|
KC (patient)
Kent Cochrane (August 5, 1951 – March 27, 2014), also known as Patient K.C., was a widely studied Canadian memory disorder patient who has been used as a case study in over 20 neuropsychology papers over the span of 25 years. In 1981, Cochrane was involved in a motorcycle accident that left him with severe anterograde amnesia, as well as temporally graded retrograde amnesia. Like other amnesic patients ( patient HM, for example), Cochrane had his semantic memory intact, but lacked episodic memory with respect to his entire past. As a case study, Cochrane has been linked to the breakdown of the single-memory single-locus hypothesis regarding amnesia, which states that an individual memory is localized to a single location in the brain. Early life Kent Cochrane was born on August 5, 1951, as the oldest of five children. They grew up in the suburbs of Toronto, Ontario. After attending a community college to study business administration, he obtained a job at a manufacturing plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anchor of the Golden Horseshoe, an urban agglomeration of 9,765,188 people (as of 2021) surrounding the western end of Lake Ontario, while the Greater Toronto Area proper had a 2021 population of 6,712,341. Toronto is an international centre of business, finance, arts, sports and culture, and is recognized as one of the most multicultural and cosmopolitan cities in the world. Indigenous peoples have travelled through and inhabited the Toronto area, located on a broad sloping plateau interspersed with rivers, deep ravines, and urban forest, for more than 10,000 years. After the broadly disputed Toronto Purchase, when the Mississauga surrendered the area to the British Crown, the British established the town of York in 1793 and later designat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occipital Lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin ''ob'', "behind", and ''caput'', "head". The occipital lobe is the visual processing center of the mammalian brain containing most of the anatomical region of the visual cortex. The primary visual cortex is Brodmann area 17, commonly called V1 (visual one). Human V1 is located on the medial side of the occipital lobe within the calcarine sulcus; the full extent of V1 often continues onto the occipital pole. V1 is often also called striate cortex because it can be identified by a large stripe of myelin, the Stria of Gennari. Visually driven regions outside V1 are called extrastriate cortex. There are many extrastriate regions, and these are specialized for different visual tasks, such as visuospatial processing, color differentiation, and motion perception. Bilateral lesions of the occipital lobe can lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Declarative Memory
Explicit memory (or declarative memory) is one of the two main types of long-term human memory, the other of which is implicit memory. Explicit memory is the conscious, intentional recollection of factual information, previous experiences, and concepts. This type of memory is dependent upon three processes: acquisition, consolidation, and retrieval. Explicit memory can be divided into two categories: episodic memory, which stores specific personal experiences, and semantic memory, which stores factual information.Tulving E. 1972. Episodic and semantic memory. In Organization of Memory, ed. E Tulving, W Donaldson, pp. 381–403. New York: Academic Explicit memory requires gradual learning, with multiple presentations of a stimulus and response. The counterpart to explicit memory is known as implicit memory, refers to memories acquired and used unconsciously such as skills (e.g. knowing how to get dressed) or perception. Unlike explicit memory, implicit memory learns rapidly, even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priming (psychology)
Priming is a phenomenon whereby exposure to one stimulus influences a response to a subsequent stimulus, without conscious guidance or intention. The priming effect refers to the positive or negative effect of a rapidly presented stimulus (priming stimulus) on the processing of a second stimulus (target stimulus) that appears shortly after. Generally speaking, the generation of priming effect depends on the existence of some positive or negative relationship between priming and target stimuli. For example, the word ''nurse'' is recognized more quickly following the word ''doctor'' than following the word ''bread''. Priming can be perceptual, associative, repetitive, positive, negative, affective, semantic, or conceptual. Priming effects involve word recognition, semantic processing, attention, unconscious processing, and many other issues, and are related to differences in various writing systems. Research, however, has yet to firmly establish the duration of priming effects, yet th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
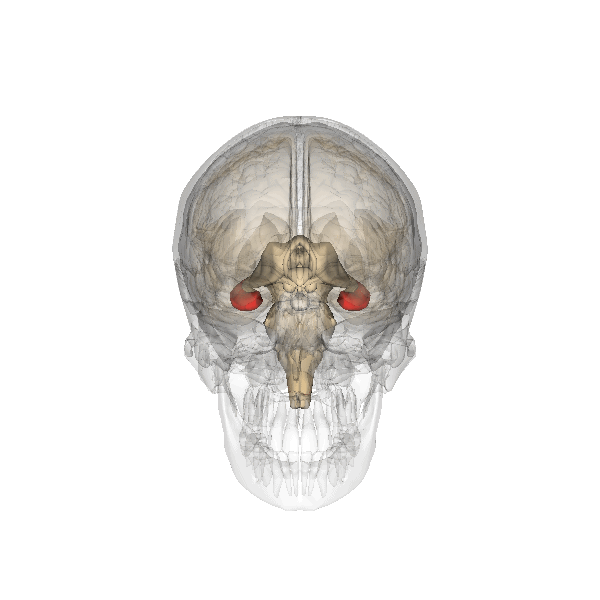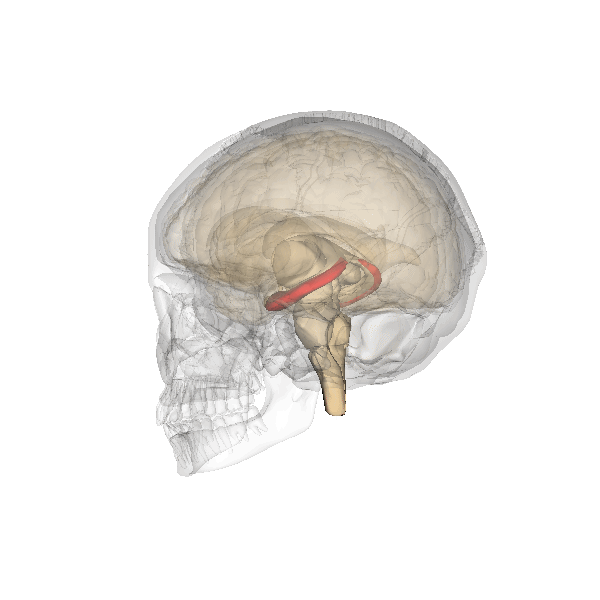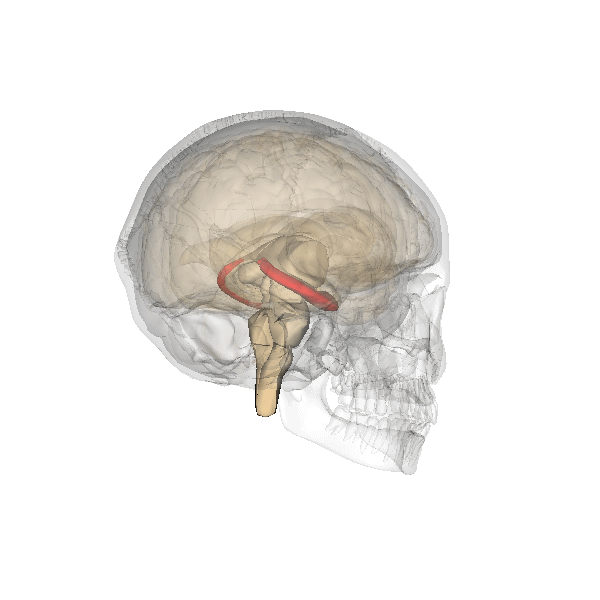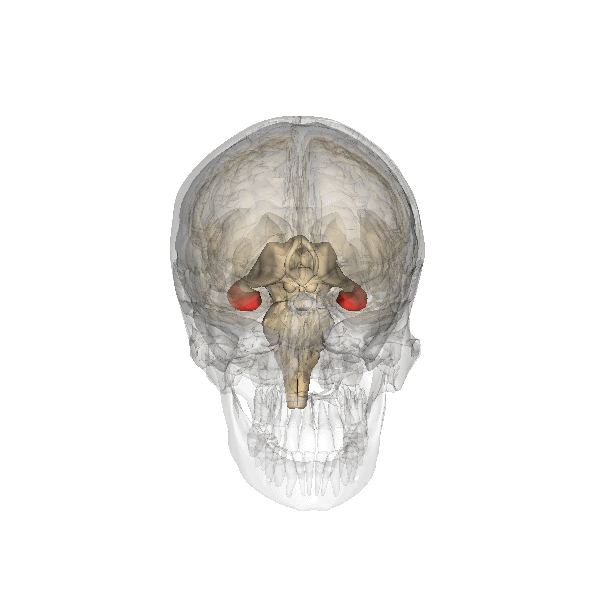
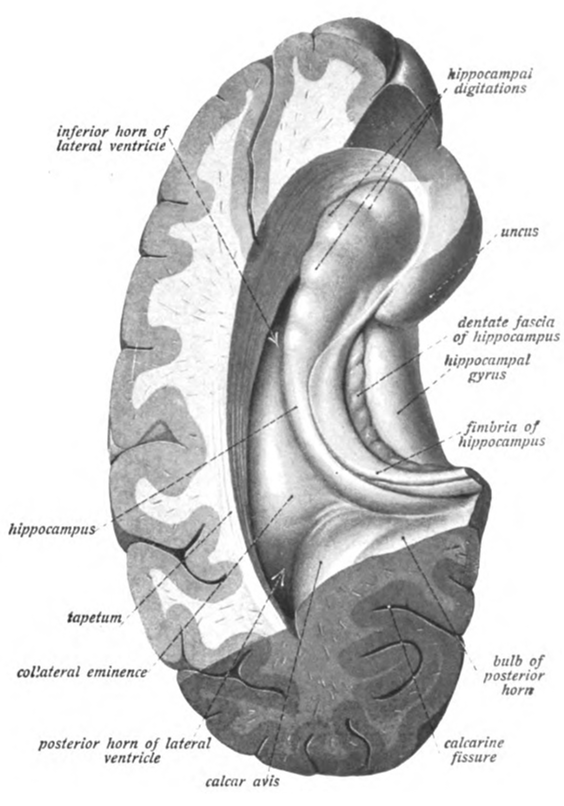
Hippocampus
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , 'seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory, and in spatial memory that enables navigation. The hippocampus is located in the allocortex, with neural projections into the neocortex in humans, as well as primates. The hippocampus, as the medial pallium, is a structure found in all vertebrates. In humans, it contains two main interlocking parts: the hippocampus proper (also called ''Ammon's horn''), and the dentate gyrus. In Alzheimer's disease (and other forms of dementia), the hippocampus is one of the first regions of the brain to suffer damage; short-term memory loss and disorientation are included among the early symptoms. Damage to the hippocampus can also result from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autopsy
An autopsy (post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death or to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present for research or educational purposes. (The term "necropsy" is generally reserved for non-human animals). Autopsies are usually performed by a specialized medical doctor called a pathologist. In most cases, a medical examiner or coroner can determine the cause of death. However, only a small portion of deaths require an autopsy to be performed, under certain circumstances. Purposes of performance Autopsies are performed for either legal or medical purposes. Autopsies can be performed when any of the following information is desired: * Determine if death was natural or unnatural * Injury source and extent on the corpse * Manner of death must be determined * Post mortem interval * Determining the deceas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functioning properly. Signs and symptoms of a stroke may include an inability to move or feel on one side of the body, problems understanding or speaking, dizziness, or loss of vision to one side. Signs and symptoms often appear soon after the stroke has occurred. If symptoms last less than one or two hours, the stroke is a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also called a mini-stroke. A hemorrhagic stroke may also be associated with a severe headache. The symptoms of a stroke can be permanent. Long-term complications may include pneumonia and loss of bladder control. The main risk factor for stroke is high blood pressure. Other risk factors include high blood cholesterol, tobacco smoking, obesity, diabetes mellitus, a previous TIA, end-st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Attack
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck or jaw. Often it occurs in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms. Women more often present without chest pain and instead have neck pain, arm pain or feel tired. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest. Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonoetic Consciousness
Autonoetic consciousness is the human ability to mentally place oneself in the past and future (i.e. mental time travel) or in counterfactual situations (i.e. alternative outcomes), and to thus be able to examine one's own thoughts. One's sense of self affects their behavior, in the present, past and future. It relates to how one reflects on their own past behavior, how they feel about it, and this in turn determines if they do it again. It is episodic memory that deals with self-awareness, memories of the self and inward thoughts that may be projected onto future actions of an individual. It was "proposed by Endel Tulving for self-awareness, allowing the rememberer to reflect on the contents of episodic memory". Moreover, autonoetic consciousness involves behaviors such as mental time travel, self-projection, and episodic future thinking, all of which have often been proposed as exclusively human capacities. The self Autonoetic consciousness is important in our formation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noetic Consciousness
In philosophy, noetics is a purposed branch of metaphysics concerned with the study of mind as well as intellect. There is also a reference to the science of noetics, which covers the field of thinking and knowing, thought and knowledge, as well as mental operations, processes, states, and products through the data of the written word. Philosophy The term itself means “the proper exercise of nous” whereas ''nous'' (“mind, understanding, intellect”) is described as “the highest faculty in man, through which - provided it is purified - he knows God or the inner essences or principles of created things through direct apprehension or spiritual perception”. In ancient Greek and medieval philosophy, noetic topics included the doctrine of the active intellect (Aristotle, Averroes) and the doctrine of the Divine Intellect (Plotinus). The entire philosophy of noetics, which include the notions by Immanuel Kant, John Locke, René Descartes, Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, and Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocampal
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , 'seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory, and in spatial memory that enables navigation. The hippocampus is located in the allocortex, with neural projections into the neocortex in humans, as well as primates. The hippocampus, as the medial pallium, is a structure found in all vertebrates. In humans, it contains two main interlocking parts: the hippocampus proper (also called ''Ammon's horn''), and the dentate gyrus. In Alzheimer's disease (and other forms of dementia), the hippocampus is one of the first regions of the brain to suffer damage; short-term memory loss and disorientation are included among the early symptoms. Damage to the hippocampus can also result from oxygen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |