|
Kaliyug
''Kali Yuga'', in Hinduism, is the fourth and worst of the four '' yugas'' (world ages) in a '' Yuga Cycle'', preceded by ''Dvapara Yuga'' and followed by the next cycle's '' Krita (Satya) Yuga''. It is believed to be the present age, which is full of conflict and sin. The "Kali" of ''Kali Yuga'' means "strife", "discord", "quarrel", or "contention" and ''Kali Yuga'' is associated with the demon Kali (not to be confused with the goddess K─ül─½). According to Puranic sources, Krishna's death marked the end of ''Dvapara Yuga'' and the start of ''Kali Yuga'', which is dated to 17/18 February 3102 BCE. Lasting for 432,000 years (1,200 divine years), ''Kali Yuga'' began years ago and has years left as of CE. ''Kali Yuga'' will end in the year 428,899 CE. Etymology '' Yuga'' ( sa, Óż»ÓźüÓżŚ), in this context, means "an age of the world", where its archaic spelling is ''yug'', with other forms of ''yugam'', , and ''yuge'', derived from ''yuj'' ( sa, Óż»ÓźüÓż£Ó ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kali (demon)
In Hinduism, Kali ( Devan─ügari: , IAST: ', with both vowels short; from a root ', 'suffer, hurt, startle, confuse') is the being who reigns during the age of the Kali Yuga and acts as the nemesis of Kalki, the tenth and final avatar of the Hindu preserver deity, Vishnu. Mahabharata According to the Mahabharata, the gandharva Kali became jealous when he was late to Princess Damayanti's marriage ceremony and discovered she had overlooked the deities Indra, Agni, Varuna, and Yama (and ultimately himself) to choose Nala as her husband. In anger, Kali spoke to his companion Dvapara, the personification of Dvapara Yuga: Kali traveled to Nala's kingdom of Nishadhas and waited twelve long years for the right moment to strike. Because Nala had rendered himself impure by not washing his feet before his prayers, Kali was able to bewitch his soul. Kali then appeared before Pushkara and invited him to play a game of dice with his brother, guaranteeing Nala's downfall. Dwapara took the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
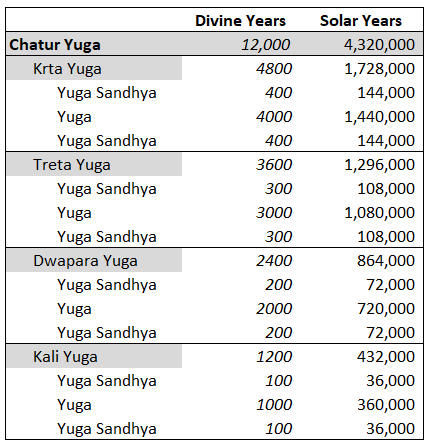
Yuga Cycle
A ''Yuga'' Cycle ( ''chatur yuga'', ''maha yuga'', etc.) is a cyclic age (epoch) in Hindu cosmology. Each cycle lasts for 4,320,000 years (12,000 divine years) and repeats four ''yugas'' (world ages): '' Krita (Satya) Yuga'', ''Treta Yuga'', '' Dvapara Yuga'', and '' Kali Yuga''. As a ''Yuga'' Cycle progresses through the four ''yugas'', each '' yuga's'' length and humanity's general moral and physical state within each ''yuga'' decrease by one-fourth. ''Kali Yuga'', which lasts for 432,000 years, is believed to have started in 3102 BCE. Near the end of ''Kali Yuga'', when virtues are at their worst, a cataclysm and a re-establishment of '' dharma'' occur to usher in the next cycle's ''Satya Yuga'', prophesied to occur by Kalki. There are 71 ''Yuga'' Cycles in a ''manvantara'' (age of Manu) and 1,000 ''Yuga'' Cycles in a ''kalpa'' (day of Brahma). Lexicology A ''Yuga'' Cycle has several names. Age or ''Yuga'' ( sa, Óż»ÓźüÓżŚ, , an age of the gods): : "Age" and "''Yuga''", some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kali
Kali (; sa, ÓżĢÓżŠÓż▓ÓźĆ, ), also referred to as Mahakali, Bhadrakali, and Kalika ( sa, ÓżĢÓżŠÓż▓Óż┐ÓżĢÓżŠ), is a Hinduism, Hindu goddess who is considered to be the goddess of ultimate power, time, destruction and change in Shaktism. In this tradition, she is considered as a ferocious form of goddess Mahadevi, the supreme of all powers, or the ultimate reality. She is the first of the ten Mahavidyas in the Hindu Tantras (Hinduism), tantric tradition. Kali's earliest appearance is when she emerged from Shiva. She is regarded as the ultimate manifestation of Shakti, and the mother of all living beings. The goddess is stated to destroy evil in order to protect the innocent. Over time, Kali has been worshipped by devotional movements and T├Āntric sects variously as the Divine Mother, Mother of the Universe, Principal energy Adi Shakti. Shaktism, Shakta Hindu and Tantra, Tantric sects additionally worship her as the ultimate reality or ''Brahman''. She is also seen as the divi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Zero
A year zero does not exist in the Anno Domini (AD) calendar year system commonly used to number years in the Gregorian calendar (nor in its predecessor, the Julian calendar); in this system, the year is followed directly by year . However, there is a year zero in both the astronomical year numbering system (where it coincides with the Julian year ), and the ISO 8601:2004 system, the interchange standard for all calendar numbering systems (where year zero coincides with the Gregorian year ; see conversion table). There is also a year zero in most Buddhist and Hindu calendars. Historical, astronomical and ISO year numbering systems Historians The ''Anno Domini'' era was introduced in 525 by Scythian monk Dionysius Exiguus (c. 470 ŌĆō c. 544), who used it to identify the years on his Easter table. He introduced the new era to avoid using the '' Diocletian era'', based on the accession of Roman Emperor Diocletian, as he did not wish to continue the memory of a persecutor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandurang Vaman Kane
Pandurang Vaman Kane (pronounced ''Kaa-nay'') (7 May 1880 ŌĆō 18 April 1972) was a notable Indologist and Sanskrit scholar. He received India's highest civilian award Bharat Ratna in 1963 for his scholarly work that spanned more than 40 years of active academic research that resulted in 6,500 pages of ''History of Dharma┼ø─üstra''. The historian Ram Sharan Sharma says: "Pandurang Vaman Kane, a great Sanskritist wedded to social reform, continued the earlier tradition of scholarship. His monumental work entitled the "History of the Dharmasastra", published in five volumes in the twentieth century, is an encyclopedia of ancient social laws and customs. This enables us to study the social processes in History of India, ancient India." Early life He was born in a village called Parasuram near Chiplun in Ratnagiri district of Maharashtra on 7 May 1880 in a Chitpavan, Chitpavan Brahmin family Important works Dr. Kane is famous for his masterpiece, magnum opus in English, ''History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surya Siddhanta
The ''Surya Siddhanta'' (; ) is a Sanskrit treatise in Indian astronomy dated to 505 CE,Menso Folkerts, Craig G. Fraser, Jeremy John Gray, John L. Berggren, Wilbur R. Knorr (2017)Mathematics Encyclopaedia Britannica, Quote: "(...) its Hindu inventors as discoverers of things more ingenious than those of the Greeks. Earlier, in the late 4th or early 5th century, the anonymous Hindu author of an astronomical handbook, the ''Surya Siddhanta'', had tabulated the sine function (...)" in fourteen chapters.Plofkerpp. 71ŌĆō72 The ''Surya Siddhanta'' describes rules to calculate the motions of various planets and the moon relative to various constellations, diameters of various planets, and calculates the orbits of various astronomical bodies. The text is known from a palm-leaf manuscript, and several newer manuscripts. It was composed or revised c. 800 CE from an earlier text also called the ''Surya Siddhanta''. The ''Surya Siddhanta'' text is composed of verses made up of two lines, each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryabhatiya
''Aryabhatiya'' (IAST: ') or ''Aryabhatiyam'' ('), a Sanskrit astronomical treatise, is the ''magnum opus'' and only known surviving work of the 5th century Indian mathematician Aryabhata. Philosopher of astronomy Roger Billard estimates that the book was composed around 510 CE based on historical references it mentions. Structure and style Aryabhatiya is written in Sanskrit and divided into four sections; it covers a total of 121 verses describing different moralitus via a mnemonic writing style typical for such works in India (see definitions below): 1. Gitikapada (13 verses): large units of timeŌĆökalpa, manvantara, and yugaŌĆöwhich present a cosmology different from earlier texts such as Lagadha's Vedanga Jyotisha (ca. 1st century BCE). There is also a table of ine (jya), given in a single verse. The duration of the planetary revolutions during a mahayuga is given as 4.32 million years. 2. Ganitapada (33 verses): covering mensuration (kß╣Żetra vy─üvah─üra); arithmetic and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Asiatic Society Of Mumbai
The Asiatic Society of Mumbai (formerly ''Asiatic Society of Bombay'') is a learned society in the field of Asian studies based in Mumbai, India. It can trace its origin to the Literary Society of Bombay which first met in Mumbai on 26 November 1804, and was founded by Sir James Mackintosh. It was formed with the intention of "promoting useful knowledge, particularly such as is now immediately connected with India". After the Royal Asiatic Society, Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland was established in London in 1823, the Literary Society of Bombay became affiliated with it and was known as the Bombay Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society (BBRAS) since 1830. The ''Bombay Geographical Society'' merged with it in 1873, followed by the ''Anthropological Society of Bombay'' in 1896. In 1954, it was separated from the Royal Asiatic Society and renamed the Asiatic Society of Bombay. In 2002, it acquired its present name. It is funded by an annual grant from the Central Govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puranas
Purana (; sa, , '; literally meaning "ancient, old"Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of Literature (1995 Edition), Article on Puranas, , page 915) is a vast genre of Indian literature about a wide range of topics, particularly about legends and other traditional lore. The Puranas are known for the intricate layers of symbolism depicted within their stories. Composed originally in Sanskrit and in Languages of India, other Indian languages,John Cort (1993), Purana Perennis: Reciprocity and Transformation in Hindu and Jaina Texts (Editor: Wendy Doniger), State University of New York Press, , pages 185-204 several of these texts are named after major Hindu gods such as Vishnu, Shiva, Brahma, and Adi Shakti. The Puranic genre of literature is found in both Hinduism and Jainism. The Puranic literature is encyclopedic, and it includes diverse topics such as cosmogony, cosmology, genealogies of gods, goddesses, kings, heroes, sages, and demigods, folk tales, pilgrimages, temples, medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vishnu Smriti
Vishnu Smriti (IAST: ) is one of the latest books of the Dharma┼ø─üstra tradition in Hinduism and the only one which does not deal directly with the means of knowing dharma. The text has a strong bhakti orientation, requiring daily puja to the god Vishnu. It is also known for its handling of the controversial subject of the practice of sati (the burning of a widow on her husbandŌĆÖs funeral pyre). A Banaras pandit, Nandapandita, was the first to write a commentary on the Vishnu Smriti in 1622, but the book was not translated into English until 1880 by Julius Jolly. Source, authority and dating It is commonly agreed upon that the Vishnu Smriti relies heavily on previous Dharmashastra texts, such as the Manusmriti and Yajnavalkya smrti. However, some scholars see it as a Vaishnava recast of the Kathaka Dharmasutra while others say that the Kathakagrhya and metrical verses were added later. Precise dating eludes scholars, with limits being placed anywhere between 300BCE and 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manusmriti
The ''Manusmß╣øiti'' ( sa, Óż«Óż©ÓźüÓżĖÓźŹÓż«ÓźāÓżżÓż┐), also known as the ''M─ünava-Dharma┼ø─üstra'' or Laws of Manu, is one of the many legal texts and constitution among the many ' of Hinduism. In ancient India, the sages often wrote their ideas on how society should run in the manuscripts. It is believed that the original form of ''Manusmriti'' was changed as many things written in the manuscript contradict each other. Over fifty manuscripts of the ''Manusmriti'' are now known, but the earliest discovered, most translated and presumed authentic version since the 18th century has been the "Kolkata (formerly Calcutta) manuscript with Kulluka Bhatta commentary". Modern scholarship states this presumed authenticity is false, and the various manuscripts of ''Manusmriti'' discovered in India are inconsistent with each other, and within themselves, raising concerns of its authenticity, insertions and interpolations made into the text in later times. The metrical text is in Sansk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahabharata
The ''Mah─übh─ürata'' ( ; sa, Óż«Óż╣ÓżŠÓżŁÓżŠÓż░ÓżżÓż«ÓźŹ, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the ''R─üm─üyaß╣ća''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the Kurukshetra War and the fates of the Kaurava and the P─üß╣ćßĖŹava princes and their successors. It also contains philosophical and devotional material, such as a discussion of the four "goals of life" or ''puruß╣Ż─ürtha'' (12.161). Among the principal works and stories in the ''Mah─übh─ürata'' are the '' Bhagavad Gita'', the story of Damayanti, the story of Shakuntala, the story of Pururava and Urvashi, the story of Savitri and Satyavan, the story of Kacha and Devayani, the story of Rishyasringa and an abbreviated version of the ''R─üm─üyaß╣ća'', often considered as works in their own right. Traditionally, the authorship of the ''Mah─übh─ürata'' is attributed to Vy─üsa. There have been many attempts to unravel its historical growth and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |