|
Kalles Fraktaler
Kalles Fraktaler is a free Windows-based fractal In mathematics, a fractal is a geometric shape containing detailed structure at arbitrarily small scales, usually having a fractal dimension strictly exceeding the topological dimension. Many fractals appear similar at various scales, as illu ... zoom computer program used for zooming into fractals such as the Mandelbrot set and the Burning Ship fractal at very high speed, utilizing Perturbation and Series Approximation. Functionality Kalles Fraktaler focuses on zooming into fractals. This is possible in the included fractal formulas such like the Mandelbrot set, Burning ship or so called "TheRedshiftRider" fractals. Many tweaks can visualize phenomena better or solve glitches concerning the calculation issues. Other functions are color seeds, slopes for showing iteration depths or entering location parameters in the complex plane. The via zooming reached location can be saved as a KFR file. The rendered image can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractal-generating Software
Fractal-generating software is any type of graphics software that generates images of fractals. There are many fractal generating programs available, both free and commercial. Mobile apps are available to play or tinker with fractals. Some programmers create fractal software for themselves because of the novelty and because of the challenge in understanding the related mathematics. The generation of fractals has led to some very large problems for pure mathematics. Fractal generating software creates mathematical beauty through visualization. Modern computers may take seconds or minutes to complete a single high resolution fractal image. Images are generated for both simulation (modeling) and random fractals for art. Fractal generation used for modeling is part of realism in computer graphics. Fractal generation software can be used to mimic natural landscapes with fractal landscapes and scenery generation programs. Fractal imagery can be used to introduce irregularity to an ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalles Fraktaler Adventurous-forest 00024 1
Kalles may refer to: * Kalles Kaviar, a brand of Swedish caviar * Kalles (Bithynia) Cales or Kales ( grc, Κάλης), also Calles or Kalles (Κάλλης), was an emporium or trading place on the coast of ancient Bithynia at the mouth of a river of the same name. Cales was 120 stadia east of Elaeus. It is located near Alaplı ..., a town of ancient Bithynia * Kalles (river), a river of Asia Minor {{dab, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for servers, and Windows IoT for embedded systems. Defunct Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile, and Windows Phone. The first version of Windows was released on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Windows is the most popular desktop operating system in the world, with 75% market share , according to StatCounter. However, Windows is not the most used operating system when including both mobile and desktop OSes, due to Android's massive growth. , the most recent version of Windows is Windows 11 for consumer PCs and tablets, Windows 11 Enterprise for corporations, and Windows Server 2022 for servers. Genealogy By marketing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractal
In mathematics, a fractal is a geometric shape containing detailed structure at arbitrarily small scales, usually having a fractal dimension strictly exceeding the topological dimension. Many fractals appear similar at various scales, as illustrated in successive magnifications of the Mandelbrot set. This exhibition of similar patterns at increasingly smaller scales is called self-similarity, also known as expanding symmetry or unfolding symmetry; if this replication is exactly the same at every scale, as in the Menger sponge, the shape is called affine self-similar. Fractal geometry lies within the mathematical branch of measure theory. One way that fractals are different from finite geometric figures is how they scale. Doubling the edge lengths of a filled polygon multiplies its area by four, which is two (the ratio of the new to the old side length) raised to the power of two (the conventional dimension of the filled polygon). Likewise, if the radius of a filled sphere i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
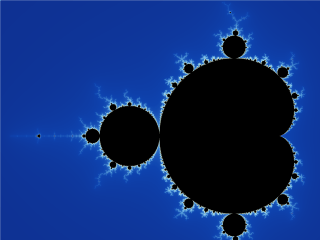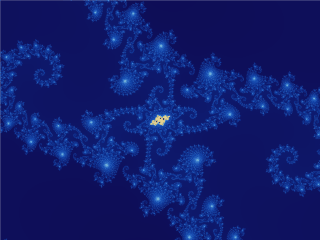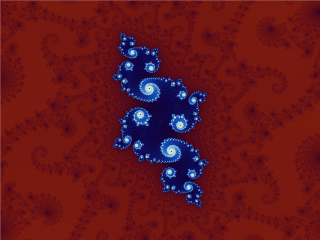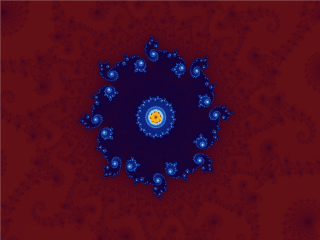
Mandelbrot Set
The Mandelbrot set () is the set of complex numbers c for which the function f_c(z)=z^2+c does not diverge to infinity when iterated from z=0, i.e., for which the sequence f_c(0), f_c(f_c(0)), etc., remains bounded in absolute value. This set was first defined and drawn by Robert W. Brooks and Peter Matelski in 1978, as part of a study of Kleinian groups. Afterwards, in 1980, Benoit Mandelbrot obtained high-quality visualizations of the set while working at IBM's Thomas J. Watson Research Center in Yorktown Heights, New York. Images of the Mandelbrot set exhibit an elaborate and infinitely complicated boundary that reveals progressively ever-finer recursive detail at increasing magnifications; mathematically, one would say that the boundary of the Mandelbrot set is a ''fractal curve''. The "style" of this recursive detail depends on the region of the set boundary being examined. Mandelbrot set images may be created by sampling the complex numbers and testing, for each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burning Ship Fractal
The Burning Ship fractal, first described and created by Michael Michelitsch and Otto E. Rössler in 1992, is generated by iterating the function: :z_ = (, \operatorname \left(z_n\right), +i, \operatorname \left(z_n\right), )^2 + c, \quad z_0=0 in the complex plane \mathbb which will either escape or remain bounded. The difference between this calculation and that for the Mandelbrot set is that the real and imaginary components are set to their respective absolute values before squaring at each iteration. The mapping is non-analytic because its real and imaginary parts do not obey the Cauchy–Riemann equations.Michael Michelitsch and Otto E. Rössler (1992). "The "Burning Ship" and Its Quasi-Julia Sets". In: ''Computers & Graphics'' Vol. 16, No. 4, pp. 435–438, 1992. Reprinted in Clifford A. Pickover Ed. (1998). ''Chaos and Fractals: A Computer Graphical Journey — A 10 Year Compilation of Advanced Research''. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier. Implementation The bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plotting Algorithms For The Mandelbrot Set
] There are many programs and Algorithm, algorithms used to plot the Mandelbrot set and other fractals, some of which are described in fractal-generating software. These programs use a variety of algorithms to determine the color of individual pixels efficiently. Escape time algorithm The simplest algorithm for generating a representation of the Mandelbrot set is known as the "escape time" algorithm. A repeating calculation is performed for each ''x'', ''y'' point in the plot area and based on the behavior of that calculation, a color is chosen for that pixel. Unoptimized naïve escape time algorithm In both the unoptimized and optimized escape time algorithms, the ''x'' and ''y'' locations of each point are used as starting values in a repeating, or iterating calculation (described in detail below). The result of each iteration is used as the starting values for the next. The values are checked during each iteration to see whether they have reached a critical "escape" condi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burning Ship
The Burning Ship fractal, first described and created by Michael Michelitsch and Otto E. Rössler in 1992, is generated by iterating the function: :z_ = (, \operatorname \left(z_n\right), +i, \operatorname \left(z_n\right), )^2 + c, \quad z_0=0 in the complex plane \mathbb which will either escape or remain bounded. The difference between this calculation and that for the Mandelbrot set is that the real and imaginary components are set to their respective absolute values before squaring at each iteration. The mapping is non-analytic because its real and imaginary parts do not obey the Cauchy–Riemann equations.Michael Michelitsch and Otto E. Rössler (1992). "The "Burning Ship" and Its Quasi-Julia Sets". In: ''Computers & Graphics'' Vol. 16, No. 4, pp. 435–438, 1992. Reprinted in Clifford A. Pickover Ed. (1998). ''Chaos and Fractals: A Computer Graphical Journey — A 10 Year Compilation of Advanced Research''. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier. Implementation The b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iteration
Iteration is the repetition of a process in order to generate a (possibly unbounded) sequence of outcomes. Each repetition of the process is a single iteration, and the outcome of each iteration is then the starting point of the next iteration. In mathematics and computer science, iteration (along with the related technique of recursion) is a standard element of algorithms. Mathematics In mathematics, iteration may refer to the process of iterating a function, i.e. applying a function repeatedly, using the output from one iteration as the input to the next. Iteration of apparently simple functions can produce complex behaviors and difficult problems – for examples, see the Collatz conjecture and juggler sequences. Another use of iteration in mathematics is in iterative methods which are used to produce approximate numerical solutions to certain mathematical problems. Newton's method is an example of an iterative method. Manual calculation of a number's square root is a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GUI Kalles Fraktaler2+
The GUI ( "UI" by itself is still usually pronounced . or ), graphical user interface, is a form of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and audio indicator such as primary notation, instead of text-based UIs, typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of CLIs (command-line interfaces), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard. The actions in a GUI are usually performed through direct manipulation of the graphical elements. Beyond computers, GUIs are used in many handheld mobile devices such as MP3 players, portable media players, gaming devices, smartphones and smaller household, office and industrial controls. The term ''GUI'' tends not to be applied to other lower- display resolution types of interfaces, such as video games (where HUD (''head-up display'') is preferred), or not including flat screens like volumetric displ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaussian Jitter
In electronics and telecommunications, jitter is the deviation from true periodicity of a presumably periodic signal, often in relation to a reference clock signal. In clock recovery applications it is called timing jitter. Jitter is a significant, and usually undesired, factor in the design of almost all communications links. Jitter can be quantified in the same terms as all time-varying signals, e.g., root mean square (RMS), or peak-to-peak displacement. Also, like other time-varying signals, jitter can be expressed in terms of spectral density. Jitter period is the interval between two times of maximum effect (or minimum effect) of a signal characteristic that varies regularly with time. Jitter frequency, the more commonly quoted figure, is its inverse. ITU-T G.810 classifies jitter frequencies below 10 Hz as wander and frequencies at or above 10 Hz as jitter. Jitter may be caused by electromagnetic interference and crosstalk with carriers of other signals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractal Software
In mathematics, a fractal is a geometric shape containing detailed structure at arbitrarily small scales, usually having a fractal dimension strictly exceeding the topological dimension. Many fractals appear similar at various scales, as illustrated in successive magnifications of the Mandelbrot set. This exhibition of similar patterns at increasingly smaller scales is called self-similarity, also known as expanding symmetry or unfolding symmetry; if this replication is exactly the same at every scale, as in the Menger sponge, the shape is called affine self-similar. Fractal geometry lies within the mathematical branch of measure theory. One way that fractals are different from finite geometric figures is how they scale. Doubling the edge lengths of a filled polygon multiplies its area by four, which is two (the ratio of the new to the old side length) raised to the power of two (the conventional dimension of the filled polygon). Likewise, if the radius of a filled sphere i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |