|
Jyotiḥśāstra
A ' is a text from a classical body of literature on the topic of Hindu astrology, known as , dating to the medieval period of Classical Sanskrit literature (roughly the 3rd to 9th centuries CE) Only the most important ones exist in scholarly editions or translations, such as the Yavanajataka (3rd century), Brihat Samhitā (6th century), Brihat Parashara Hora Shastra (7th century) or Sārāvalī (8th century), while many remain unedited in Sanskrit or vernacular manuscripts. Such classical texts should be distinguished from modern works. There are a great number of contemporary publications, reflecting the persisting importance of astrology in Hindu culture, and the corresponding economical attractivity of the market in India. Notable modern authors include Sri Yukteswar Giri (1855–1936), Bangalore Venkata Raman (1912–1998), and Sanjay Rath (b. 1963). Classification Pingree classifies as ''jyotihshastra'' (treatises on jyotisha) manuscripts on astronomy, mathematics, astrol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Astrology
Jyotisha or Jyotishya (from Sanskrit ', from ' “light, heavenly body" and ''ish'' - from Isvara or God) is the traditional Hindu system of astrology, also known as Hindu astrology, Indian astrology and more recently Vedic astrology. It is one of the six auxiliary disciplines in Hinduism, that is connected with the study of the Vedas. The ''Vedanga Jyotisha'' is one of the earliest texts about astronomy within the Vedas. Some scholars believe that the horoscopic astrology practiced in the Indian subcontinent came from Hellenistic religion, Hellenistic influences, however, this is a point of intense debate and other scholars believe that Jyotisha developed independently although it may have interacted with Greek astrology. Following a judgement of the Andhra Pradesh High Court in 2001 which favoured astrology, some Indian universities now offer advanced degrees in Hindu astrology. The scientific consensus is that Astrology and science, astrology is a pseudoscience. Etymology J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
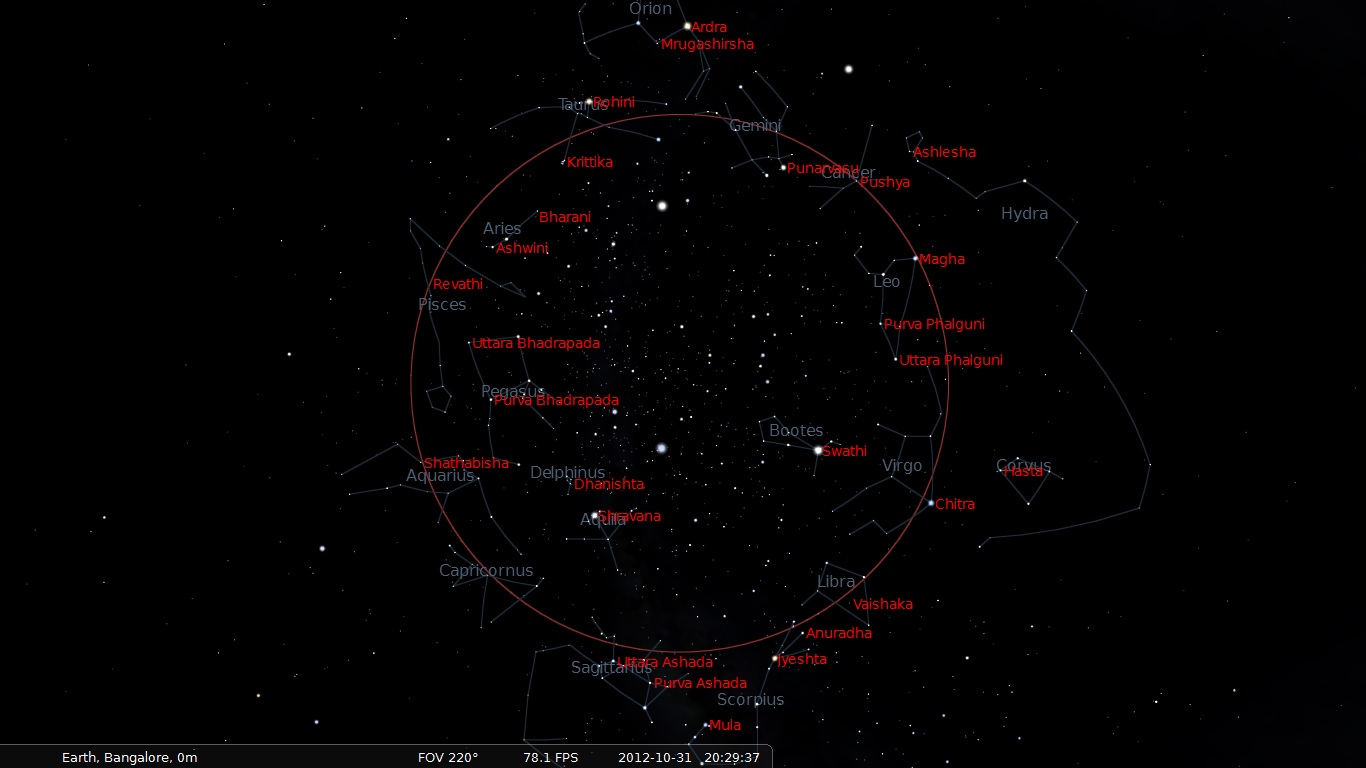
Hindu Astrology
Jyotisha or Jyotishya (from Sanskrit ', from ' “light, heavenly body" and ''ish'' - from Isvara or God) is the traditional Hindu system of astrology, also known as Hindu astrology, Indian astrology and more recently Vedic astrology. It is one of the six auxiliary disciplines in Hinduism, that is connected with the study of the Vedas. The ''Vedanga Jyotisha'' is one of the earliest texts about astronomy within the Vedas. Some scholars believe that the horoscopic astrology practiced in the Indian subcontinent came from Hellenistic influences, however, this is a point of intense debate and other scholars believe that Jyotisha developed independently although it may have interacted with Greek astrology. Following a judgement of the Andhra Pradesh High Court in 2001 which favoured astrology, some Indian universities now offer advanced degrees in Hindu astrology. The scientific consensus is that astrology is a pseudoscience. Etymology Jyotisha, states Monier-Williams, is rooted in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jyotisha
Jyotisha or Jyotishya (from Sanskrit ', from ' “light, heavenly body" and ''ish'' - from Isvara or God) is the traditional Hindu system of astrology, also known as Hindu astrology, Indian astrology and more recently Vedic astrology. It is one of the six auxiliary disciplines in Hinduism, that is connected with the study of the Vedas. The ''Vedanga Jyotisha'' is one of the earliest texts about astronomy within the Vedas. Some scholars believe that the horoscopic astrology practiced in the Indian subcontinent came from Hellenistic influences, however, this is a point of intense debate and other scholars believe that Jyotisha developed independently although it may have interacted with Greek astrology. Following a judgement of the Andhra Pradesh High Court in 2001 which favoured astrology, some Indian universities now offer advanced degrees in Hindu astrology. The scientific consensus is that astrology is a pseudoscience. Etymology Jyotisha, states Monier-Williams, is rooted in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yavanajataka
The Yavanajātaka (Sanskrit: ''yavana'' 'Greek' + ''jātaka'' ' nativity' = 'nativity according to the Greeks'), written by Sphujidhvaja, is an ancient text in Indian astrology. According to David Pingree, it is a later versification of an earlier translation into Sanskrit of a Greek text, thought to have been written around 120 CE in Alexandria, on horoscopy. Based on Pingree's interpretation and emendations, the original translation, made in 149–150 CE by "Yavanesvara" ("Lord of the Greeks") under the rule of the Western Kshatrapa king Rudrakarman I, is lost; only a substantial portion of the versification 120 years later by Sphujidhvaja under Rudrasena II has survived. However, according to the recent research by Mak based on a newly discovered manuscript and other documents, Pingree's date interpretation as well as a number of crucial readings such as zero and other bhūtasaṃkhyā were based on his own emendation, not supported by what was written on the manuscripts. Furth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brihat Parashara Hora Shastra
The Brihat Parashara Hora Shastra (Sanskrit: बृहत् पराशर होरा शास्त्र; IAST: '; abbreviated to BPHS) is the most comprehensive extant Śāstra on Vedic natal astrology, in particular the Horā branch (predictive astrology, e.g. horoscopes). Though ascribed to Maharṣi Parāśara, the origin and date of the original composition is unknown. The most popular version of the BPHS consists of 97 chapters, a 1984 translation by R. Santhanam. Nomenclature 'bṛhat parāśara horā śāstra' (बृहत् पराशर होरा शास्त्र) can be loosely translated to examples such as 'the great book on horoscopy by Parashara' or 'Great Parashara's manual on Horoscopic astrology': * 'bṛhat' (बृहत्) means 'great, large, wide, vast, abundant, compact, solid, massy, strong, mighty' or 'full-grown, old' or 'extended or bright (as a luminous body)' or 'clear, loud (said of sounds)'. * 'parāśara' (पराश� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sārāvalī
:''Kalyanavarman is also the name of a member of the Varman dynasty (5th century).'' The ''Sārāvalī'' of is a foundational compilation of Indian astrology, dating to ca. 800 CE, somewhat post-dating the ' An English translation was published by N.N. Krishna Rau and V.B. Choudhari in 1961 (in two volumes. 1983 reprint by Renjan Publications). References *David Pingree David Edwin Pingree (January 2, 1933, New Haven, Connecticut – November 11, 2005, Providence, Rhode Island) was an American historian of mathematics in the ancient world. He was a University Professor and Professor of History of Mathematics ..., ' (J. Gonda (Ed.) ''A History of Indian Literature'', Vol VI Fasc 4), p. 81 External links *http://www.astrojyoti.com/saravalipage1.htm Hindu astrological texts {{astrology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brihat Parasara Horashastra
The Brihat Parashara Hora Shastra (Sanskrit: बृहत् पराशर होरा शास्त्र; IAST: '; abbreviated to BPHS) is the most comprehensive extant Śāstra on Vedic natal astrology, in particular the Horā branch (predictive astrology, e.g. horoscopes). Though ascribed to Maharṣi Parāśara, the origin and date of the original composition is unknown. The most popular version of the BPHS consists of 97 chapters, a 1984 translation by R. Santhanam. Nomenclature 'bṛhat parāśara horā śāstra' (बृहत् पराशर होरा शास्त्र) can be loosely translated to examples such as 'the great book on horoscopy by Parashara' or 'Great Parashara's manual on Horoscopic astrology': * 'bṛhat' (बृहत्) means 'great, large, wide, vast, abundant, compact, solid, massy, strong, mighty' or 'full-grown, old' or 'extended or bright (as a luminous body)' or 'clear, loud (said of sounds)'. * 'parāśara' (पराशर) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaimini Sutras (Hindu Astrology)
Jaimini Sutras, also known as Upadesa Sutras is an ancient Sanskrit text on the predictive part of Hindu astrology, attributed to the sage Jaimini, the founder of the Purva Mimamsa branch of Hindu philosophy, a disciple of Vyasa and grandson of Parashara. It comprises nine hundred and thirty-six sutras or aphorisms arranged in four chapters, and though having several distinct features of its own, the Jaimini System, which is a unique system, appears as an offshoot of the Parashari System only; wherever it deviates, it is not found to be in conflict with the Parashari system, and gives due importance to Rahu and Ketu, the two Lunar Nodes. Jaimini Sutras, arranged in four chapters, cover Karakamsa, Arudha, Upapada and navamsa in the first chapter; Longevity, Diseases, Profession, Progeny and Spouse, in the second; Longevity, Nature and cause of death, in the third; and in the fourth chapter it covers the account of pre-natal epoch. The Jaimini System of prognostication is distinctly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaimini
Sage Jaimini was an ancient Indian scholar who founded the Mīmāṃsā school of Hindu philosophy. He is considered to be a disciple of Rishi/Sage Veda Vyasa, the son of Parāśara Rishi. Traditionally attributed to be the author of the ''Mimamsa Sutras'' James Lochtefeld (2002), The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1 & 2, Rosen Publishing, , pages 438, 437-438, 746 and ''Jaimini Sutras'', he is estimated to have lived around 4th to 2nd century BCE. Some scholars place him between 250 BCE and 50 CE. His school is considered non-theistic,FX Clooney (1997), What’s a god? The quest for the right understanding of devatā in Brāhmaṅical ritual theory (Mīmāṃsā), International Journal of Hindu Studies, August 1997, Volume 1, Issue 2, pages 337-385 but one that emphasized rituals parts of the Vedas as essential to Dharma.P. Bilimoria (2001), Hindu doubts about God: Towards Mimamsa Deconstruction, in Philosophy of Religion: Indian Philosophy (Editor: Roy Perrett), Vol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brihat Jataka
''Brihat Jataka'' or ''Brihat Jatakam'' or ''Brihajjatakam'' (Sanskrit: बृहज्जातकम्), is one of the five principal texts written by Varāhamihira, the other four being ''Panchasiddhantika'', ''Brihat Samhita'', ''Laghu Jataka'' and ''Yogayatra''. It is also one of the five major treatises on Hindu predictive astrology, the other four being ''Saravali'' of Kalyanavarma, ''Sarvartha Chintamani'' of Venkatesh, ''Jataka Parijata'' of Vaidyanatha and ''Phaladeepika'' of Mantreswara. The study of this classic text makes one grasp the fundamentals of astrology. Structure ''Brihat Jataka'' is considered a standard textbook on Vedic astrology, and sometimes described as "India's foremost astrological text". The work covers the wide and complex range of predictive astrology. The brevity employed in its composition is noteworthy. In an article titled "On the Authenticity of the (Modern) Brhat Parasara Hora Sastra" published in the July and August 2009 issues of ''Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hora Sara
''Hora Sara'' is an ancient treatise on Hindu astrology, specifically as it relates to Divination. It was written in Sanskrit Sloka format. Its author, Prithuyasas, was the son of Varahamihira (505–587 CE). Prithuyasas contradicts his father; for example, in respect to Vihaga yoga, a Nabhasa yoga that arises when all planets occupy the 4th and the 10th, he has assigned auspicious results. ''Hora Sara'' was represented in Hora Ratna of Bala Bhadra authored during the reign of Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan Shihab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram (5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), better known by his regnal name Shah Jahan I (; ), was the fifth emperor of the Mughal Empire, reigning from January 1628 until July 1658. Under his emperorship, the Mugha .... Where the author writes, "Just as Varaha is a synonym of astrology, his son, Prithuyasas, occupies the zenith in the astrology’s world through his work, Hora Sara". This work on astrology covers a wide range of topics through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |