|
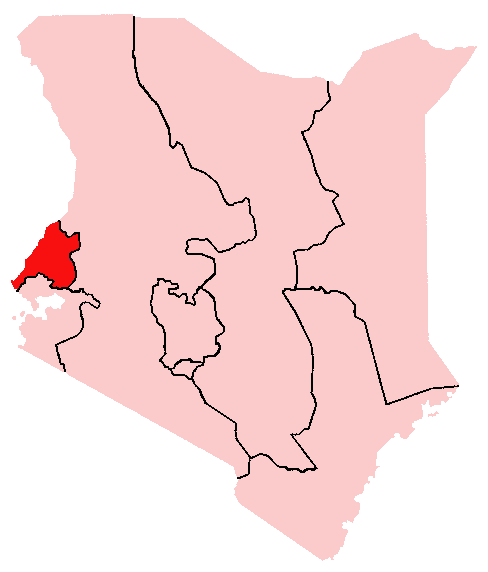
Kabras
The Kabras, or Kabarasi, are a subtribe of the Luhya people of Kenya. They reside in Malava that is in the Kabras Division of Kakamega District, which is neighboured by the Isukha, Banyala, Tsotso, and the Tachoni. The exact origin of the Luhya people is currently disputed, but there are historians who believe that the group came from Bethlehem and migrated to their present-day location by way of the so-called Great Bantu Migration. The Kabras dialect called Lukabaras is similar to Tachoni. However, the Kabras have spread to other regions as a result of intermarriages and movement to seek greener pastures in formal employment. These people are described as adaptable, easily absorbing other cultural values and beliefs. This can be demonstrated in the way many Kabras practice the Christian and Muslim faiths. One notable cultural practice involves circumcision and bride-price required for marriage. History Kabrasi clans were named after the heads of the families. They include Abanz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luhya People
The Luhya (also known as ''Abaluyia'' or Luyia) comprise a number of Bantu ethnic groups native to western Kenya. They are divided into 20 culturally and linguistically related tribes. ''Luhya'' refers to both the 20 Luhya clans and their respective languages collectively called Luhya languages. There are 20 (and by other accounts, 21, when the Suba are included) clans that make up the Luhya. Each has a distinct dialect best on thelocality of the speakers.The different dialects shows maturity of the luhya language. The Luhya language can only be equated to the Baganda,Soga and Lugisu language in Uganda. The Luhya culture is similary to Great lakes region Bantu speakers that stretches all the way from their anceral land in DRC. The word ''Luhya'' or ''Luyia'' in some of the dialects means "the north", and ''Abaluhya (Abaluyia)'' thus means "people from the north". Other translations are "those of the same hearth." The seventeen sub-tribes are the Bukusu (''Aba-Bukusu''), Idakho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lukabaras
Luhya (; also Luyia, Luhia or Luhiya) is a Bantu language of western Kenya. Dialects The various Luhya tribes speak several related languages and dialects, though some of them are no closer to each other than they are to neighboring non-Luhya languages. For example, the Bukusu people are ethnically Luhya, but the Bukusu dialect is a variety of Masaba. (See Luhya people for details.) However, there is a core of mutually intelligible In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between languages or dialects in which speakers of different but related varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. It is sometimes used as an ... dialects that comprise Luhya proper: *Hanga *Tsotso *Marama *Kisa *Kabras *East Nyala Comparison A comparison between two dialects of Luhya proper, and to two other Bantu languages spoken by the Luhya: Comparison to Bantu Phonology The following is the phonology of the Luwanga dialect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachoni
The Tachoni (meaning "We shall be back") are Kalenjin who were assimilated by the Luhya people of western Kenya, sharing the land with the Bukusu tribe. They live mainly in Webuye, Chetambe Hills, Ndivisi (of Bungoma County) Matete sub-county and Lugari sub-county in Kakamega County. Most Tachoni clans living in Bungoma speak the ' Olutachoni dialect of the Luhya language, and they are subsequently often mistaken as Bukusus. They spread to Trans-Nzoia County especially around Kitale, and to Uasin Gishu County near Turbo, Eldoret. Among the Tachoni clans are Abakobolo, Abamuongo, Abamarakalu, Abangachi, Abasang'alo, Abasamo, Abayumbu (mostly around Webuye), Abamuchembi, Abachambai, Abacharia, Abakabini, Abamakhuli, Abasioya, Abaabichu, Abamachina, Abamutama, Abakafusi, Abasonge, Abasaniaka, Abaabiya, Abakubwayi, Abamweya, Abachimuluku. Note that the morpheme 'aba' means 'people'. The Abakhusia/abasamo of Kabras are also Tachonis who speak Kikabras. Circumcision The tribe is r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zacchaeus Chesoni
Zacchaeus Chesoni (born c. 1936 - 5 September 1999) was Chief Justice of Kenya and chairman of the Electoral Commission . Chesoni hails from the Kabras sub tribe Bamachina clan close to Chimoi area around Webuye Webuye, previously named Broderick Falls, is an industrial town in Bungoma County, Kenya. Located on the main road to Uganda, the town is home to the Pan African Paper Mills, the largest paper factory in the region, as well as a number of heav .... References Kenyan judges Kenyan Luhya people 1999 deaths Place of birth missing Chief justices of Kenya 1936 births {{Kenya-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bukusu
The Bukusu people ( Bukusu: ''Babukusu'') are one of the seventeen Kenyan tribes of the Luhya Bantu people of East Africa residing mainly in the counties of Bungoma and Trans Nzoia. They are closely related to other Luhya people and the Gisu of Uganda. Calling themselves ''BaBukusu'', they are the largest tribe of the Luhya nation, making up about 34% of the Luhya population. They speak the Bukusu dialect. Origins The Bukusu myths of origin state that the first man, Mwambu (the discoverer or inventor), was made from mud by Wele Khakaba(Meaning God the Creator) at a place called Mumbo (which translates to 'west'). God then created a woman known as Sela to be his wife. Mwambu and his descendants moved out of Mumbo and settled on the foothills of Mount Elgon (known to them as Masaba), from where their descendants grew to form the current Bukusu population. Anthropologists believe that the Bukusu did not become distinct from the rest of the Luhya population until the late 18t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiriki
Tiriki is one of sixteen clans and dialects of the Abaluyia people of Western Kenya. The word ''Tiriki'' is also used to refer to their Geographical Location in Hamisi Division, Vihiga County, in the Western province of Kenya. Hamisi Constituency now Hamisi Sub County is one of the longest in Kenya stretching from kiboswa(Ny'angori) to Shiru which borders Kapsabet and Musunji which borders Kakamega Forest. Some also moved to nandi county and occupied aldai and other parts of nandi county. Administrative Tiriki is located in the Republic of Kenya in Vihiga County. Vihiga County is one of the five counties that formed the former Western Province. The other counties in the former Western Province are Kakamega (which Vihiga was previously a part of), Bungoma, and Busia. Trans Nzoia county is located in the former Rift Valley but has a majority Abaluyia population. Nandi County in the former Rift Valley province also has a sizable but minority Abaluyia population. The name Hamis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wanga
The Wanga kingdom is a Bantu kingdom within Kenya, consisting of the Wanga (Abawanga) tribe of the Luhya people (Abaluyia). At its peak the kingdom covered an expansive area from Jinja in west to Naivasha in the East African Rift. The Wanga kingdom was a significant African empire and the most organized structure of government in pre-colonial Kenya politically, economically, and militarily. In 2016 the Wanga numbered around 700,000, mostly occupying the Kakamega County, Western Province, Kenya. The seat of power is located in Mumias. The Wanga are one of 19 tribes of the Luhya people. There are 22 clans that comprise the Wanga tribe. The Wanga retain the Nabongo, as their monarch. The Abashitse clan holds the royal lineage of the Nabongo. The current Nabongo is Peter Mumia II. Etymology The name Wanga is eponymous, originating from name of the kingdoms founder, Nabongo Wanga. The name Wanga refers to the people as well as their descent and geographical location. The ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantu Expansion
The Bantu expansion is a hypothesis about the history of the major series of migrations of the original Proto-Bantu-speaking group, which spread from an original nucleus around Central Africa across much of sub-Saharan Africa. In the process, the Proto-Bantu-speaking settlers displaced or absorbed pre-existing hunter-gatherer and pastoralist groups that they encountered. The primary evidence for this expansion is linguistic – a great many of the languages which are spoken across Sub-Equatorial Africa are remarkably similar to each other, suggesting the common cultural origin of their original speakers. The linguistic core of the Bantu languages, which comprise a branch of the Atlantic-Congo language family, was located in the southern regions of Cameroon. However, attempts to trace the exact route of the expansion, to correlate it with archaeological evidence and genetic evidence, have not been conclusive; thus although the expansion is widely accepted as having taken place, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsotso
The Tsotso or ''Abatsotso'' are a tribe of the Luhya nation in Kenya. They occupy three locations in Lurambi division of Kakamega District. The three locations are Bukura, north Butsotso and south Butsotso. See also * Luhya people * Luhya languages The Great Lakes Bantu languages, also known as Lacustrine Bantu and Bantu zone J, are a group of Bantu languages of East Africa. They were recognized as a group by the ''Tervuren'' team, who posited them as an additional zone (zone J) to Guthrie' ... {{Africa-ethno-group-stub References 1. http://www.reliefweb.int/rw/fullMaps_Af.nsf/luFullMap/14A6905F99640EF98525766A0065CCB6/$File/map.pdf?OpenElement Luhya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachoni Dialect (Luhya)
Masaba (''Lumasaaba''), sometimes known as Gisu (''Lugisu'') after one of its dialects, is a Bantu language spoken by more than two million people in East Africa. The Gisu dialect in eastern Uganda is mutually intelligible with Bukusu, spoken by ethnic Luhya in western Kenya. ''Masaba'' is the local name of Mount Elgon and the name of the son of the ancestor of the Gisu tribe. Like other Bantu languages, Lumasaba nouns are divided into several sets of noun classes. These are similar to the genders in Germanic and Romance languages, except that instead of the usual two or three, there are around eighteen different noun classes. The language has a quite complex verb morphology. Varieties Varieties of Masaba are as follows:Maho (2009) *Gisu (''Lugisu'') *Kisu *Bukusu (''Lubukusu''; ethnic Luhya) *Syan *Tachoni (''Lutachoni''; ethnic Luhya) *Dadiri (''Ludadiri'') *Buya (''Lubuya'') Dadiri is spoken in the north, Gisu in the center, and Buya in the center and south of Masaba territo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kikuyu People
The Kikuyu (also ''Agĩkũyũ/Gĩkũyũ'') are a Bantu ethnic group native to Central Kenya. At a population of 8,148,668 as of 2019, they account for 17.13% of the total population of Kenya, making them Kenya's largest ethnic group. The term ''Kikuyu'' is derived from the Swahili form of the word Gĩkũyũ. is derived from the word mũkũyũ which means sycamore fig (''mũkũyũ'') tree". Hence ''Agĩkũyũ'' in the Kikuyu language translates to "Children Of The Big Sycamore". The alternative name ''Nyũmba ya Mũmbi'', which encompasses ''Embu'', ''Gikuyu'', and ''Meru'', translates to "House of the Potter" (or "Creator"). History Origin The Kikuyu belong to the Northeastern Bantu branch. Their language is most closely related to that of the Embu and Mbeere. Geographically, they are concentrated in the vicinity of Mount Kenya. The exact place that the Northeast Bantu speakers migrated from after the initial Bantu expansion is uncertain. Some authorities sugge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenya
) , national_anthem = "Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"() , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Nairobi , coordinates = , largest_city = Nairobi , official_languages = Constitution (2009) Art. 7 ational, official and other languages"(1) The national language of the Republic is Swahili. (2) The official languages of the Republic are Swahili and English. (3) The State shall–-–- (a) promote and protect the diversity of language of the people of Kenya; and (b) promote the development and use of indigenous languages, Kenyan Sign language, Braille and other communication formats and technologies accessible to persons with disabilities." , languages_type = National language , languages = Swahili , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2019 census , religion = , religion_year = 2019 census , demonym = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)