|
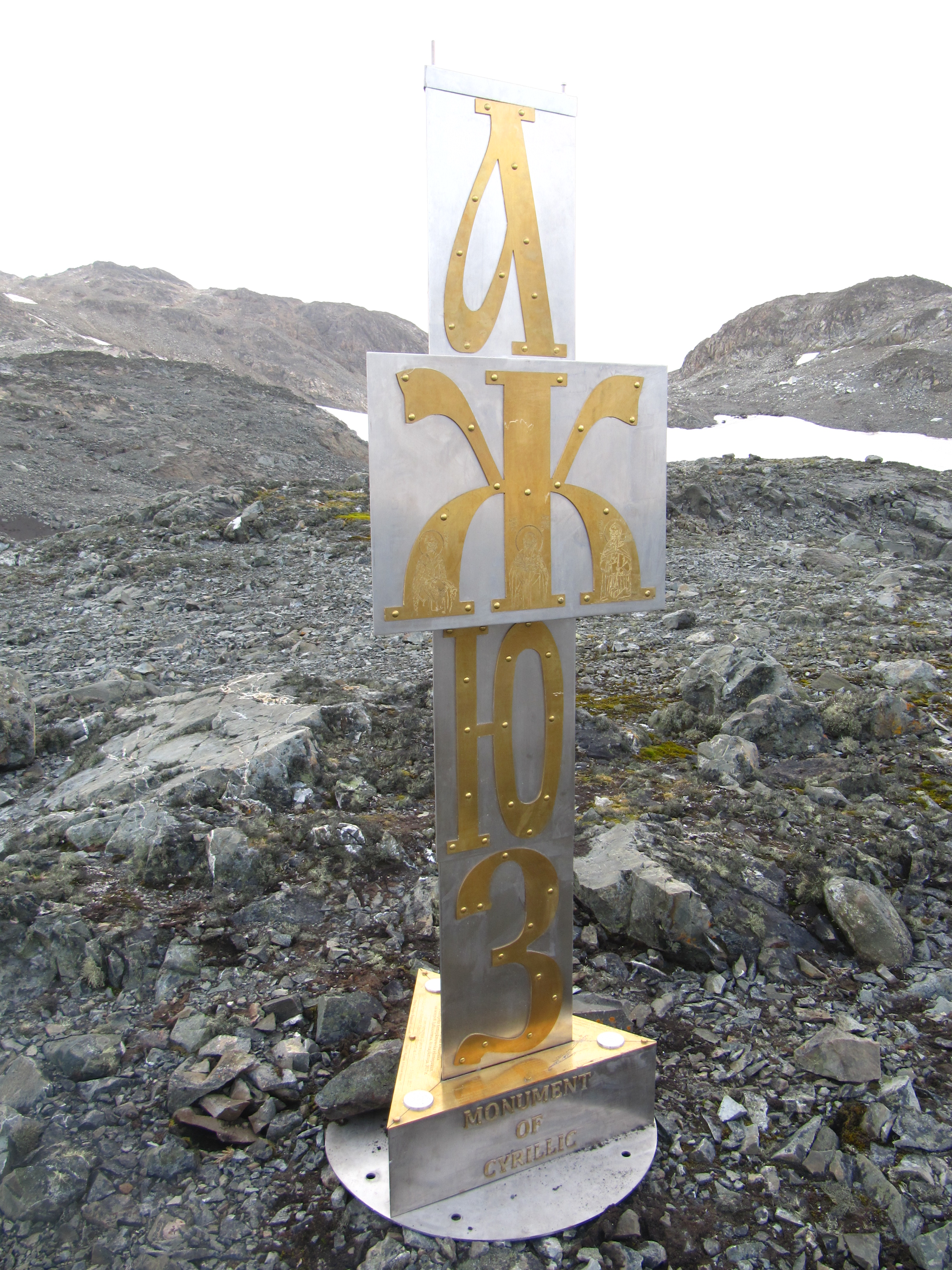
Ka With Hook
Ka with hook (Ӄ ӄ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. It is formed from the Cyrillic letter Ka (К к) by the addition of a hook. Ka with hook is widely used in the alphabets of Siberia and the Russian Far East: Chukchi, Koryak, Alyutor, Itelmen, Yukaghir, Yupik, Aleut, Nivkh, Ket, Tofalar and Selkup languages, where it represents the voiceless uvular plosive . It has been sometimes used in the Khanty language as a substitute for Cyrillic letter Ka with descender, Қ қ, which also stands for . It was also used in the old Abkhaz and the Ossetian alphabets. Computing codes See also Other Cyrillic letters used to write the sound : *Ҡ ҡ : Cyrillic letter Bashkir Qa *Ԟ ԟ : Cyrillic letter Aleut Ka *Ԛ ԛ : Cyrillic letter Qa *Cyrillic characters in Unicode As of Unicode version 15.0 Cyrillic script is encoded across several blocks: * CyrillicU+0400–U+04FF 256 characters * Cyrillic SupplementU+0500–U+052F 48 characters * Cyrill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrillic Script
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic languages, Slavic, Turkic languages, Turkic, Mongolic languages, Mongolic, Uralic languages, Uralic, Caucasian languages, Caucasian and Iranian languages, Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia. , around 250 million people in Eurasia use Cyrillic as the official script for their national languages, with Russia accounting for about half of them. With the accession of Bulgaria to the European Union on 1 January 2007, Cyrillic became the third official script of the European Union, following the Latin script, Latin and Greek alphabet, Greek alphabets. The Early Cyrillic alphabet was developed during the 9th century AD at the Preslav Literary School in the First Bulgarian Empire during the reign of tsar Simeon I of Bulgar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
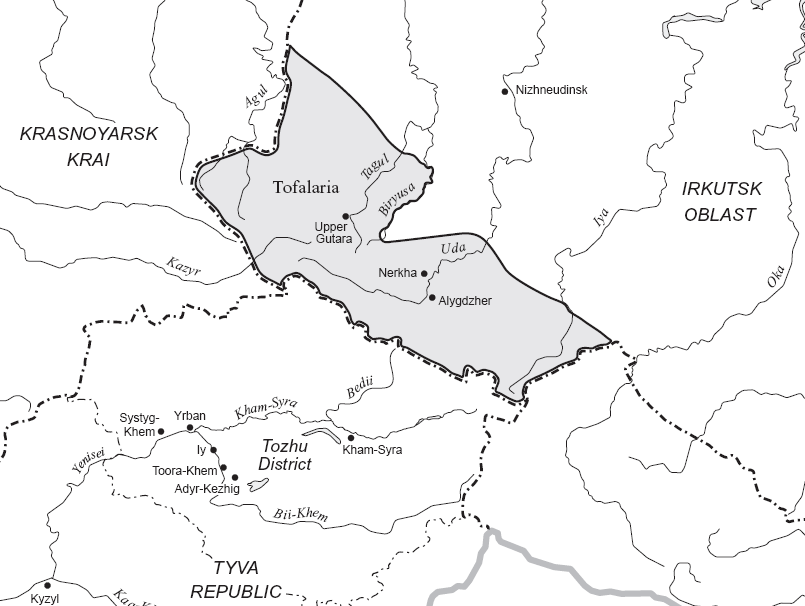
Tofa Language
Tofa, also known as Tofalar or Karagas, is a moribund Turkic language spoken in Russia's Irkutsk Oblast by the Tofalars. Recent estimates for speakers run from 93 people to fewer than 40. Classification Tofa is most closely related to the Tuvan language and forms a dialect continuum with it. Tuha and Tsengel Tuvan may be dialects of either Tuvan or Tofa. Tofa shares a number of features with these languages, including the preservation of *d as /d/ (as in ''hodan'' "hare" - compare Uzbek ''quyon'') and the development of low tones on historically short vowels (as in *''et'' > ''èt'' "meat, flesh"). Alexander Vovin (2017) notes that Tofa and other Siberian Turkic languages, especially Sayan Turkic, have Yeniseian loanwords. Geographical and demographical distribution The Tofa, who are also known as the Tofalar or Karagas, are an indigenous people living in southwestern Irkutsk Oblast, in Russia. The region they inhabit is informally known as Tofalaria. They are traditionally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrillic Characters In Unicode
As of Unicode version 15.0 Cyrillic script is encoded across several blocks: * CyrillicU+0400–U+04FF 256 characters * Cyrillic SupplementU+0500–U+052F 48 characters * Cyrillic Extended-AU+2DE0–U+2DFF 32 characters * Cyrillic Extended-BU+A640–U+A69F 96 characters * Cyrillic Extended-CU+1C80–U+1C8F 9 characters * Cyrillic Extended-DU+1E030–U+1E08F 63 characters * Phonetic ExtensionsU+1D2B, U+1D78 2 Cyrillic characters * Combining Half MarksU+FE2E–U+FE2F 2 Cyrillic characters The characters in the range U+0400–U+045F are basically the characters from ISO 8859-5 moved upward by 864 positions. The next characters in the Cyrillic block, range U+0460–U+0489, are historical letters, some being still used for Church Slavonic. The characters in the range U+048A–U+04FF and the complete Cyrillic Supplement block (U+0500-U+052F) are additional letters for various languages that are written with Cyrillic script. Two characters in the block Phonetic Extensions block comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qa (Cyrillic)
Qa (Ԛ ԛ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. Its form is based on the Latin letter Q (Q q). Depending on the font, the uppercase form can look like a reversed Cyrillic letter Р. Qa is used in the alphabet of the Kurdish language and in the old alphabet of the Abkhaz language. In both it represents the voiceless uvular plosive .http://unicode.org/L2/L2007/07003-n3194-cyrillic.pdf It was also used in the old alphabet of the Ossetian language. This character appeared in newspapers and articles such as 1955's ''Кӧрдо''. The letter was also used in the scrapped version of the Azerbaijani alphabet, it was however eliminated and replaced by Ҝ in Dagestan. Computing codes See also Other Cyrillic letters used to write the sound : *Қ қ : Cyrillic letter Ka with descender *Ӄ ӄ : Cyrillic letter Ka with hook *Ҡ ҡ : Cyrillic letter Bashkir Qa *Ԟ ԟ : Cyrillic letter Aleut Ka *Cyrillic characters in Unicode As of Unicode version 15.0 Cyrillic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleut Ka
{{Cyrillic-alphabet-stub ...
Aleut Ka (Ԟ ԟ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. It is formed from the Cyrillic letter Ka (К к) by adding a stroke to the upper diagonal arm. Aleut Ka was used in the alphabet of the Aleut language in the 19th century, where it represented the voiceless uvular plosive . During the revival of the Aleut Cyrillic alphabet in the 1980s it has been replaced by the Ka with hook. Computing codes See also Other Cyrillic letters used to write the sound : *Қ қ : Cyrillic letter Ka with descender *Ӄ ӄ : Cyrillic letter Ka with hook *Ҡ ҡ : Cyrillic letter Bashkir Qa *Ԛ ԛ : Cyrillic letter Qa *Cyrillic characters in Unicode As of Unicode version 15.0 Cyrillic script is encoded across several blocks: * CyrillicU+0400–U+04FF 256 characters * Cyrillic SupplementU+0500–U+052F 48 characters * Cyrillic Extended-AU+2DE0–U+2DFF 32 characters * Cyrillic Extended-BU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bashkir Qa
{{Cyrillic-alphabet-stub ...
Bashkir Qa or Bashkir Ka (Ҡ ҡ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. It is formed from the Cyrillic letter Ka (К к) with the top extending horizontally to the left. It is a letter corresponding to Қ in Siberian Tatar language. It is used in the alphabet of the Bashkir language and Siberian Tatar language, where it represents the voiceless uvular plosive . It is represented in the Arabic script as ق. Computing codes See also Other Cyrillic letters used to write the sound : *Қ қ : Cyrillic letter Ka with descender *Ӄ ӄ : Cyrillic letter Ka with hook *Ԟ ԟ : Cyrillic letter Aleut Ka *Ԛ ԛ : Cyrillic letter Qa *Cyrillic characters in Unicode As of Unicode version 15.0 Cyrillic script is encoded across several blocks: * CyrillicU+0400–U+04FF 256 characters * Cyrillic SupplementU+0500–U+052F 48 characters * Cyrillic Extended-AU+2DE0–U+2DFF 32 characters * Cyrillic Extended-BU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossetian Language
Ossetian (, , ), commonly referred to as Ossetic and rarely as Ossete (), is an Eastern Iranian language that is spoken predominantly in Ossetia, a region situated on both sides of the Greater Caucasus. It is the native language of the Ossetian people, and is one of the few Iranian languages spoken in Europe; it is a relative and possibly a descendant of the extinct Scythian, Sarmatian, and Alanic languages. The northern half of the Ossetia region is part of Russia and is known as North Ossetia–Alania, while the southern half is part of the ''de facto'' country of South Ossetia (recognized by the United Nations as Russian-occupied territory that is ''de jure'' part of Georgia). Ossetian-speakers number about 614,350, with 451,000 recorded in Russia per the 2010 Russian census. History and classification Ossetian is the spoken and literary language of the Ossetians, an Iranian ethnic group living in the central part of the Caucasus and constituting the basic population of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
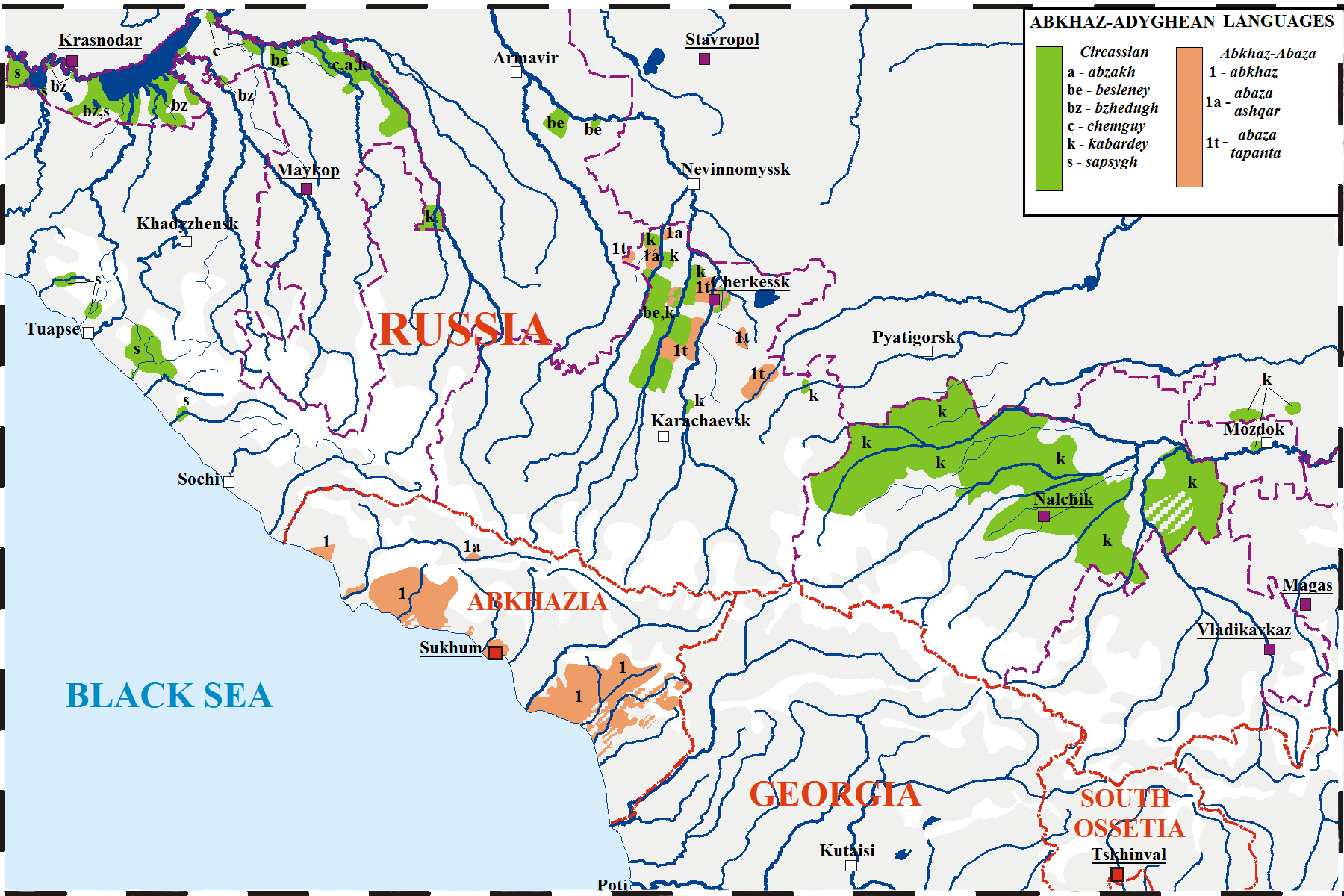
Abkhaz Language
Abkhaz ( ; ), sometimes spelled Abxaz and also known as Abkhazian, is a Northwest Caucasian language most closely related to Abaza. It is spoken mostly by the Abkhaz people. It is one of the official languages of Abkhazia, where around 100,000 people speak it. Furthermore, it is spoken by thousands of members of the Abkhazian diaspora in Turkey, Georgia's autonomous republic of Adjara, Syria, Jordan, and several Western countries. 27 October is the day of the Abkhazian language in Georgia. Classification Abkhaz is a Northwest Caucasian language and is thus related to Adyghe. The language of Abkhaz is especially close to Abaza, and they are sometimes considered dialects of the same language,''B. G. Hewitt Abkhaz 1979;'' page 1. Abazgi, of which the literary dialects of Abkhaz and Abaza are simply two ends of a dialect continuum. Grammatically, the two are very similar; however, the differences in phonology are substantial, it also contains elements characteristic of Kabar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ka With Descender
Ka with descender (Қ қ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script used in a number of non-Slavic languages spoken in the territory of the former Soviet Union, including: * the Turkic languages Kazakh, Uighur, Uzbek and several smaller languages ( Karakalpak, Shor and Tofa), where it represents the voiceless uvular plosive . * Iranian languages such as Tajik and Ossetic (before 1924; now superseded by the digraph ). Since is represented by the letter ق ''qāf'' in the Arabic alphabet, Қ is sometimes referred to as "Cyrillic Qaf". * Eastern varieties of the Khanty language, where it also represents . * the Abkhaz language where it represents the voiceless velar plosive . (The Cyrillic letter Ka (К к) is used to represent .) It was introduced in 1905 for the spelling of Abkhaz. From 1928 to 1938, Abkhaz was spelled with the Latin alphabet, and the corresponding letter was the Latin letter K with descender (Ⱪ ⱪ). Its ISO 9 transliteration is ( w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanty Language
Khanty (also spelled Khanti or Hanti), previously known as Ostyak (), is a Uralic language spoken by the Khanty people, primarily in the Khanty–Mansi and Yamalo-Nenets autonomous okrugs and the Aleksandrovsky and Kargosoksky districts of Tomsk Oblast in Russia. The closest living relatives of Khanty are Hungarian and Mansi. According to the 2010 Russian census, there were around 9,600 Khanty-speaking people in Russia. The Khanty people are rapidly experiencing a language shift to Russian. The Khanty language has many dialects. The western group includes the Obdorian, Ob, and Irtysh dialects. The eastern group includes the Surgut and Vakh-Vasyugan dialects, which, in turn, are subdivided into thirteen other dialects. All these dialects differ significantly from each other by phonetic, morphological, and lexical features to the extent that the three main "dialects" (northern, southern and eastern) are mutually unintelligible. Thus, based on their significant multifactorial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiceless Uvular Plosive
The voiceless uvular plosive or stop is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. It is pronounced like a voiceless velar plosive , except that the tongue makes contact not on the soft palate but on the uvula. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is q. There is also the voiceless pre-uvular plosiveInstead of "pre-uvular", it can be called "advanced uvular", "fronted uvular", "post-velar", "retracted velar" or "backed velar". For simplicity, this article uses only the term "pre-uvular". in some languages, which is articulated slightly more front compared with the place of articulation of the prototypical uvular consonant, though not as front as the prototypical velar consonant. The International Phonetic Alphabet does not have a separate symbol for that sound, though it can be transcribed as or (both symbols denote an advanced ) or ( retracted ). The equivalent X-SAMPA symbols are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selkup Language
Selkup language is the language of the Selkups, belonging to the Samoyedic group of the Uralic language family. It is spoken by some 1,570 people (1994 est.) in the region between the Ob and Yenisei Rivers (in Siberia). The language name ''Selkup'' comes from the Russian "", based on the native name used in the Taz dialect, шӧльӄумыт әты ''šöľqumyt әty'', lit. ''forest-man language''. Different dialects use different names. Selkup is fractured in an extensive dialect continuum whose ends are no longer mutually intelligible. The three main varieties are the Taz (Northern) dialect (, ''tazovsky dialekt''), which became the basis of the Selkup written language in the 1930s, Tym (Central) dialect (, ''tymsky dialekt''), and Ket dialect (, ''ketsky dialekt''). It is not related to the Ket language. Phonology There are 25 vowel and 16 consonant phonemes in the Taz dialect. * Voicing is not phonemic. Stops and fricatives may be voiced between vowels or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |