|
K-distribution
In probability and statistics, the generalized K-distribution is a three-parameter family of continuous probability distributions. The distribution arises by compounding two gamma distributions. In each case, a re-parametrization of the usual form of the family of gamma distributions is used, such that the parameters are: * the mean of the distribution, * the usual shape parameter. K-distribution is a special case of variance-gamma distribution, which in turn is a special case of generalised hyperbolic distribution. A simpler special case of the generalized K-distribution is often referred as ''the'' K-distribution. Density Suppose that a random variable X has gamma distribution with mean \sigma and shape parameter \alpha, with \sigma being treated as a random variable having another gamma distribution, this time with mean \mu and shape parameter \beta. The result is that X has the following probability density function (pdf) for x>0: :f_X(x; \mu, \alpha, \beta)= \frac \, \lef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Distribution
A product distribution is a probability distribution constructed as the distribution of the product of random variables having two other known distributions. Given two statistically independent random variables ''X'' and ''Y'', the distribution of the random variable ''Z'' that is formed as the product Z = XY is a ''product distribution''. Algebra of random variables The product is one type of algebra for random variables: Related to the product distribution are the ratio distribution, sum distribution (see List of convolutions of probability distributions) and difference distribution. More generally, one may talk of combinations of sums, differences, products and ratios. Many of these distributions are described in Melvin D. Springer's book from 1979 ''The Algebra of Random Variables''. Derivation for independent random variables If X and Y are two independent, continuous random variables, described by probability density functions f_X and f_Y then the probability density ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Pusey
Peter Nicholas Pusey (born 30 December 1942) is a British physicist. He is an Emeritus Professor of Physics at the School of Physics and Astronomy of the University of Edinburgh.People directory University of Edinburgh, retrieved 2016-03-12. Research Pusey is a pioneer of (DLS) and is known for elucidating the structure and dynamics of concentrated s. He contributed to the development, underlying theory and applications of DLS. He was among the first to apply photon correlation techniques and ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
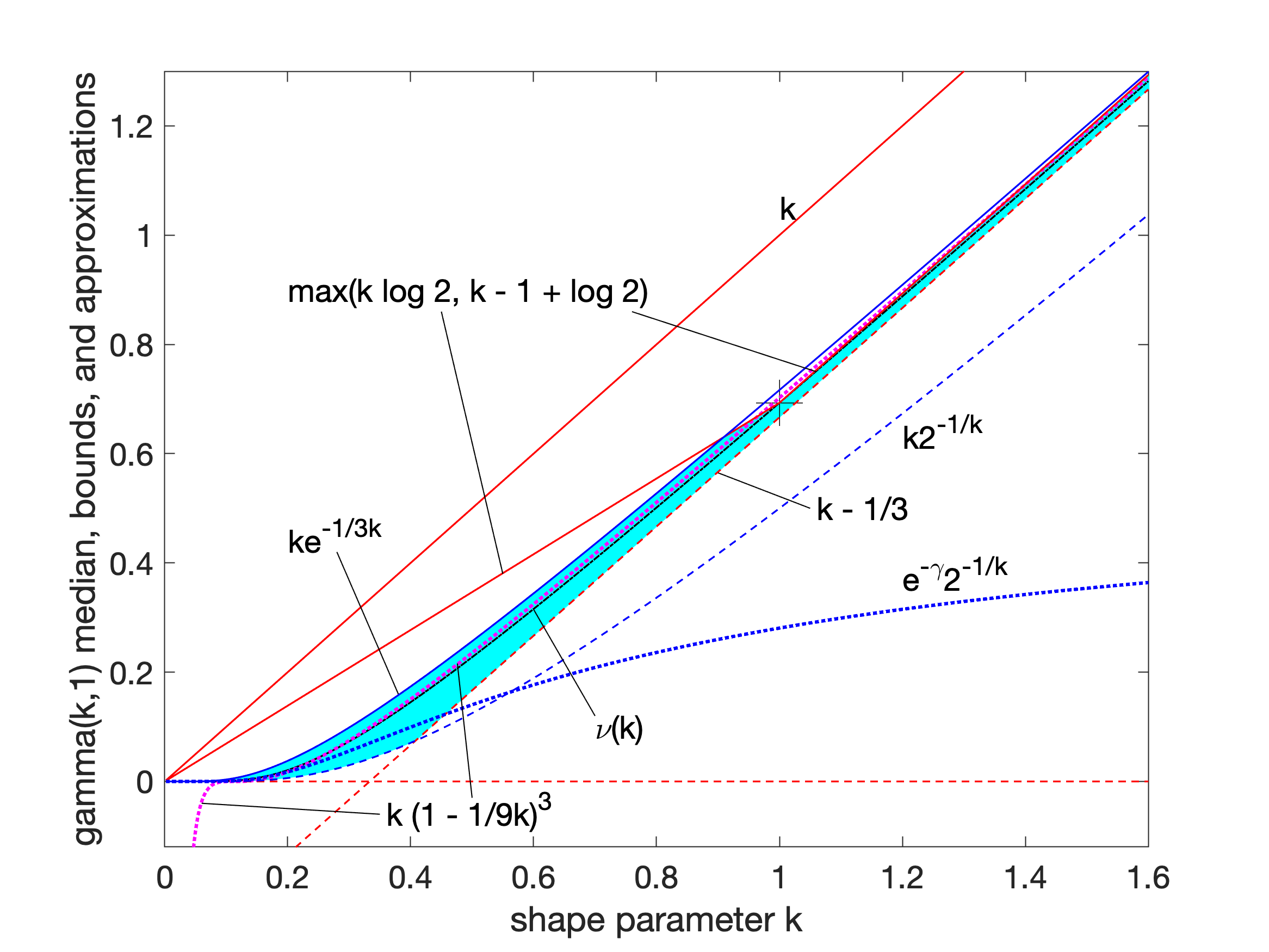
Gamma Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the gamma distribution is a two-parameter family of continuous probability distributions. The exponential distribution, Erlang distribution, and chi-square distribution are special cases of the gamma distribution. There are two equivalent parameterizations in common use: #With a shape parameter k and a scale parameter \theta. #With a shape parameter \alpha = k and an inverse scale parameter \beta = 1/ \theta , called a rate parameter. In each of these forms, both parameters are positive real numbers. The gamma distribution is the maximum entropy probability distribution (both with respect to a uniform base measure and a 1/x base measure) for a random variable X for which E 'X''= ''kθ'' = ''α''/''β'' is fixed and greater than zero, and E n(''X'')= ''ψ''(''k'') + ln(''θ'') = ''ψ''(''α'') − ln(''β'') is fixed (''ψ'' is the digamma function). Definitions The parameterization with ''k'' and ''θ'' appears to be more common in econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability
Probability is the branch of mathematics concerning numerical descriptions of how likely an Event (probability theory), event is to occur, or how likely it is that a proposition is true. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1, where, roughly speaking, 0 indicates impossibility of the event and 1 indicates certainty."Kendall's Advanced Theory of Statistics, Volume 1: Distribution Theory", Alan Stuart and Keith Ord, 6th Ed, (2009), .William Feller, ''An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications'', (Vol 1), 3rd Ed, (1968), Wiley, . The higher the probability of an event, the more likely it is that the event will occur. A simple example is the tossing of a fair (unbiased) coin. Since the coin is fair, the two outcomes ("heads" and "tails") are both equally probable; the probability of "heads" equals the probability of "tails"; and since no other outcomes are possible, the probability of either "heads" or "tails" is 1/2 (which could also be written ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Distributions
Continuity or continuous may refer to: Mathematics * Continuity (mathematics), the opposing concept to discreteness; common examples include ** Continuous probability distribution or random variable in probability and statistics ** Continuous game, a generalization of games used in game theory ** Law of Continuity, a heuristic principle of Gottfried Leibniz * Continuous function, in particular: ** Continuity (topology), a generalization to functions between topological spaces ** Scott continuity, for functions between posets ** Continuity (set theory), for functions between ordinals ** Continuity (category theory), for functors ** Graph continuity, for payoff functions in game theory * Continuity theorem may refer to one of two results: ** Lévy's continuity theorem, on random variables ** Kolmogorov continuity theorem, on stochastic processes * In geometry: ** Parametric continuity, for parametrised curves ** Geometric continuity, a concept primarily applied to the conic secti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Signal Processing
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving information about the objects' locations and speeds. Radar was developed secretly for military use by several countries in the period before and during World War II. A key development was the cavity magnetron in the United Kingdom, which allowed the creation of relatively small systems with sub-meter resolution. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Cross-section
Radar cross-section (RCS), also called radar signature, is a measure of how detectable an object is by radar. A larger RCS indicates that an object is more easily detected. An object reflects a limited amount of radar energy back to the source. The factors that influence this include: *the material with which the target is made; *the size of the target relative to the wavelength of the illuminating radar signal; *the absolute size of the target; *the incident angle (angle at which the radar beam hits a particular portion of the target, which depends upon the shape of the target and its orientation to the radar source); *the reflected angle (angle at which the reflected beam leaves the part of the target hit; it depends upon incident angle); *the polarization of the transmitted and the received radiation with respect to the orientation of the target. While important in detecting targets, strength of emitter and distance are not factors that affect the calculation of an RCS becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is the mathematical function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of different possible outcomes for an experiment. It is a mathematical description of a random phenomenon in terms of its sample space and the probabilities of events (subsets of the sample space). For instance, if is used to denote the outcome of a coin toss ("the experiment"), then the probability distribution of would take the value 0.5 (1 in 2 or 1/2) for , and 0.5 for (assuming that the coin is fair). Examples of random phenomena include the weather conditions at some future date, the height of a randomly selected person, the fraction of male students in a school, the results of a survey to be conducted, etc. Introduction A probability distribution is a mathematical description of the probabilities of events, subsets of the sample space. The sample space, often denoted by \Omega, is the set of all possible outcomes of a random phe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic-aperture Radar
Synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) is a form of radar that is used to create two-dimensional images or three-dimensional reconstructions of objects, such as landscapes. SAR uses the motion of the radar antenna over a target region to provide finer spatial resolution than conventional stationary beam-scanning radars. SAR is typically mounted on a moving platform, such as an aircraft or spacecraft, and has its origins in an advanced form of side looking airborne radar (SLAR). The distance the SAR device travels over a target during the period when the target scene is illuminated creates the large ''synthetic'' antenna aperture (the ''size'' of the antenna). Typically, the larger the aperture, the higher the image resolution will be, regardless of whether the aperture is physical (a large antenna) or synthetic (a moving antenna) – this allows SAR to create high-resolution images with comparatively small physical antennas. For a fixed antenna size and orientation, objects which are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whittaker Function
In mathematics, a Whittaker function is a special solution of Whittaker's equation, a modified form of the confluent hypergeometric equation introduced by to make the formulas involving the solutions more symmetric. More generally, introduced Whittaker functions of reductive groups over local fields, where the functions studied by Whittaker are essentially the case where the local field is the real numbers and the group is SL2(R). Whittaker's equation is :\frac+\left(-\frac+\frac+\frac\right)w=0. It has a regular singular point at 0 and an irregular singular point at ∞. Two solutions are given by the Whittaker functions ''M''κ,μ(''z''), ''W''κ,μ(''z''), defined in terms of Kummer's confluent hypergeometric functions ''M'' and ''U'' by :M_\left(z\right) = \exp\left(-z/2\right)z^M\left(\mu-\kappa+\tfrac, 1+2\mu, z\right) :W_\left(z\right) = \exp\left(-z/2\right)z^U\left(\mu-\kappa+\tfrac, 1+2\mu, z\right). The Whittaker function W_(z) is the same as those with opposite val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moment (mathematics)
In mathematics, the moments of a function are certain quantitative measures related to the shape of the function's graph. If the function represents mass density, then the zeroth moment is the total mass, the first moment (normalized by total mass) is the center of mass, and the second moment is the moment of inertia. If the function is a probability distribution, then the first moment is the expected value, the second central moment is the variance, the third standardized moment is the skewness, and the fourth standardized moment is the kurtosis. The mathematical concept is closely related to the concept of moment in physics. For a distribution of mass or probability on a bounded interval, the collection of all the moments (of all orders, from to ) uniquely determines the distribution (Hausdorff moment problem). The same is not true on unbounded intervals (Hamburger moment problem). In the mid-nineteenth century, Pafnuty Chebyshev became the first person to think systematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric Jakeman
Eric Jakeman (born 1939) is a British mathematical physicist specialising in the statistics and quantum statistics of waves. He is an Emeritus Professor at the University of Nottingham. Education Jakeman was educated at The Brunts School in Mansfield, England. He received a degree in mathematical physics from Birmingham University in 1960, and a PhD in superconductivity theory in 1963. Career He was the head of the scattering and quantum optics section at the Defence Research Agency, a visiting professor at Imperial College London, an honorary secretary of the Institute of Physics from 1994 until 2003, and finally a Professor of Applied Statistical Optics at the University of Nottingham from 1996. He was a member of the Council of the European Physical Society The European Physical Society (EPS) is a non-profit organisation whose purpose is to promote physics and physicists in Europe through methods such as physics outreach. Formally established in 1968, its membershi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |