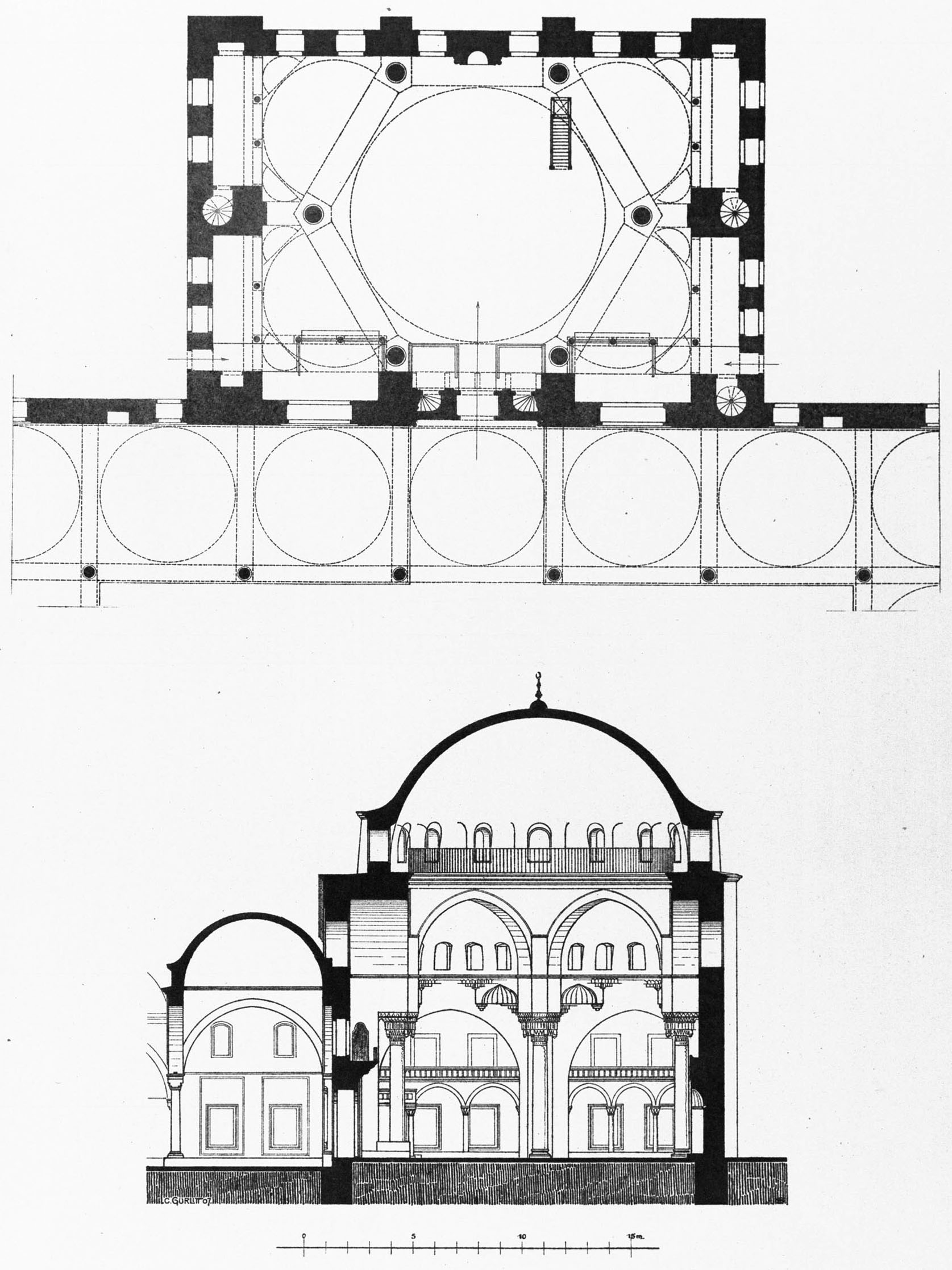
The Kara Ahmed Pasha Mosque or Gazi Ahmed Pasha Mosque ( tr, Kara Ahmet Paşa Camii) is a 16th-century Ottoman mosque near the city walls in Istanbul, Turkey. It was designed by the imperial architect Mimar Sinan and completed in around 1572. History The mosque was commissioned by Kara Ahmed Pasha who was married to Fatma Sultan, a daughter of Selim I. He became grand vizier under Suleiman the Magnificent in 1553 but was executed by strangulation two years later in 1555. The mosque was planned in around 1555 but only constructed between 1565 and 1571–72 after the pasha had been fully exonerated. Architecture The courtyard is surrounded by the cells of a ''medrese'' and a ''dershane'', or main classroom. Attractive apple green and yellow tiles grace the porch, while blue and white ones are found on the east wall of the prayer hall. These tiles date from the mid 16th century. The diameter dome is supported by six red granite columns. Of the three galleries, the wooden ceiling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatih
Fatih () is a district of and a municipality (''belediye'') in Istanbul, Turkey, and home to almost all of the provincial authorities (including the governor's office, police headquarters, metropolitan municipality and tax office) but not the courthouse. It encompasses the peninsula coinciding with old Constantinople. In 2009, the district of Eminönü, which had been a separate municipality located at the tip of the peninsula, was once again remerged into Fatih because of its small population. Fatih is bordered by the Golden Horn to the north and the Sea of Marmara to the south, while the Western border is demarked by the Theodosian wall and the east by the Bosphorus Strait. History Byzantine era Historic Byzantine districts encompassed by present-day Fatih include: ''Exokiónion'', ''Aurelianae'', ''Xerólophos'', '' ta Eleuthérou'', ''Helenianae'', ''ta Dalmatoú'', ''Sígma'', '' Psamátheia'', ''ta Katakalón'', ''Paradeísion'', ''ta Olympíou'', ''ta Kýrou'', '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Vizier
Grand vizier ( fa, وزيرِ اعظم, vazîr-i aʾzam; ota, صدر اعظم, sadr-ı aʾzam; tr, sadrazam) was the title of the effective head of government of many sovereign states in the Islamic world. The office of Grand Vizier was first held by officials in the later Abbasid Caliphate. It was then held in the Ottoman Empire, the Mughal Empire, the Sokoto Caliphate the Safavid Empire and Morocco. In the Ottoman Empire, the Grand Vizier held the imperial seal and could convene all other viziers to attend to affairs of the state; the viziers in conference were called "''Kubbealtı'' viziers" in reference to their meeting place, the ''Kubbealtı'' ('under the dome') in Topkapı Palace. His offices were located at the Sublime Porte. Today, the Prime Minister of Pakistan is referred to in Urdu as ''Wazir-e-azam'', which translates literally to Grand Vizier. Initially, the Grand Viziers were exclusively of Turk origin in the Ottoman Empire. However, after there were troubles b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Mosques In Istanbul
Ottoman is the Turkish spelling of the Arabic masculine given name Uthman ( ar, عُثْمان, ‘uthmān). It may refer to: Governments and dynasties * Ottoman Caliphate, an Islamic caliphate from 1517 to 1924 * Ottoman Empire, in existence from 1299 to 1922 ** Ottoman dynasty, ruling family of the Ottoman Empire *** Osmanoğlu family, modern members of the family * Ottoman architecture Ethnicities and languages * Ottoman Armenians, the Armenian ethnic group in the Ottoman Empire * Ottoman Greeks, the Greek ethnic group in the Ottoman Empire * Ottoman Serbs, the Serbian ethnic group in the Ottoman Empire * Ottoman Turks, the Turkic ethnic group in the Ottoman Empire ** Ottoman Turkish alphabet ** Ottoman Turkish language, the variety of the Turkish language that was used in the Ottoman Empire Products * Ottoman bed, a type of storage bed * Ottoman (furniture), padded stool or footstool * Ottoman (textile), fabric with a pronounced ribbed or corded effect, often made of silk or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimar Sinan Buildings
Traditionally, Iranian architects were known as ''Mi'mars''. The Persian dictionary of ''Mo'in'' defines Mi'mar as: #That who devises the design and plan of a building, and overlooks its construction. #A Banna #That who is responsible for the building, developing, and repairs of a structure or edifice (Emārat). Classical words ''Banna'', ''Mohandes'', ''Ostad'', and ''Amal'' which appear in classical manuals and references of Islamic architecture. Although many scholars do not recognize the Mimar and the Architect to historically be the same, they do agree that their responsibilities overlap extensively. In this list, they are taken to be the same. The list is in chronological order and selectively spans the Islamic age based on available records. There is little, if any, record of the numerous masters of architecture that built some of the early Islamic and pre-Islamic world's wonders of Iran. It is unknown who built the palaces of Bishapur, Firouzabad, Persepolis, Susa, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Buildings And Structures Completed In 1572
Religion is usually defined as a social-cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, transcendental, and spiritual elements; however, there is no scholarly consensus over what precisely constitutes a religion. Different religions may or may not contain various elements ranging from the divine, sacred things, faith,Tillich, P. (1957) ''Dynamics of faith''. Harper Perennial; (p. 1). a supernatural being or supernatural beings or "some sort of ultimacy and transcendence that will provide norms and power for the rest of life". Religious practices may include rituals, sermons, commemoration or veneration (of deities or saints), sacrifices, festivals, feasts, trances, initiations, funerary services, matrimonial services, meditation, prayer, music, art, dance, public service, or other aspects of human culture. Religions have sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


