|
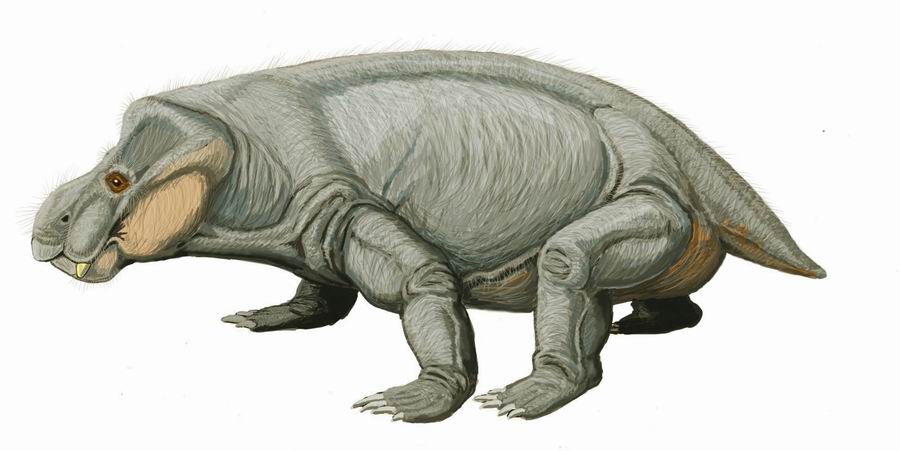
Kannemeyeriiformes
Kannemeyeriiformes is a group of large-bodied Triassic dicynodonts. As a clade, Kannemeyeriiformes has been defined to include the species '' Kannemeyeria simocephalus'' and all dicynodonts more closely related to it than to the species ''Lystrosaurus murrayi''. Evolutionary history Despite being the most species-rich group of dicynodonts in the Triassic Period, kannemeyeriiforms exhibit much less diversity in terms of their anatomy and ecological roles than the dicynodonts from the Permian Period. Lystrosauridae is thought to be the most closely related group (sister taxon) to Kannemeyeriiformes, and since the earliest lystrosaurids are known from the Late Permian, the divergence of these two groups must have occurred at least as far back as this time, implying that a long ghost lineage must exist. Although no kannemeyeriiforms have been found in the Late Permian yet, the recent discovery of '' Sungeodon'' helps fill a gap in the early fossil record of the group by showing th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repelinosaurus
''Repelinosaurus'' is an extinct genus of dicynodont from the Purple Claystone Formation of Luang Prabang in Laos, Southeast Asia that lived at around the time of the Permian-Triassic boundary and possibly dates to the earliest Early Triassic. Its type and only known species is ''R. robustus''. ''Repelinosaurus'' was originally described as the earliest known kannemeyeriiform dicynodont, supporting the idea of a more rapid radiation of the Triassic kannemeyeriiform dicynodonts during the Early Triassic following the Permian mass extinction. However, it may alternatively be more closely related to the Permian ''Dicynodon''. The discovery of a potential early kannemeyeriiform in an understudied locality like Laos highlights the importance of such places in dicynodont research, which has been largely focused on historically important localities such as the Karoo Basin of South Africa. Description ''Repelinosaurus'' was a medium-sized dicynodont (largest skull length of ) currently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicynodont
Dicynodontia is an extinct clade of anomodonts, an extinct type of non-mammalian therapsid. Dicynodonts were herbivorous animals with a pair of tusks, hence their name, which means 'two dog tooth'. Members of the group possessed a horny, typically toothless beak, unique amongst all synapsids. Dicynodonts first appeared in Southern Pangaea during the mid-Permian, ca. 270–260 million years ago, and became globally distributed and the dominant herbivorous animals in the Late Permian, ca. 260–252 Mya. They were devastated by the end-Permian Extinction that wiped out most other therapsids ca. 252 Mya. They rebounded during the Triassic but died out towards the end of that period. They were the most successful and diverse of the non-mammalian therapsids, with over 70 genera known, varying from rat-sized burrowers to elephant-sized browsers. Characteristics The dicynodont skull is highly specialised, light but strong, with the synapsid temporal openings at the rear of the sku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinokannemeyeria
''Sinokannemeyeria'' is a genus of kannemeyeriiform dicynodont that lived during the Anisian age of Middle Triassic period in what is now Shanxi, China.J. Liu. 2015. New discoveries from the Sinokannemeyeria-Shansisuchus Assemblage Zone: 1. Kannemeyeriiformes from Shanxi, China. Vertebrata PalAsiatica 53(1):16-28 Description ''Sinokannemeyeria'' was about in length and in weight. It had relatively short, stumpy legs which were held slightly sprawling gait to the sides of its body. The limb girdles were formed into large, heavy plates of bone to support the weight of the wide, heavily built body. ''Sinokannemeyeria'' was probably not a fast or agile animal. The front of the jaw had a small horn-covered beak, and there were two small tusks growing from bulbous projections on the upper jaw. These tusks could have been used to dig up roots. Compared to '' Kannemeyeria'', it had broader snout, smaller temporal fenestrae and lower temporal crests. ''Sinokannemeyeria'' may had ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uralokannemeyeria
''Uralokannemeyeria'' is an extinct genus of kannemeyeriiform dicynodont known from the Middle Triassic Donguz Formation of Bashkortostan, Russia Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh .... References Anomodont genera Kannemeyeriiformes Prehistoric synapsids of Europe Fossil taxa described in 1971 {{anomodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angonisaurus
''Angonisaurus'' is an extinct genus of kannemeyeriiform dicynodont from the Middle Triassic of Africa between 247 and 242 million years ago.Hancox, P. John, Kenneth D. Angielczyk, and Bruce S. Rubidge. "Angonisaurus and Shansiodon, Dicynodonts (Therapsida, Anomodontia) from Subzone C of the Cynognathus Assemblage Zone (Middle Triassic) of South Africa." ''Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology'' 33.3 (2013): 655-76. Only one species, ''Angonisaurus cruickshanki'' has been assigned to this genus. This genus is thought to have been widely spread but rare in southern Gondwana. Though few in number, the fossil record of ''Angonisaurus cruickshanki'' contains multiple specimens giving it a measurable stratigraphic range. Sexually dimorphic features are found in ''Angonisaurus'' which include presence or absence of tusks and difference is size and robustness of the temporal arch and the rostral. Discovery and naming ''Angonisaurus'' was discovered in the African Karoo Basin in 1983. Bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannemeyeria Simocephalus
''Kannemeyeria'' is a genus of dicynodont that lived during the Anisian age of Middle Triassic period in what is now Africa and South America. The generic name is given in honor of Dr. Daniel Rossouw Kannemeyer, the South African fossil collector who discovered the original specimen. It is one of the first representatives of the family, and hence one of the first large herbivores of the Triassic. Description ''Kannemeyeria'' was about in length, about the size of an ox. Although it had a large head, it was lightweight due to the size of the eye sockets and nasal cavity. It also had limb girdles which formed massive plates of bone that helped support its heavily built body. ''Kannemeyeria'' was well-adapted to living as a herbivore; it had a powerful beak and strong jaw muscles built for shearing plant material. ''Kannemeyeria'' had a massive head with unusually large openings for the eyes, nostrils and jaw muscles. It evidently tore up roots, stripped leaves from the vegeta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stahleckeriidae
Stahleckeriidae is a family of dicynodont therapsids whose fossils are known from the Triassic of North America, South America, Asia and Africa. Classification Phylogeny Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ... from Kammerer ''et al.'' (2013): Genera References Kannemeyeriiformes Induan first appearances Norian extinctions Prehistoric therapsid families {{anomodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinodontosauridae
''Dinodontosaurus'' (meaning "terrible-toothed lizard") is a genus of dicynodont therapsid. It was medium to large dicynodont of the Triassic (with skull up to long) and had a beak corneum. It lived in the Middle Triassic but disappeared in the Upper Triassic. Species * ''Dinodontosaurus tener'' is the most common species of dicynodont that existed in the Middle Triassic, and more common in the fossil layers that age in Rio Grande do Sul, in Rota Paleontológica. They are found mainly in the Paleontological Site Chiniquá in São Pedro do Sul and Candelária, where a group of ten pups were found together, demonstrating that these animals had strategies for coexistence in a group and caring for their offspring. ''Diodontosaurus pedroanum'' Tupi-Caldas, 1936 and ''Dinodontosaurus oliveirai'', Romer A Reference Card or "Romer" is a device for increasing the accuracy when reading a grid reference from a map. Made from transparent plastic, paper or other materials, they are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sungeodon
''Sungeodon'' is an extinct genus of dicynodont therapsid from the Early Triassic of China. It is known from a single type species In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen( ..., ''Sungeodon kimkraemerae'', which was named in 2014. ''Sungeodon'' is the earliest member of a group of dicynodonts called Kannemeyeriiformes, which would radiate later in the Triassic to become the dominant large herbivores of terrestrial ecosystems. Before its discovery no kannemeyeriiform dicynodonts were known from the Early Triassic. The presence of ''Sungeodon'' in the earliest Triassic Jiucaiyuan Formation indicates that dicynodonts diversified soon after the Permian-Triassic extinction event, mirroring the explosive radiations of other tetrapod groups such as archosaurs soon after the extinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stahleckeria
''Stahleckeria'' is an extinct genus of Middle Triassic (Ladinian) dicynodonts.''Stahleckeria'' at .org It lived about 240 million years ago in what is now and . As a member of the group Kannemeyeriiformes, it was similar to the genus '' Kannemeyeria'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |