|
Kagura Suzu
are a set of twelve bells used in dance. The set consists of three tiers of bells suspended by coiled brass wires from a central handle: two bells on the top tier, four bells on the middle tier, and six bells for the bottom tier. The shape of the bells are thought to have been inspired from the fruits of the tree ('' Michelia compressa''). The term refers to small bells in general, but can refer to two Japanese instruments associated with Shinto ritual: # A single large crotal bell similar in shape to a sleigh bell and having a slit on one side. # A handheld bell-tree with small crotal bells strung in three levels on a spiraling wire. The larger form may be hung from a rafter in front of a Shinto shrine and sounded by a robe or ribbons that hang within reach of the worshipper. The smaller is supported atop a handle and is held by female shrine attendants () costumed in traditional robes, white-powdered faces, and wearing Heian-period coiffure during performances of dan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzu MET DP353272
Suzu may refer to: *Suzu (bell), small Japanese bells used in Shinto *Suzu, Ishikawa, city in Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan * Sabzuyeh, Neyriz, also known as Sūzū, a village in Neyriz County, Fars Province, Iran Temple names Suzu () was a Chinese temple name. It may refer to: *Emperor Ming of Jin (299–325) *Yuan Xie (died 508), regent of Northern Wei People *, Japanese footballer *, Japanese freestyle swimmer *, Japanese actress and model *, Japanese actress *, Japanese professional wrestler Fictional characters * Bobobo suzu, a fictional character from the anime/manga series ''Bobobo-bo Bo-bobo'' * Suzu, a fiction character from the anime, manga, and light novel series ''Nagasarete Airantō'' * Suzu Nyanko, the human pseudonym of Sailor Tin Nyanko, in the Sailor Moon metaseries * Suzu Hōjō, protagonist of In This Corner of the World *Suzu, a survivor of the fallen Crogenitor empire in Maxis' Action RPG, Darkspore ''Darkspore'' was a video game that borrowed creature e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Shinto
This is the glossary of Shinto, including major terms on the subject. Words followed by an asterisk (*) are illustrated by an image in one of the photo galleries. __NOTOC__ A * – A red papier-mâché cow bobblehead toy; a kind of ''engimono'' and an ''omiyage'' (a regional souvenir in Japan) that is considered symbolic of Aizu. * – A type of fan held by aristocratic women of the Heian period when formally dressed; it is brightly painted with tassels and streamers on the ends. Held today in Shinto by a ''miko'' in formal costume for festivals. See also ''hiôgi''. * – The term's meaning is not limited to moral evil, and includes misfortune, inferiority and unhappiness. * - A malevolent fire spirit, demon or devil. * - Also known as the ''Akujin'', the ''Kibi-no-Ananowatari-no-Kami'' and as the ''Anato-no-Kami'', ''Akuru'' is a malevolent ''kami'' that is mentioned in the ''Keikoki'' (records regarding the time of the Emperor Keiko), the ''Nihonshoki'' (Chronicles of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exorcism In Shinto
Exorcism () is the religious or spiritual practice of evicting demons, jinns, or other malevolent spiritual entities from a person, or an area, that is believed to be possessed. Depending on the spiritual beliefs of the exorcist, this may be done by causing the entity to swear an oath, performing an elaborate ritual, or simply by commanding it to depart in the name of a higher power. The practice is ancient and part of the belief system of many cultures and religions. Buddhism The practice of reciting or listening to the Paritta began very early in the history of Buddhism. It is a Buddhist practice of reciting certain verses and scriptures from Pali Canon in order to ward off misfortune or danger. The belief in the effective spiritual power to heal, or protect, of the '' Sacca-kiriyā'', or asseveration of something quite true is an aspect of the work ascribed to the ''paritta''. Several scriptures in the Paritta like Metta Sutta, Dhajagga Sutta, or Ratana Sutta can be reci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinto In Japan
Shinto () is a religion from Japan. Classified as an East Asian religion by scholars of religion, its practitioners often regard it as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintoists'', although adherents rarely use that term themselves. There is no central authority in control of Shinto, with much diversity of belief and practice evident among practitioners. A polytheistic and animistic religion, Shinto revolves around supernatural entities called the . The are believed to inhabit all things, including forces of nature and prominent landscape locations. The are worshiped at household shrines, family shrines, and ''jinja'' public shrines. The latter are staffed by priests, known as , who oversee offerings of food and drink to the specific enshrined at that location. This is done to cultivate harmony between humans and and to solicit the latter's blessing. Other common rituals include the dances, rites of passag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talismans
A talisman is any object ascribed with religious or magical powers intended to protect, heal, or harm individuals for whom they are made. Talismans are often portable objects carried on someone in a variety of ways, but can also be installed permanently in architecture. Talismans are closely linked with amulets, fulfilling many of the same roles, but a key difference is in their form and materiality, with talismans often taking the form of objects (eg., clothing, weaponry, or parchment) which are inscribed with magic texts. Talismans have been used in many civilizations throughout history, with connections to astrological, scientific, and religious practices; but the theory around preparation and use has changed in some cultures with more recent, new age, talismanic theory. Talismans are used for a wide array of functions, such as: the personal protection of the wearer, loved ones or belongings, aiding in fertility, and helping crop production. Etymology The word ''talisman'' c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Musical Instruments
Traditional Japanese musical instruments, known as in Japanese, are musical instruments used in the traditional folk music of Japan. They comprise a range of string, wind, and percussion instruments. Percussion instruments *; also spelled – clapper made from wooden slats connected by a rope or cord * – wooden or bamboo clappers * – pellet drum, used as a children's toy * – small, ornately decorated hourglass-shaped drum * – hand-held bell tree with three tiers of pellet bells * – small drum used in * – small flat gong * – a pair of sticks which are beaten together slowly and rhythmically * (also called ) – clapper made from a pair of flat wooden sticks * – woodblock carved in the shape of a fish, struck with a wooden stick; often used in Buddhist chanting * – hand drum * or () – singing bowls used by Buddhist monks in religious practice or rituals * – hourglass-shaped double-headed drum; struck only on one side * – clapper made from wooden slats conne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standing Bell
A standing bell or resting bell is an inverted bell, supported from below with the rim uppermost. Such bells are normally bowl-shaped, and exist in a wide range of sizes, from a few centimetres to a metre in diameter. They are often played by striking, but some—known as singing bowls—may also be played by rotating a mallet around the outside rim to produce a sustained musical note. Struck bowls are used in some Buddhist religious practices to accompany periods of meditation and chanting. Struck and singing bowls are widely used for music making, meditation and relaxation, as well for personal spirituality. They have become popular with music therapists, sound healers and yoga practitioners. Standing bells originated in China. An early form called took the shape of a stemmed goblet, mounted with rim uppermost, and struck on the outside with a mallet. The manufacture and use of bowls specifically for 'singing' is believed to be a modern phenomenon. Bowls that were capable of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dōtaku
are Japanese bells smelted from relatively thin bronze and richly decorated. Dotaku were used for about 400 years, between the second century B.C. and the second century C.E. (corresponding to the end of the Yayoi era), and were nearly only used as decorations for rituals. They were richly decorated with patterns representing nature and animals, among which the dragonfly, praying mantis and spider are featured. Historians believe that ''dōtaku'' were used to pray for good harvests, as the animals featured are natural enemies of insect pests that attack paddy fields. According to Japanese folklore, dōtaku were used as emergency bells (such as a watch tower’s bell); intended especially in cases of invasion, particularly invaders from the Korean peninsula. When sentinels spotted invaders, they loudly rang the dōtaku as an alarm, so that people could hide themselves or their possessions, and to alert warriors to prepare themselves to repel the enemy. There is a dotaku museum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
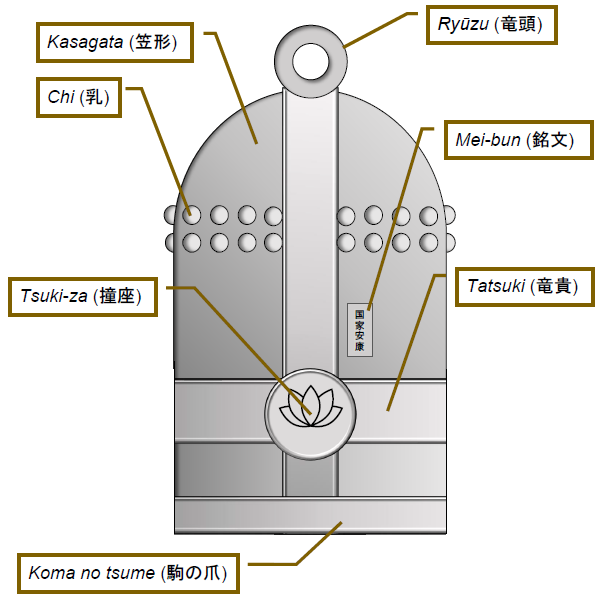
Bonshō
, also known as or are large bells found in Buddhist temples throughout Japan, used to summon the monks to prayer and to demarcate periods of time. Rather than containing a clapper, are struck from the outside, using either a handheld mallet or a beam suspended on ropes. The bells are usually made from bronze, using a form of expendable mould casting. They are typically augmented and ornamented with a variety of bosses, raised bands and inscriptions. The earliest of these bells in Japan date to around 600 CE, although the general design is of much earlier Chinese origin and shares some of the features seen in ancient Chinese bells. The bells' penetrating and pervasive tone carries over considerable distances, which led to their use as signals, timekeepers and alarms. In addition, the sound of the bell is thought to have supernatural properties; it is believed, for example, that it can be heard in the underworld. The spiritual significance of means that they play an im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzuki Harunobu
Suzuki Harunobu ( ja, 鈴木 春信; ) was a Japanese designer of woodblock print art in the style. He was an innovator, the first to produce full-color prints () in 1765, rendering obsolete the former modes of two- and three-color prints. Harunobu used many special techniques, and depicted a wide variety of subjects, from classical poems to contemporary beauties. Like many artists of his day, Harunobu also produced a number of , or erotic images. During his lifetime and shortly afterwards, many artists imitated his style. A few, such as Harushige, even boasted of their ability to forge the work of the great master. Much about Harunobu's life is unknown. Influences Though some scholars assert that Harunobu was originally from Kyoto, pointing to possible influences from Nishikawa Sukenobu, much of his work, in particular his early work, is in the Edo style. His work shows evidence of influences from many artists, including Torii Kiyomitsu, Ishikawa Toyonobu, the Kawamata s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_MET_DT11855.jpg)