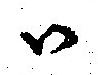|
Kamarupi Prakrit
Kamarupi Prakrit is the Attested language, postulated Middle Indo-Aryan (MIA) Prakrit language used in ancient Kamarupa (5th–12th century). This language has been derived from Gauda-Kamarupi Prakrit and the historical ancestor of the Kamatapuri lects and the modern Assamese language;"In this study I refer to the western dialect of Asamiya as ''Kamrupi'', and the historical ancestor of proto-Kamata and proto-Asamiya as ''proto-Kamrupa''." and can be dated prior to 1250 CE, when the proto-Kamta language, the parent of the Kamatapuri lects, began to develop. Though not substantially proven, the existence of the language that predated the Kamatapuri lects and modern Assamese is widely believed to be descended from it. The evidence of this MIA exist in systematic errors in the Sanskrit language used in the Kamarupa inscriptions. A distinguishing characteristic of Kamarupa inscriptions is the replacement of ''ś'' and ''ṣ'' by ''s'', which is contrary to Vararuci's rule, the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kamarupa
Kamarupa (; also called Pragjyotisha or Pragjyotisha-Kamarupa), an early state during the Classical period on the Indian subcontinent, was (along with Davaka) the first historical kingdom of Assam. The Kamrupa word first appeared in the Samudragupta Allahabad Edict before that there is no mention of existence of this word. Though Kamarupa prevailed from 350 to 1140 CE, Davaka was absorbed by Kamarupa in the 5th century CE."As regards the eastern limits of the kingdom, Davaka was absorbed within Kamarupa under Kalyanavarman and the outlying regions were brought under subjugation by Mahendravarman." Ruled by three dynasties from their capitals in present-day Guwahati, North Guwahati and Tezpur, Kamarupa at its height covered the entire Brahmaputra Valley, parts of North Bengal, Bhutan and northern part of Bangladesh, and at times portions of what is now West Bengal, Bihar and Sylhet. Though the historical kingdom disappeared by the 12th century to be replaced by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sukumar Sen (linguist)
Sukumar Sen (16 January 1900 – 3 March 1992) was an Indian linguist and historian of the Bengali literature, who was also well versed in Pāli, Prakrit and Sanskrit. Life Sen was born on 16 January 1900 in a prominent kayastha family to Harendra Nath Sen, a lawyer and Nabanalini Devi. His hometown was Gotan, near Shyamsundar in the Purba Bardhaman district. Sen was educated at the Burdwan Municipal High School, Burdwan, 1917. He obtained an F.A. in 1919 from Burdwan Raj College, then affiliated with the University of Calcutta. He received a divisional scholarship and earned first class honours in Sanskrit from the Government Sanskrit college, Sanskrit College in 1921. He studied Comparative Philology in Kolkata, scoring the highest marks in 1923. Linguists Suniti Kumar Chatterji and Irach Jehangir Sorabji Taraporewala were his teachers. He received a Premchand Roychand Scholarship and a PhD degree. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Odia Language
Odia (;"Odia" ''Lexico''. , ISO 15919, ISO: , ; formerly rendered as Oriya) is a classical languages of India, classical Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Indian state of Odisha. It is the Languages with official status in India, official language in Odisha (formerly rendered as Orissa), where native speakers make up 82% of the population, and it is also spoken in parts of West Bengal, Jharkhand, Andhra Pradesh and Chhattisgarh. Odia is one of the Languages with official status in India, official languages of India; it is the official language of Odisha and the second official language of Jharkhand. The Odia language has various dialects varieties, including the Baleswari Odia (Northern dialect), Kataki, Dhenkanalia, Anugulia(central dialect), Ganjami O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bengali Language
Bengali, also known by its endonym and exonym, endonym Bangla (, , ), is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language belonging to the Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is native to the Bengal region (Bangladesh, India's West Bengal and Tripura) of South Asia. With over 242 million native speakers and another 43 million as second language speakers as of 2025, Bengali is the List of languages by number of native speakers, sixth most spoken native language and the List of languages by total number of speakers, seventh most spoken language by the total number of speakers in the world. Bengali is the Official language, official, National language, national, and most widely spoken language of Bangladesh, with 98% of Bangladeshis using Bengali as their first language. It is the second-most widely spoken scheduled languages of India, language in India. It is the official language of the Indian states of West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nidhanpur Inscription Of Bhaskar Varman
Nidhanpur is a village in Sylhet District, Bangladesh. This ancient village, earlier within Kamarupa Kingdom, is known for discovery of many Copper plate grants of Kamarupa kings such as Bhutivarman and Bhaskaravarman. Inscription of Bhaskaravarman gives detailed account of land grants given to Brahmins. Copper plates found mostly in Panchakhanda pargana where historians opined that actual granted lands are located. See also * Nidhanpur copperplate inscription * Varman Dynasty The Varman dynasty (350–650) was the first historical dynasty of the Kamarupa kingdom. It was established by Pushyavarman, a contemporary of Samudragupta. The earlier Varmans were subordinates of the Gupta Empire, but as the power of the Gup ... References Villages in Sylhet District Villages in Sylhet Division {{Sylhet-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Visarga
In Sanskrit phonology, Visarga () is the name of the voiceless glottal fricative, written in Devanagari as '' . It was also called, equivalently, ' by earlier grammarians. The word ''visarga'' () literally means "sending forth, discharge". Visarga is an allophone of and in pausa (at the end of an utterance). Since is a common inflectional suffix (of nominative singular, second person singular, etc.), visarga appears frequently in Sanskrit texts. In the traditional order of Sanskrit sounds, visarga and anusvāra appear between vowels and stop consonants. The precise pronunciation of visarga in Vedic texts may vary between Śākhās. Some pronounce a slight echo of the preceding vowel after the aspiration: will be pronounced , and will be pronounced . Visarga is not to be confused with colon. Types The visarga is commonly found in writing, resembling the punctuation mark of colon or as two tiny circles one above the other. This form is retained by most Indic scripts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Word Stem
In linguistics, a word stem is a word part responsible for a word's lexical meaning. The term is used with slightly different meanings depending on the morphology of the language in question. For instance, in Athabaskan linguistics, a verb stem is a root that cannot appear on its own and that carries the tone of the word. Typically, a stem remains unmodified during inflection with few exceptions due to apophony (for example in Polish, ("city") and ("in the city"); in English, ''sing'', ''sang'', and ''sung'', where it can be modified according to morphological rules or peculiarities, such as sandhi). Word stem comparisons across languages have helped reveal cognates that have allowed comparative linguists to determine language families and their history. Root vs stem The word ''friendship'' is made by attaching the morpheme ''-ship'' to the root word ''friend'' (which some linguists also call a stem). While the inflectional plural morpheme ''-s'' can be attached to '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Declension
In linguistics, declension (verb: ''to decline'') is the changing of the form of a word, generally to express its syntactic function in the sentence by way of an inflection. Declension may apply to nouns, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, and determiners. It serves to indicate grammatical number, number (e.g. singular, dual, plural), grammatical case, case (e.g. nominative case, nominative, accusative case, accusative, genitive case, genitive, or dative case, dative), grammatical gender, gender (e.g. masculine, feminine, or neuter), and a number of other grammatical categories. Inflectional change of verbs is called Grammatical conjugation, conjugation. Declension occurs in many languages. It is an important aspect of language families like Quechuan languages, Quechuan (i.e., languages native to the Andes), Indo-European languages, Indo-European (e.g. German language, German, Icelandic language, Icelandic, Irish language, Irish, Baltic language, Lithuanian and Latvian, Slavic lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sibilant
Sibilants (from 'hissing') are fricative and affricate consonants of higher amplitude and pitch, made by directing a stream of air with the tongue towards the teeth. Examples of sibilants are the consonants at the beginning of the English words ''sip'', ''zip'', ''ship'', and ''genre''. The symbols in the International Phonetic Alphabet used to denote the sibilant sounds in these words are, respectively, . Sibilants have a characteristically intense sound, which accounts for their paralinguistic use in getting one's attention (e.g. calling someone using "psst!" or quieting someone using "shhhh!"). Overview In the hissing sibilants and , the back of the tongue forms a narrow channel (is '' grooved'') to focus the stream of air more intensely, resulting in a high pitch. With the hushing sibilants (occasionally termed ''shibilants''), such as English , , , and , the tongue is flatter, and the resulting pitch lower. A broader category is stridents, which include more fricati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Analogy
Analogy is a comparison or correspondence between two things (or two groups of things) because of a third element that they are considered to share. In logic, it is an inference or an argument from one particular to another particular, as opposed to deduction, induction, and abduction. It is also used where at least one of the premises, or the conclusion, is general rather than particular in nature. It has the general form ''A is to B as C is to D''. In a broader sense, analogical reasoning is a cognitive process of transferring some information or meaning of a particular subject (the analog, or source) onto another (the target); and also the linguistic expression corresponding to such a process. The term analogy can also refer to the relation between the source and the target themselves, which is often (though not always) a similarity, as in the biological notion of analogy. Analogy plays a significant role in human thought processes. It has been argued that analogy li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vowels
A vowel is a speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract, forming the nucleus of a syllable. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in quantity (length). They are usually voiced and are closely involved in prosodic variation such as tone, intonation and stress. The word ''vowel'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "vocal" (i.e. relating to the voice). In English, the word ''vowel'' is commonly used to refer both to vowel sounds and to the written symbols that represent them (, , , , , and sometimes and ). Definition There are two complementary definitions of vowel, one phonetic and the other phonological. *In the phonetic definition, a vowel is a sound, such as the English "ah" or "oh" , produced with an open vocal tract; it is median (the air escapes along the middle of the tongue), oral (at least some of the airflow must escape through the mouth), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |