|
Kamenka, Mezensky District, Arkhangelsk Oblast
Kamenka (russian: Ка́менка) is a rural locality (a settlement) in Mezensky District of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia, located on the left bank of the Mezen River at the mouth of the Kamenka River (hence the name of the settlement), some northwest of Mezen. Municipally, it is the administrative center of Kamenskoye Urban Settlement, one of the two urban settlements in Mezensky Municipal District. Population: History In 1882, a sawmill was built in the mouth of the Kamenka River by the Rushnikov brothers. There was timber rafting on the Mezen, which persisted until the 1990s. Kamenka was one of the places where the logs were lifted from the water. The sawmill produced boards, all of which were exported. At the time, it was part of Mezensky Uyezd of Arkhangelsk Governorate. On July 15, 1929 the uyezds were abolished, and Mezensky District Mezensky District (russian: Мезе́нский райо́н) is an administrative district (raion), one of the twenty-one in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arkhangelsk Oblast
Arkhangelsk Oblast (russian: Арха́нгельская о́бласть, ''Arkhangelskaya oblast'') is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). It includes the Arctic Ocean, Arctic archipelagos of Franz Josef Land and Novaya Zemlya, as well as the Solovetsky Islands in the White Sea. Arkhangelsk Oblast also has administrative jurisdiction over the Nenets Autonomous Okrug (NAO). Including the NAO, Arkhangelsk Oblast has an area of 587,400 km2. Its population (including the NAO) was 1,227,626 as of the Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census. The classification of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Arkhangelsk, with a population of 301,199 as of the 2021 Census, is the administrative center of the oblast.Charter, Article 5 The second largest city is the nearby Severodvinsk, home to Sevmash, a major shipyard for the Russian Navy. Among the oldest populated places of the oblast are Kholmogory, Arkhangelsk Oblast, Kholmogory, Kargopol, and S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arkhangelsk Governorate
Arkhangelsk Governorate (russian: link=no, Архангельская губерния, ''Arkhangelskaya guberniya'') was an administrative division (a '' guberniya'') of the Russian Empire and Russian SFSR, which existed from 1796 until 1929. Its seat was in Arkhangelsk. The governorate was located in the north of the Russian Empire and bordered Tobolsk Governorate in the east, Vologda Governorate in the south, Olonets Governorate in the southwest, Sweden (later Grand Duchy of Finland and later independent Finland) in the west, and Norway in north-west. In the north, the governorate was limited by the White and Barents Seas. The area of the governorate is currently split between Arkhangelsk and Murmansk Oblasts, the Komi Republic, the Republic of Karelia, and the Nenets Autonomous Okrug. History In 1780, the Archangelgorod Governorate, with its center in Arkhangelsk, was abolished and transformed into the Vologda Viceroyalty. The viceroyalty was subdivided into three oblast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
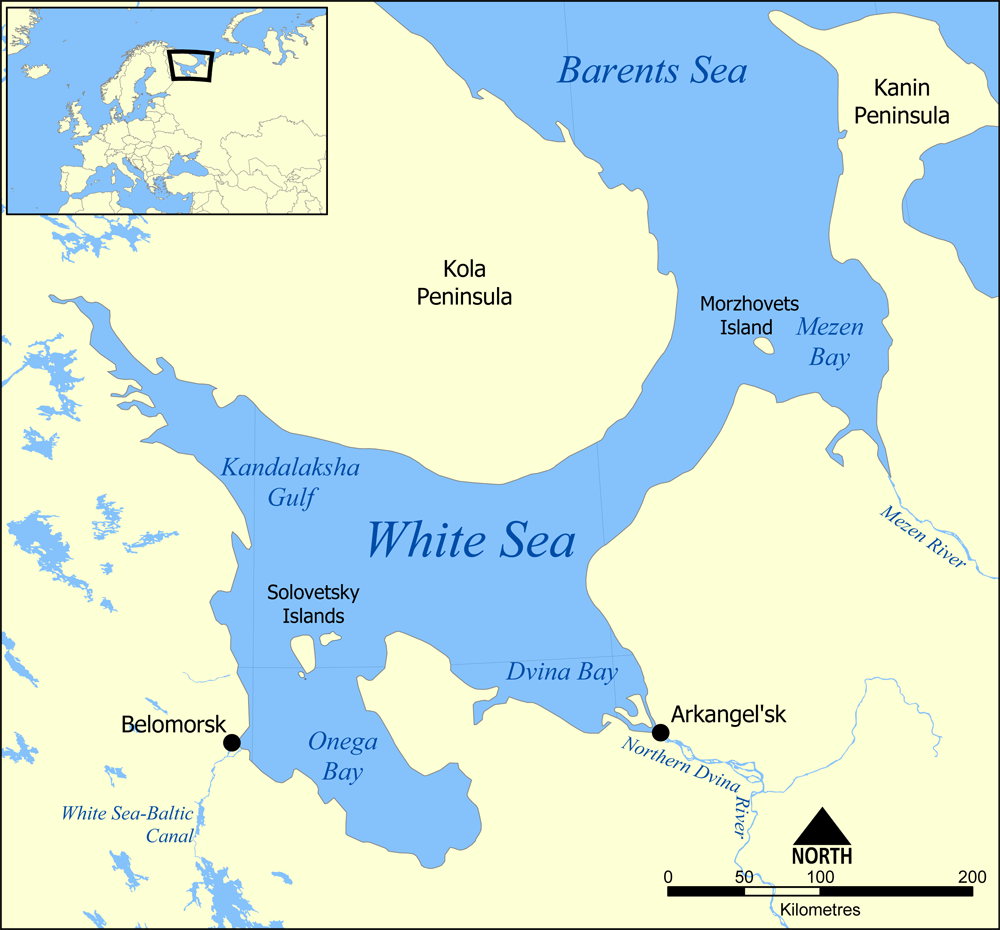
Kuloy River (White Sea)
The Kuloy (russian: Кулой) is a river in Pinezhsky and Mezensky Districts of Arkhangelsk Oblast in Russia. Its mouth is located in the Mezen Bay of the White Sea. It is long, and the area of its basin . The principal tributaries of the Kuloy are the Kyolda (left), the Nemnyuga (right), and the Soyana (left). In the upper course, the Kuloy is known as the Sotka; the total length of the Sotka and the Kuloy is . In the low course, the Sotka approaches the middle course of the Pinega and passes within several kilometers from the Pinega. In this place, close to the settlement of Pinega, the Kuloy-Pinega Canal was constructed in 1926—1928, however, currently the canal is pretty much neglected. Below the mouth of the canal the river is known as the Kuloy; above the mouth, the river is known as the Sotka. The lower of the course of Kuloy, downstream from the selo of Kulogory, are navigable; the course adjacent to the canal is not navigable anymore. There is no passenger navi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winter Road
A winter road is a seasonal road only usable during the winter, i.e. it has to be re-built every year. This road typically runs over land and over frozen lakes, rivers, swamps, and sea ice.Proskin et al, 2011. Guidelines for the Construction and Operation of Winter Roads, Transportation Association of Canada.- IHSA, 2014. Best practices for building and working safely on ice covers in Ontario, Mississauga, Ontario, 43 p.- NorthWest Territories Transportation, 2015. Guidelines for safe ice construction, Yellowknife, NWT, Canada, 44 p.Spencer, P.A., Strandberg, A.G. and Maddock, W.A., 2008. Ice and toundra road design for module transport, Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Ships and Marine Structures in Cold Regions (ICETECH), Banff. Segments of a winter road that cross an expanse of floating ice are also referred to as an ice road or an ice bridge. The foundations underlying over-land segments is most often native soil or muskeg frozen to a given depth, and local ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamenka Airport
Kamenka may refer to: ;People *Eugene Kamenka, Australian philosopher, socialist ;Places *Kamenka Urban Settlement, a municipal formation which the town of district significance of Kamenka in Kamensky District of Penza Oblast, Russia is incorporated as * Kamenka, Russia, several inhabited localities in Russia *Kamenka, an alternative name of the town of Taskala, Kazakhstan *Camenca, capital of the Administrative Region of Camenca of Transnistria * Kamianka (other) (''Kamenka''), several inhabited localities in Ukraine ;Rivers *Kamenka (Ob), a minor tributary of the Ob in Novosibirsk Oblast * Kamenka (Saint Petersburg), a river in Lakhta-Olgino Municipal Okrug near Saint Petersburg *Kamenka (Iset), a tributary of the Iset in Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia *Kamenka (Nerl), a tributary of the Nerl in Vladimir Oblast, Russia ;Other *Kamenka (island), an island in Lake Peipsi-Pihkva (between Estonia and Russia) *5385 Kamenka, an asteroid discovered by Lyudmila Chernykh, Soviet a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rossiyskaya Gazeta
' (russian: Российская газета, lit. Russian Gazette) is a Russian newspaper published by the Government of Russia. The daily newspaper serves as the official government gazette of the Government of the Russian Federation, publishing government-related affairs such as official decrees, statements and documents of state bodies, the promulgation of newly approved laws, Presidential decrees, and government announcements. History ''Rossiyskaya Gazeta'' was founded in 1990 by the Supreme Soviet of the Russian SFSR during the '' glasnost'' reforms in Soviet Union, shortly before the country dissolved in 1991. ''Rossiyskaya Gazeta'' became official government newspaper of the Russian Federation, replacing ''Izvestia'' and '' Sovetskaya Rossiya'' newspapers, which were both privatized after the Soviet Union's dissolution. The role of ''Rossiyskaya Gazeta'' is determined by the Law of the Russian Federation N 5-FZ, dated 14 June 1994 and entitled "''On the Procedure of P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
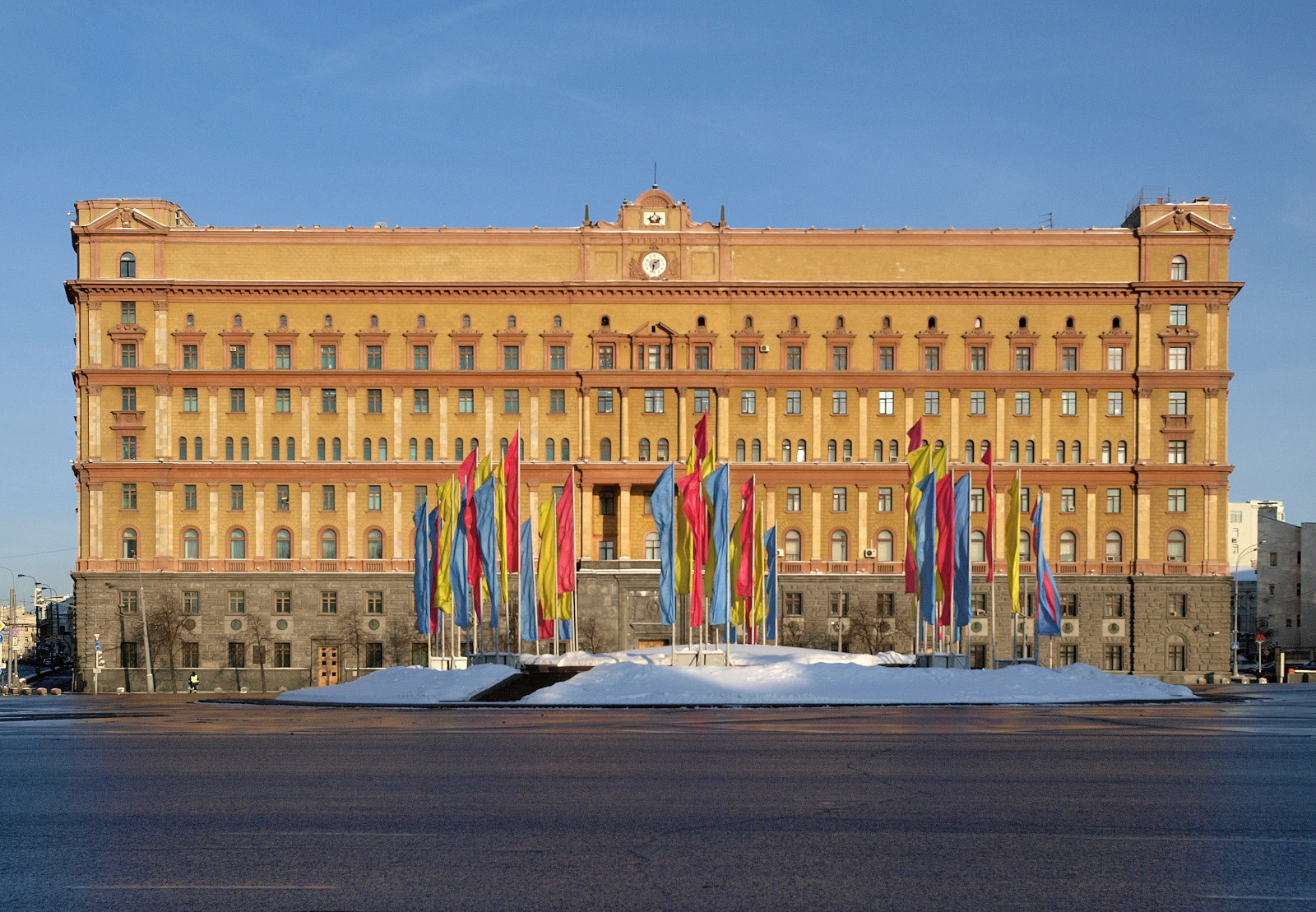
Federal Security Service (Russia)
The Federal Security Service of the Russian Federation (FSB) RF; rus, Федеральная служба безопасности Российской Федерации (ФСБ России), Federal'naya sluzhba bezopasnosti Rossiyskoy Federatsii, fʲɪdʲɪˈralʲnəjə ˈsluʐbə bʲɪzɐˈpasnəstʲɪ rɐˈsʲijskəj fʲɪdʲɪˈratsɨɪ) is the principal security agency of Russia and the main successor agency to the Soviet Union's KGB; its immediate predecessor was the Federal Counterintelligence Service (FSK) which was reorganized into the FSB in 1995. The three major structural successor components of the former KGB that remain administratively independent of the FSB are the Foreign Intelligence Service (SVR), the Federal Protective Service (FSO), and the Main Directorate of Special Programs of the President of the Russian Federation (GUSP). The primary responsibilities are within the country and include counter-intelligence, internal and border security, counter-terr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Border Security Zone Of Russia
A Border Security Zone in Russia is the designation of a Border zone, strip of land (usually, though not always, along a Russian external border) where economic activity and access are restricted in line with the Frontier Regime Regulations set by the Federal Security Service (FSB). For foreign tourists to visit the zone a permit issued by the local FSB department is required. The restricted access zone (of width generally, but e.g., running as much as deep along the Estonian border) was established in the Soviet Union in 1934, and later expanded, at times including vast territories. In 1935–1936, in order to secure the western border of the Soviet Union, many nationalities considered unreliable (Poles, Germans, Ingrian Finns, Estonians, Latvians) were population transfer in the Soviet Union, forcibly transferred from the zone by forces of NKVD. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, the borders of the new Russian Federation were dramatically different, but the zone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pravda Severa
''Pravda Severa'' (russian: "Правда Севера", Truth of the North) is a Russian Arkhangelsk-based newspaper, published since 1917. It is issued three times a week on Tuesday, Wednesday and Saturday in the A3 format. The Wednesday circulation is 20,050 copies, with 7,000—8,000 copies on Tuesday and Saturday. Notes Russian-language newspapers published in Russia 1917 establishments in Russia Arkhangelsk Publications established in 1917 {{Russia-newspaper-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mezensky Uyezd
Mezensky Uyezd (''Мезенский уезд'') was one of the subdivisions of the Arkhangelsk Governorate of the Russian Empire. It was situated in the eastern part of the governorate. Its administrative centre was Mezen. Demographics At the time of the Russian Empire Census of 1897, Mezensky Uyezd had a population of 25,029. Of these, 91.2% spoke Russian, 4.4% Komi-Zyrian, 4.2% Nenets and 0.1% Romani Romani may refer to: Ethnicities * Romani people, an ethnic group of Northern Indian origin, living dispersed in Europe, the Americas and Asia ** Romani genocide, under Nazi rule * Romani language, any of several Indo-Aryan languages of the Roma ... as their native language. Демоскоп Weekly - Приложение. Справочник статистических показателей References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mezensky District
Mezensky District (russian: Мезе́нский райо́н) is an administrative district (raion), one of the twenty-one in Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia.Law #65-5-OZ As a municipal division, it is incorporated as Mezensky Municipal District.Law #258-vneoch.-OZ It is located in the northeast of the oblast and borders with Nenets Autonomous Okrug in the northeast, Ust-Tsilemsky District of the Komi Republic in the east, Leshukonsky and Pinezhsky Districts in the south, and with Primorsky District in the southwest. From the north, the district borders the White Sea. The area of the district is . Its administrative center is the town of Mezen. Population: The population of Mezen accounts for 34.6% of the total district's population. History The area was originally populated by speakers of Uralic languages and then colonized by the Novgorod Republic. After the fall of Novgorod, the area became a part of the Grand Duchy of Moscow. Komi started moving to the Mezen in the 14th and 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timber Rafting
Timber rafting is a method of transporting felled tree trunks by tying them together to make rafts, which are then drifted or pulled downriver, or across a lake or other body of water. It is arguably, after log driving, the second cheapest means of transporting felled timber. Both methods may be referred to as timber floating. Historical rafting Unlike log driving, which was a dangerous task of floating separate logs, floaters or raftsmen could enjoy relative comfort of navigation, with cabins built on rafts, steering by means of oars and possibility to make stops. On the other hand, rafting requires wider waterflows. Timber rafts were also used as a means of transportation of people and goods, both raw materials (ore, fur, game) and man-made. Theophrastus (''Hist. Plant.'' 5.8.2) records how the Romans imported Corsican timber by way of a huge raft propelled by as many as fifty masts and sails. This practice used to be common in many parts of the world, especially North A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |