|
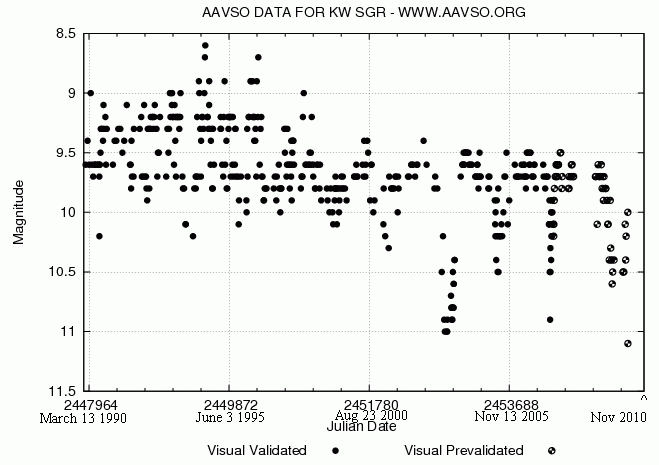
KW Sagittarii
KW Sagittarii is a red supergiant, located approximately away from the Sun in the direction of the constellation Sagittarius. It is one of the largest-known stars. If placed at the center of the Solar System, the star's surface would engulf Mars. Variability KW Sagitarii was discovered to be variable in 1928 from a study of photographic plates. It varies erratically in brightness over a range of about two magnitudes. It is classified as a semiregular variable, although the listed period of 670 days is poorly defined. The peculiar cool spectrum has led to comparisons with symbiotic variables, but it is no longer considered to be a cataclysmic binary. Distance A distance of 2,420 parsecs is based on the assumption of membership on the Sagittarius OB5 association. The parallax derived from the Hipparcos mission is negative so doesn't give much information about the distance except that it is likely to be large. The Gaia Data Release 2 parallax is and implies a distance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Star Designation
In astronomy, a variable star designation is a unique identifier given to variable stars. It uses a variation on the Bayer designation format, with an identifying label (as described below) preceding the Latin genitive of the name of the constellation in which the star lies. See List of constellations for a list of constellations and the genitive forms of their names. The identifying label can be one or two Latin letters or a ''V'' plus a number (e.g. V399). Examples are R Coronae Borealis, YZ Ceti, V603 Aquilae. Naming The current naming system is: *Stars with existing Greek letter Bayer designations are not given new designations. *Otherwise, start with the letter R and go through Z. *Continue with RR...RZ, then use SS...SZ, TT...TZ and so on until ZZ. *Use AA...AZ, BB...BZ, CC...CZ and so on until reaching QZ, omitting J in both the first and second positions.Most of this system was invented in Germany, which was still on Fraktur at the time, in which the majuscules "I" and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hipparcos
''Hipparcos'' was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the first high-precision measurements of the intrinsic brightnesses (compared to the less precise apparent brightness), proper motions, and parallaxes of stars, enabling better calculations of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial velocity measurements from spectroscopy, astrophysicists were able to finally measure all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting ''Hipparcos Catalogue'', a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision ''Tycho Catalogue'' of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. ''Hipparcos' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hipparcos Objects
''Hipparcos'' was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the first high-precision measurements of the intrinsic brightnesses (compared to the less precise apparent brightness), proper motions, and parallaxes of stars, enabling better calculations of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial velocity measurements from spectroscopy, astrophysicists were able to finally measure all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting ''Hipparcos Catalogue'', a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision ''Tycho Catalogue'' of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. ''Hipparcos'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M-type Supergiants
Type M or M type may refer to: Science and technology * Type M, a xD-Picture Card * Type M, a name for the 15 amp BS 546 electrical plug * Vaio Type M, a kind of Vaio computer from Sony * M-type asteroid * m-type filter, an electronic filter * M-type star * M-types, an implementation of inductive type Other uses * Audi Type M, a 1920s car * Beretta 92FS Compact Type M, a pistol * MG M-type, a sports car See also * M class (other) M class or M-class may refer to: Military * M-class cruiser, a planned German light cruiser class * M-class destroyer, several classes of destroyer ** Admiralty M-class destroyer, a class of British destroyers built 1913–1916 and served in World ... * Class M (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiregular Variable Stars
In astronomy, a semiregular variable star, a type of variable star, is a giant or supergiant of intermediate and late (cooler) spectral type showing considerable periodicity in its light changes, accompanied or sometimes interrupted by various irregularities. Periods lie in the range from 20 to more than 2000 days, while the shapes of the light curves may be rather different and variable with each cycle. The amplitudes may be from several hundredths to several magnitudes (usually 1-2 magnitudes in the V filter). Classification The semiregular variable stars have been sub-divided into four categories for many decades, with a fifth related group defined more recently. The original definitions of the four main groups were formalised in 1958 at the tenth general assembly of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). The General Catalogue of Variable Stars (GCVS) has updated the definitions with some additional information and provided newer reference stars where old examples such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VX Sagittarii
VX Sagittarii is an extreme asymptotic giant branch star located more than 1.5 kiloparsec away from the Sun in the constellation of Sagittarius. It is a pulsating variable star with an unusually large magnitude range. It is also one of the largest stars discovered so far, with a radius varying between . It is the most luminous known AGB star, at bolometric magnitude –8.6, which is even brighter than the theoretical limit at –8.0. Observations The star is classed as a cool semiregular variable of type SRc with a pulsational period of 732 days. The variations sometimes have an amplitude comparable to a long period variable, at other times they are much smaller. The spectral type varies between M4e around visual maximum and M9.8e at minimum light, and the luminosity class is Ia indicating a bright supergiant. The spectrum shows emission lines indicating that the star is losing mass through a strong stellar wind. The annual parallax of VX Sagittarii has bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mu Cephei
Mu Cephei ( Latinized from μ Cephei, abbreviated Mu Cep or μ Cep), also known as Herschel's Garnet Star, Erakis, or HD 206936, is a red supergiant or hypergiant star in the constellation Cepheus. It appears garnet red and is located at the edge of the IC 1396 nebula. Since 1943, the spectrum of this star has served as a spectral standard by which other stars are classified. Mu Cephei is visually nearly 100,000 times brighter than the Sun, with an absolute visual magnitude of −7.6. It is also one of the largest known stars with a radius around or over 1,000 times that of the sun (), and were it placed in the Sun's position it would engulf the orbit of Mars and Jupiter. History The deep red color of Mu Cephei was noted by William Herschel, who described it as "a very fine deep garnet colour, such as the periodical star ο Ceti". It is thus commonly known as Herschel's "Garnet Star". Mu Cephei was called ''Garnet sidus'' by Giuseppe Piazzi in his catalogue. An a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KY Cygni
KY Cygni is a red supergiant of spectral class M3.5Ia located in the constellation Cygnus. It is approximately 5,000 light-years away. Observations KY Cyg lies near the bright open cluster NGC 6913, but is not thought to be a member. The location is close to the bright star γ Cygni. It was identified as a variable star in 1930, and later named as KY Cygni. The spectrum was given the MK classification of M3 Ia, with only minor adjustments since. KY Cygni is heavily reddened due to interstellar extinction, losing an estimated 7.75 magnitudes at visual wavelengths. It would be a naked eye star if no light was lost. Properties KY Cygni is classified as a luminous red supergiant with a strong stellar wind. It is losing mass at around and has been described as a cool hypergiant. Its properties are uncertain, but the temperature is around 3,500 K. A model fit based on K-band infrared brightness gives a luminosity of , corresponding to a radius of . Another model ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V354 Cephei
V354 Cephei is a red supergiant star located within the Milky Way. It is an irregular variable located over 8,900 light-years away from the Sun. It has an estimated radius of . If it were placed in the center of the Solar System, it would extend to between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. Identification V354 Cephei is identified as a red supergiant variable star and included on surveys such as IRAS and 2MASS, but prior to its inclusion in the General Catalogue of Variable Stars in 1981, it was referred to only by its listings on relatively obscure catalogs. It is too faint to be included in catalogs such as the Henry Draper Catalogue or Bonner Durchmusterung. It was included on a 1947 Dearborn Observatory survey as star 41575, but that ID is hardly ever used. V354 Cephei has been referred to as Case 75. This is from one of several listings of cool stars made using the Burrell Schmidt telescope at the Warner and Swasey Observatory of Case Western Reserve University, alth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The term ''Milky Way'' is a translation of the Latin ', from the Greek ('), meaning "milky circle". From Earth, the Milky Way appears as a band because its disk-shaped structure is viewed from within. Galileo Galilei first resolved the band of light into individual stars with his telescope in 1610. Until the early 1920s, most astronomers thought that the Milky Way contained all the stars in the Universe. Following the 1920 Great Debate between the astronomers Harlow Shapley and Heber Curtis, observations by Edwin Hubble showed that the Milky Way is just one of many galaxies. The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with an estimated D25 isophotal diameter of , but only about 1,000 light years thick at the spiral arms (more at the bulg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Most Luminous Stars
This is a list of stars arranged by their absolute magnitude – their intrinsic stellar luminosity. This cannot be observed directly, so instead must be calculated from the apparent magnitude (the brightness as seen from Earth), the distance to each star, and a correction for interstellar extinction. The entries in the list below are further corrected to provide the bolometric magnitude, i.e. integrated over all wavelengths; this relies upon measurements in multiple photometric filters and extrapolation of the stellar spectrum based on the stellar spectral type and/or effective temperature. Entries give the bolometric luminosity in multiples of the luminosity of the Sun () and the bolometric absolute magnitude. As with all magnitude systems in astronomy, the latter scale is logarithmic and inverted i.e. more negative numbers are more luminous. Most stars on this list are not bright enough to be visible to the naked eye from Earth, because of their high distances, high exti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emily Levesque
Emily Levesque (born 1984) is an American astronomer and assistant professor in the Department of Astronomy at the University of Washington. She is renowned for her work on massive stars and using these stars to investigate galaxy formation. In 2014, she received the Annie Jump Cannon Award for her innovative work on gamma ray bursts and the Sloan Fellowship in 2017. In 2015, Levesque, Rachel Bezanson, and Grant R. Tremblay published an influential paper, which critiqued the use of the Physics GRE as an admissions cutoff criterion for astronomy postgraduate programs by showing there was no statistical correlation between applicant's score and later success in their academic careers. Subsequently, the American Astronomical Society adopted the stance that the Physics GRE should not be mandatory for graduate school applications, and many graduate astronomy programs have since removed the Physics GRE as a required part of their graduate school applications. She is also the author ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |